commit
0c79aba2c7
184 changed files with 24750 additions and 0 deletions
-
64CMakeLists.txt
-
3lib/.gitignore
-
70lib/stormpy/__init__.py
-
2lib/stormpy/expressions/__init__.py
-
2lib/stormpy/info/__init__.py
-
2lib/stormpy/logic/__init__.py
-
3lib/stormpy/storage/__init__.py
-
36lib/stormpy/storage/action.py
-
34lib/stormpy/storage/state.py
-
32resources/pybind11/.appveyor.yml
-
35resources/pybind11/.gitignore
-
3resources/pybind11/.gitmodules
-
112resources/pybind11/.travis.yml
-
184resources/pybind11/CMakeLists.txt
-
37resources/pybind11/CONTRIBUTING.md
-
36resources/pybind11/LICENSE
-
2resources/pybind11/MANIFEST.in
-
123resources/pybind11/README.md
-
11resources/pybind11/docs/_static/theme_overrides.css
-
81resources/pybind11/docs/advanced/cast/chrono.rst
-
85resources/pybind11/docs/advanced/cast/custom.rst
-
50resources/pybind11/docs/advanced/cast/eigen.rst
-
113resources/pybind11/docs/advanced/cast/functional.rst
-
41resources/pybind11/docs/advanced/cast/index.rst
-
144resources/pybind11/docs/advanced/cast/overview.rst
-
154resources/pybind11/docs/advanced/cast/stl.rst
-
634resources/pybind11/docs/advanced/classes.rst
-
142resources/pybind11/docs/advanced/exceptions.rst
-
311resources/pybind11/docs/advanced/functions.rst
-
229resources/pybind11/docs/advanced/misc.rst
-
13resources/pybind11/docs/advanced/pycpp/index.rst
-
299resources/pybind11/docs/advanced/pycpp/numpy.rst
-
96resources/pybind11/docs/advanced/pycpp/object.rst
-
57resources/pybind11/docs/advanced/pycpp/utilities.rst
-
143resources/pybind11/docs/advanced/smart_ptrs.rst
-
287resources/pybind11/docs/basics.rst
-
90resources/pybind11/docs/benchmark.py
-
99resources/pybind11/docs/benchmark.rst
-
222resources/pybind11/docs/changelog.rst
-
410resources/pybind11/docs/classes.rst
-
53resources/pybind11/docs/compiling.rst
-
308resources/pybind11/docs/conf.py
-
251resources/pybind11/docs/faq.rst
-
45resources/pybind11/docs/index.rst
-
93resources/pybind11/docs/intro.rst
-
20resources/pybind11/docs/limitations.rst
-
BINresources/pybind11/docs/pybind11-logo.png
-
BINresources/pybind11/docs/pybind11_vs_boost_python1.png
-
427resources/pybind11/docs/pybind11_vs_boost_python1.svg
-
BINresources/pybind11/docs/pybind11_vs_boost_python2.png
-
427resources/pybind11/docs/pybind11_vs_boost_python2.svg
-
247resources/pybind11/docs/reference.rst
-
22resources/pybind11/docs/release.rst
-
362resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/attr.h
-
1464resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/cast.h
-
160resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/chrono.h
-
560resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/common.h
-
47resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/complex.h
-
177resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/descr.h
-
239resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/eigen.h
-
105resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/eval.h
-
79resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/functional.h
-
1169resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/numpy.h
-
154resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/operators.h
-
65resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/options.h
-
1735resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/pybind11.h
-
899resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/pytypes.h
-
256resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/stl.h
-
541resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/stl_bind.h
-
53resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/typeid.h
-
11resources/pybind11/pybind11/__init__.py
-
2resources/pybind11/pybind11/_version.py
-
11resources/pybind11/setup.cfg
-
74resources/pybind11/setup.py
-
111resources/pybind11/tests/CMakeLists.txt
-
227resources/pybind11/tests/conftest.py
-
249resources/pybind11/tests/constructor_stats.h
-
175resources/pybind11/tests/object.h
-
45resources/pybind11/tests/pybind11_tests.cpp
-
12resources/pybind11/tests/pybind11_tests.h
-
62resources/pybind11/tests/test_alias_initialization.cpp
-
79resources/pybind11/tests/test_alias_initialization.py
-
117resources/pybind11/tests/test_buffers.cpp
-
57resources/pybind11/tests/test_buffers.py
-
149resources/pybind11/tests/test_callbacks.cpp
-
98resources/pybind11/tests/test_callbacks.py
-
59resources/pybind11/tests/test_chrono.cpp
-
116resources/pybind11/tests/test_chrono.py
-
68resources/pybind11/tests/test_class_args.cpp
-
6resources/pybind11/tests/test_class_args.py
-
55resources/pybind11/tests/test_constants_and_functions.cpp
-
21resources/pybind11/tests/test_constants_and_functions.py
-
41resources/pybind11/tests/test_copy_move_policies.cpp
-
15resources/pybind11/tests/test_copy_move_policies.py
-
53resources/pybind11/tests/test_docstring_options.cpp
-
32resources/pybind11/tests/test_docstring_options.py
-
134resources/pybind11/tests/test_eigen.cpp
-
135resources/pybind11/tests/test_eigen.py
-
68resources/pybind11/tests/test_enum.cpp
-
108resources/pybind11/tests/test_enum.py
@ -0,0 +1,64 @@ |
|||
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0.0) |
|||
project(pystorm) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
find_package(storm REQUIRED) |
|||
add_subdirectory(resources/pybind11) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
file(GLOB_RECURSE STORM_CORE_SOURCES ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/src/core/*.cpp) |
|||
|
|||
pybind11_add_module(stormpy.core ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/src/mod_core.cpp ${STORM_CORE_SOURCES}) |
|||
target_include_directories(stormpy.core PUBLIC ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR} ${storm_INCLUDE_DIR}) |
|||
target_link_libraries(stormpy.core PRIVATE storm) |
|||
|
|||
file(GLOB_RECURSE STORM_INFO_SOURCES ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/src/info/*.cpp) |
|||
|
|||
pybind11_add_module(stormpy.info ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/src/mod_info.cpp ${STORM_INFO_SOURCES}) |
|||
target_include_directories(stormpy.info PUBLIC ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR} ${storm_INCLUDE_DIR}) |
|||
target_link_libraries(stormpy.info PRIVATE storm) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
file(GLOB_RECURSE STORM_EXPRESSIONS_SOURCES ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/src/expressions/*.cpp) |
|||
|
|||
pybind11_add_module(stormpy.expressions ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/src/mod_expressions.cpp ${STORM_EXPRESSIONS_SOURCES}) |
|||
target_include_directories(stormpy.expressions PUBLIC ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR} ${storm_INCLUDE_DIR}) |
|||
target_link_libraries(stormpy.expressions PRIVATE storm) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
file(GLOB_RECURSE STORM_LOGIC_SOURCES ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/src/logic/*.cpp) |
|||
|
|||
pybind11_add_module(stormpy.logic ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/src/mod_logic.cpp ${STORM_LOGIC_SOURCES}) |
|||
target_include_directories(stormpy.logic PUBLIC ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR} ${storm_INCLUDE_DIR}) |
|||
target_link_libraries(stormpy.logic PRIVATE storm) |
|||
|
|||
file(GLOB_RECURSE STORM_STORAGE_SOURCES ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/src/storage/*.cpp) |
|||
|
|||
pybind11_add_module(stormpy.storage ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/src/mod_storage.cpp ${STORM_STORAGE_SOURCES}) |
|||
target_include_directories(stormpy.storage PUBLIC ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR} ${storm_INCLUDE_DIR}) |
|||
target_link_libraries(stormpy.storage PRIVATE storm) |
|||
|
|||
#set(STORMPY_OUTPUT_DIR "${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/stormpy") |
|||
#set(STORMPY_SOURCE_DIR "${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/stormpy") |
|||
# |
|||
#if(STORM_HAVE_CLN) |
|||
# set(STORMPY_USE_CLN 1) |
|||
#else() |
|||
# set(STORMPY_USE_CLN 0) |
|||
#endif() |
|||
# |
|||
## Set configuration file |
|||
#get_directory_property(STORMPY_INCLUDE_DIRS_PROP INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES) |
|||
#foreach(arg ${STORMPY_INCLUDE_DIRS_PROP}) |
|||
# set(STORMPY_INCLUDE_DIRS "${STORMPY_INCLUDE_DIRS}${sep}${arg}") |
|||
# set(sep ":") |
|||
#endforeach() |
|||
#set(STORMPY_COMPILE_ARGS ${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS}) |
|||
#set(STORMPY_LIBRARY_DIRS "${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/src/storm") |
|||
#set(STORMPY_RPATH "${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/src/storm") |
|||
#configure_file ( |
|||
# "${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/stormpy/setup.cfg.in" |
|||
# "${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/stormpy/setup.cfg" |
|||
#) |
|||
# |
|||
|
|||
@ -0,0 +1,3 @@ |
|||
*.so |
|||
__pycache__/ |
|||
stormpy.egg-info/ |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@ |
|||
""" |
|||
It looks like you want to know about 'stormpy'. |
|||
|
|||
_.-;:q=._ |
|||
.' j=""^k;:\. |
|||
; .F ";`Y |
|||
,;.J_ ;'j |
|||
,-;"^7F : .F _________________ |
|||
,-'-_<. ;gj. _.,---""'' .' |
|||
; _,._`\. : `T"5, ; |
|||
: `?8w7 `J ,-'" -^q. ` ; |
|||
\;._ _,=' ; n58L Y. .' |
|||
F;"; .' k_ `^' j' ; |
|||
J;:: ; "y:-=' ; |
|||
L;;== |:; jT\ ; |
|||
L;:;J J:L 7:;' _ ; |
|||
I;|:.L |:k J:.' , ' . ; |
|||
|;J:.| ;.I F.: . : |
|||
;J;:L:: |.| |.J , ' ` ; ; |
|||
.' J:`J.`. :.J |. L . ; ; |
|||
; L :k:`._ ,',j J; | ` , ; ; |
|||
.' I :`=.:."_".' L J `.' |
|||
.' |.: `"-=-' |.J ; |
|||
_.-' `: : ;:; _ ; |
|||
_.-'" J: : /.;' ; ; |
|||
='_ k;.\. _.;:Y' , .' |
|||
`"---..__ `Y;."-=';:=' , .' |
|||
`""--..__ `"==="' - .' |
|||
``""---...__ itz .-' |
|||
``""---' |
|||
""" |
|||
|
|||
from . import core |
|||
from .core import * |
|||
from . import storage |
|||
from .storage import * |
|||
|
|||
core.set_up("") |
|||
|
|||
def build_model(program, formulae): |
|||
intermediate = core._build_model(program, formulae) |
|||
assert not intermediate.supports_parameters |
|||
if intermediate.model_type == ModelType.DTMC: |
|||
return intermediate.as_dtmc() |
|||
elif intermediate.model_type == ModelType.MDP: |
|||
return intermediate.as_mdp() |
|||
else: |
|||
raise RuntimeError("Not supported non-parametric model constructed") |
|||
|
|||
def build_parametric_model(program, formulae): |
|||
intermediate = core._build_parametric_model(program, formulae) |
|||
assert intermediate.supports_parameters |
|||
if intermediate.model_type == ModelType.DTMC: |
|||
return intermediate.as_pdtmc() |
|||
elif intermediate.model_type == ModelType.MDP: |
|||
return intermediate.as_pmdp() |
|||
else: |
|||
raise RuntimeError("Not supported parametric model constructed") |
|||
|
|||
def perform_bisimulation(model, formula, bisimulation_type): |
|||
if model.supports_parameters: |
|||
return core._perform_parametric_bisimulation(model, formula, bisimulation_type) |
|||
else: |
|||
return core._perform_bisimulation(model, formula, bisimulation_type) |
|||
|
|||
def model_checking(model, formula): |
|||
if model.supports_parameters: |
|||
return core._parametric_model_checking(model, formula) |
|||
else: |
|||
return core._model_checking(model, formula) |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@ |
|||
from . import expressions |
|||
from .expressions import * |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@ |
|||
from . import info |
|||
from .info import * |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@ |
|||
from . import logic |
|||
from .logic import * |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,3 @@ |
|||
from . import storage |
|||
from .storage import * |
|||
from . import state,action |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@ |
|||
class Action: |
|||
""" Represents an action in the model """ |
|||
|
|||
def __init__(self, row_group_start, row_group_end, row, model): |
|||
""" Initialize |
|||
:param row_group_start: Start index of the row group in the matrix |
|||
:param row_group_end: End index of the row group in the matrix |
|||
:param row: Index of the corresponding row in the matrix |
|||
:param model: Corresponding model |
|||
""" |
|||
self.row_group_start = row_group_start |
|||
self.row_group_end = row_group_end |
|||
self.row = row - 1 |
|||
self.model = model |
|||
assert row >= -1 and row + row_group_start <= row_group_end |
|||
|
|||
def __iter__(self): |
|||
return self |
|||
|
|||
def __next__(self): |
|||
if self.row + self.row_group_start >= self.row_group_end - 1: |
|||
raise StopIteration |
|||
else: |
|||
self.row += 1 |
|||
return self |
|||
|
|||
def __str__(self): |
|||
return "{}".format(self.row) |
|||
|
|||
def transitions(self): |
|||
""" Get transitions associated with the action |
|||
:return List of tranistions |
|||
""" |
|||
row = self.row_group_start + self.row |
|||
#return self.model.transition_matrix().get_row(self.row_group_start + self.row) |
|||
return self.model.transition_matrix.row_iter(row, row) |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@ |
|||
from . import action |
|||
|
|||
class State: |
|||
""" Represents a state in the model """ |
|||
|
|||
def __init__(self, id, model): |
|||
""" Initialize |
|||
:param id: Id of the state |
|||
:param model: Corresponding model |
|||
""" |
|||
self.id = id - 1 |
|||
self.model = model |
|||
|
|||
def __iter__(self): |
|||
return self |
|||
|
|||
def __next__(self): |
|||
if self.id >= self.model.nr_states - 1: |
|||
raise StopIteration |
|||
else: |
|||
self.id += 1 |
|||
return self |
|||
|
|||
def __str__(self): |
|||
return "{}".format(self.id) |
|||
|
|||
def actions(self): |
|||
""" Get actions associated with the state |
|||
:return List of actions |
|||
""" |
|||
row_group_indices = self.model.transition_matrix._row_group_indices |
|||
start = row_group_indices[self.id] |
|||
end = row_group_indices[self.id+1] |
|||
return action.Action(start, end, 0, self.model) |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@ |
|||
version: 1.0.{build} |
|||
os: Visual Studio 2015 |
|||
test: off |
|||
platform: |
|||
- x86 |
|||
- x64 |
|||
environment: |
|||
matrix: |
|||
- CONDA: 27 |
|||
- CONDA: 35 |
|||
install: |
|||
- ps: | |
|||
if ($env:PLATFORM -eq "x64") { $env:CMAKE_ARCH = "x64" } |
|||
if ($env:PYTHON) { |
|||
if ($env:PLATFORM -eq "x64") { $env:PYTHON = "$env:PYTHON-x64" } |
|||
$env:PATH = "C:\Python$env:PYTHON\;C:\Python$env:PYTHON\Scripts\;$env:PATH" |
|||
pip install --disable-pip-version-check --user --upgrade pip wheel |
|||
pip install pytest numpy scipy |
|||
} elseif ($env:CONDA) { |
|||
if ($env:CONDA -eq "27") { $env:CONDA = "" } |
|||
if ($env:PLATFORM -eq "x64") { $env:CONDA = "$env:CONDA-x64" } |
|||
$env:PATH = "C:\Miniconda$env:CONDA\;C:\Miniconda$env:CONDA\Scripts\;$env:PATH" |
|||
conda install -y -q pytest numpy scipy |
|||
} |
|||
- ps: | |
|||
Start-FileDownload 'http://bitbucket.org/eigen/eigen/get/3.3.0.zip' |
|||
7z x 3.3.0.zip -y > $null |
|||
$env:CMAKE_INCLUDE_PATH = "eigen-eigen-26667be4f70b" |
|||
build_script: |
|||
- cmake -A "%CMAKE_ARCH%" -DPYBIND11_WERROR=ON |
|||
- set MSBuildLogger="C:\Program Files\AppVeyor\BuildAgent\Appveyor.MSBuildLogger.dll" |
|||
- cmake --build . --config Release --target pytest -- /v:m /logger:%MSBuildLogger% |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@ |
|||
CMakeCache.txt |
|||
CMakeFiles |
|||
Makefile |
|||
cmake_install.cmake |
|||
.DS_Store |
|||
*.so |
|||
*.pyd |
|||
*.dll |
|||
*.sln |
|||
*.sdf |
|||
*.opensdf |
|||
*.vcxproj |
|||
*.filters |
|||
example.dir |
|||
Win32 |
|||
x64 |
|||
Release |
|||
Debug |
|||
.vs |
|||
CTestTestfile.cmake |
|||
Testing |
|||
autogen |
|||
MANIFEST |
|||
/.ninja_* |
|||
/*.ninja |
|||
/docs/.build |
|||
*.py[co] |
|||
*.egg-info |
|||
*~ |
|||
.DS_Store |
|||
/dist |
|||
/build |
|||
/cmake/ |
|||
.cache/ |
|||
sosize-*.txt |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,3 @@ |
|||
[submodule "tools/clang"] |
|||
path = tools/clang |
|||
url = https://github.com/wjakob/clang-cindex-python3 |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,112 @@ |
|||
language: cpp |
|||
sudo: false |
|||
matrix: |
|||
include: |
|||
- os: linux |
|||
env: PYTHON=2.7 CPP=11 GCC=4.8 |
|||
addons: |
|||
apt: |
|||
sources: [ubuntu-toolchain-r-test, kubuntu-backports] |
|||
packages: [g++-4.8, cmake] |
|||
- os: linux |
|||
env: PYTHON=3.5 CPP=11 GCC=4.8 |
|||
addons: |
|||
apt: |
|||
sources: [ubuntu-toolchain-r-test, kubuntu-backports, deadsnakes] |
|||
packages: [g++-4.8, cmake, python3.5-dev] |
|||
- sudo: true |
|||
services: docker |
|||
env: PYTHON=2.7 CPP=14 GCC=6 |
|||
- sudo: true |
|||
services: docker |
|||
env: PYTHON=3.5 CPP=14 GCC=6 DEBUG=1 |
|||
- os: osx |
|||
osx_image: xcode7.3 |
|||
env: PYTHON=2.7 CPP=14 CLANG |
|||
- os: osx |
|||
osx_image: xcode7.3 |
|||
env: PYTHON=3.5 CPP=14 CLANG |
|||
# A barebones build makes sure everything still works without optional deps (numpy/scipy/eigen) |
|||
# and also tests the automatic discovery functions in CMake (Python version, C++ standard). |
|||
- os: linux |
|||
env: BAREBONES |
|||
addons: |
|||
apt: |
|||
sources: [ubuntu-toolchain-r-test, kubuntu-backports] |
|||
packages: [g++-4.8, cmake] |
|||
install: pip install pytest |
|||
# Documentation build: |
|||
- os: linux |
|||
language: docs |
|||
env: DOCS STYLE LINT |
|||
install: pip install sphinx sphinx_rtd_theme flake8 pep8-naming |
|||
script: |
|||
- make -C docs html SPHINX_OPTIONS=-W |
|||
- tools/check-style.sh |
|||
- flake8 |
|||
cache: |
|||
directories: |
|||
- $HOME/.cache/pip |
|||
- $HOME/Library/Caches/pip |
|||
before_install: |
|||
- | |
|||
# Configure build variables |
|||
if [ "$TRAVIS_OS_NAME" = "linux" ]; then |
|||
if [ -z "$GCC" ]; then export GCC=4.8; fi |
|||
export CXX=g++-$GCC CC=gcc-$GCC; |
|||
if [ "$GCC" = "6" ]; then export DOCKER=debian:testing CXX=g++ CC=gcc; fi |
|||
elif [ "$TRAVIS_OS_NAME" = "osx" ]; then |
|||
export CXX=clang++ CC=clang; |
|||
fi |
|||
if [ -n "$CPP" ]; then export CPP=-std=c++$CPP; fi |
|||
if [ "${PYTHON:0:1}" = "3" ]; then export PY=3; fi |
|||
if [ -n "$DEBUG" ]; then export CMAKE_EXTRA_ARGS="-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug"; fi |
|||
- | |
|||
# Initialize enviornment |
|||
if [ -n "$DOCKER" ]; then |
|||
docker pull $DOCKER |
|||
export containerid=$(docker run --detach --tty \ |
|||
--volume="$PWD":/pybind11 --workdir=/pybind11 \ |
|||
--env="CC=$CC" --env="CXX=$CXX" --env="DEBIAN_FRONTEND=$DEBIAN_FRONTEND" \ |
|||
--env=GCC_COLORS=\ \ |
|||
$DOCKER) |
|||
docker exec --tty "$containerid" sh -c 'for s in 0 15; do sleep $s; apt-get update && apt-get -qy dist-upgrade && break; done' |
|||
export SCRIPT_RUN_PREFIX="docker exec --tty $containerid" |
|||
else |
|||
if [ "$TRAVIS_OS_NAME" = "linux" ]; then |
|||
pip install --user --upgrade pip virtualenv |
|||
virtualenv -p python$PYTHON venv |
|||
elif [ "$TRAVIS_OS_NAME" = "osx" ]; then |
|||
if [ "$PY" = "3" ]; then |
|||
brew update; brew install python$PY; |
|||
else |
|||
curl -fsSL -O https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py |
|||
sudo -H python get-pip.py |
|||
fi |
|||
pip$PY install --user --upgrade pip virtualenv |
|||
python$PY -m virtualenv venv |
|||
fi |
|||
source venv/bin/activate |
|||
fi |
|||
install: |
|||
- | |
|||
# Install dependencies |
|||
if [ -n "$DOCKER" ]; then |
|||
docker exec --tty "$containerid" sh -c "for s in 0 15; do sleep \$s; apt-get -qy --no-install-recommends install \ |
|||
python$PYTHON-dev python$PY-pytest python$PY-scipy \ |
|||
libeigen3-dev cmake make g++ && break; done" |
|||
else |
|||
pip install numpy scipy pytest |
|||
|
|||
wget -q -O eigen.tar.gz https://bitbucket.org/eigen/eigen/get/3.3.0.tar.gz |
|||
tar xzf eigen.tar.gz |
|||
export CMAKE_EXTRA_ARGS="${CMAKE_EXTRA_ARGS} -DCMAKE_INCLUDE_PATH=$PWD/eigen-eigen-26667be4f70b" |
|||
fi |
|||
script: |
|||
- $SCRIPT_RUN_PREFIX cmake ${CMAKE_EXTRA_ARGS} |
|||
-DPYBIND11_PYTHON_VERSION=$PYTHON |
|||
-DPYBIND11_CPP_STANDARD=$CPP |
|||
-DPYBIND11_WERROR=ON |
|||
- $SCRIPT_RUN_PREFIX make pytest -j 2 |
|||
after_script: |
|||
- if [ -n "$DOCKER" ]; then docker stop "$containerid"; docker rm "$containerid"; fi |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,184 @@ |
|||
# CMakeLists.txt -- Build system for the pybind11 modules |
|||
# |
|||
# Copyright (c) 2015 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel@inf.ethz.ch> |
|||
# |
|||
# All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
# BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
|
|||
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8.12) |
|||
|
|||
project(pybind11) |
|||
|
|||
# Check if pybind11 is being used directly or via add_subdirectory |
|||
set(PYBIND11_MASTER_PROJECT OFF) |
|||
if (CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR STREQUAL CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR) |
|||
set(PYBIND11_MASTER_PROJECT ON) |
|||
endif() |
|||
|
|||
option(PYBIND11_INSTALL "Install pybind11 header files?" ${PYBIND11_MASTER_PROJECT}) |
|||
option(PYBIND11_TEST "Build pybind11 test suite?" ${PYBIND11_MASTER_PROJECT}) |
|||
option(PYBIND11_WERROR "Report all warnings as errors" OFF) |
|||
|
|||
# Add a CMake parameter for choosing a desired Python version |
|||
set(PYBIND11_PYTHON_VERSION "" CACHE STRING "Python version to use for compiling modules") |
|||
|
|||
list(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH "${CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_DIR}/tools") |
|||
set(Python_ADDITIONAL_VERSIONS 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7) |
|||
find_package(PythonLibsNew ${PYBIND11_PYTHON_VERSION} REQUIRED) |
|||
|
|||
include(CheckCXXCompilerFlag) |
|||
|
|||
if(NOT MSVC AND NOT PYBIND11_CPP_STANDARD) |
|||
check_cxx_compiler_flag("-std=c++14" HAS_CPP14_FLAG) |
|||
check_cxx_compiler_flag("-std=c++11" HAS_CPP11_FLAG) |
|||
|
|||
if (HAS_CPP14_FLAG) |
|||
set(PYBIND11_CPP_STANDARD -std=c++14) |
|||
elseif (HAS_CPP11_FLAG) |
|||
set(PYBIND11_CPP_STANDARD -std=c++11) |
|||
else() |
|||
message(FATAL_ERROR "Unsupported compiler -- pybind11 requires C++11 support!") |
|||
endif() |
|||
|
|||
set(PYBIND11_CPP_STANDARD ${PYBIND11_CPP_STANDARD} CACHE STRING |
|||
"C++ standard flag, e.g. -std=c++11 or -std=c++14. Defaults to latest available." FORCE) |
|||
endif() |
|||
|
|||
# Cache variables so pybind11_add_module can be used in parent projects |
|||
set(PYBIND11_INCLUDE_DIR "${CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_DIR}/include" CACHE INTERNAL "") |
|||
set(PYTHON_INCLUDE_DIRS ${PYTHON_INCLUDE_DIRS} CACHE INTERNAL "") |
|||
set(PYTHON_LIBRARIES ${PYTHON_LIBRARIES} CACHE INTERNAL "") |
|||
set(PYTHON_MODULE_PREFIX ${PYTHON_MODULE_PREFIX} CACHE INTERNAL "") |
|||
set(PYTHON_MODULE_EXTENSION ${PYTHON_MODULE_EXTENSION} CACHE INTERNAL "") |
|||
|
|||
# Build a Python extension module: |
|||
# pybind11_add_module(<name> source1 [source2 ...]) |
|||
# |
|||
function(pybind11_add_module target_name) |
|||
add_library(${target_name} MODULE ${ARGN}) |
|||
target_include_directories(${target_name} |
|||
PRIVATE ${PYBIND11_INCLUDE_DIR} |
|||
PRIVATE ${PYTHON_INCLUDE_DIRS}) |
|||
|
|||
# The prefix and extension are provided by FindPythonLibsNew.cmake |
|||
set_target_properties(${target_name} PROPERTIES PREFIX "${PYTHON_MODULE_PREFIX}") |
|||
set_target_properties(${target_name} PROPERTIES SUFFIX "${PYTHON_MODULE_EXTENSION}") |
|||
|
|||
if(WIN32 OR CYGWIN) |
|||
# Link against the Python shared library on Windows |
|||
target_link_libraries(${target_name} PRIVATE ${PYTHON_LIBRARIES}) |
|||
elseif(APPLE) |
|||
# It's quite common to have multiple copies of the same Python version |
|||
# installed on one's system. E.g.: one copy from the OS and another copy |
|||
# that's statically linked into an application like Blender or Maya. |
|||
# If we link our plugin library against the OS Python here and import it |
|||
# into Blender or Maya later on, this will cause segfaults when multiple |
|||
# conflicting Python instances are active at the same time (even when they |
|||
# are of the same version). |
|||
|
|||
# Windows is not affected by this issue since it handles DLL imports |
|||
# differently. The solution for Linux and Mac OS is simple: we just don't |
|||
# link against the Python library. The resulting shared library will have |
|||
# missing symbols, but that's perfectly fine -- they will be resolved at |
|||
# import time. |
|||
|
|||
target_link_libraries(${target_name} PRIVATE "-undefined dynamic_lookup") |
|||
endif() |
|||
|
|||
if(NOT MSVC) |
|||
# Make sure C++11/14 are enabled |
|||
target_compile_options(${target_name} PUBLIC ${PYBIND11_CPP_STANDARD}) |
|||
|
|||
# Enable link time optimization and set the default symbol |
|||
# visibility to hidden (very important to obtain small binaries) |
|||
string(TOUPPER "${CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE}" U_CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE) |
|||
if (NOT ${U_CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE} MATCHES DEBUG) |
|||
# Check for Link Time Optimization support (GCC/Clang) |
|||
check_cxx_compiler_flag("-flto" HAS_LTO_FLAG) |
|||
if(HAS_LTO_FLAG AND NOT CYGWIN) |
|||
target_compile_options(${target_name} PRIVATE -flto) |
|||
endif() |
|||
|
|||
# Intel equivalent to LTO is called IPO |
|||
if(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Intel") |
|||
check_cxx_compiler_flag("-ipo" HAS_IPO_FLAG) |
|||
if(HAS_IPO_FLAG) |
|||
target_compile_options(${target_name} PRIVATE -ipo) |
|||
endif() |
|||
endif() |
|||
|
|||
# Default symbol visibility |
|||
target_compile_options(${target_name} PRIVATE "-fvisibility=hidden") |
|||
|
|||
# Strip unnecessary sections of the binary on Linux/Mac OS |
|||
if(CMAKE_STRIP) |
|||
if(APPLE) |
|||
add_custom_command(TARGET ${target_name} POST_BUILD |
|||
COMMAND ${CMAKE_STRIP} -u -r $<TARGET_FILE:${target_name}>) |
|||
else() |
|||
add_custom_command(TARGET ${target_name} POST_BUILD |
|||
COMMAND ${CMAKE_STRIP} $<TARGET_FILE:${target_name}>) |
|||
endif() |
|||
endif() |
|||
endif() |
|||
elseif(MSVC) |
|||
# /MP enables multithreaded builds (relevant when there are many files), /bigobj is |
|||
# needed for bigger binding projects due to the limit to 64k addressable sections |
|||
target_compile_options(${target_name} PRIVATE /MP /bigobj) |
|||
|
|||
# Enforce link time code generation on MSVC, except in debug mode |
|||
target_compile_options(${target_name} PRIVATE $<$<NOT:$<CONFIG:Debug>>:/GL>) |
|||
|
|||
# Fancy generator expressions don't work with linker flags, for reasons unknown |
|||
set_property(TARGET ${target_name} APPEND_STRING PROPERTY LINK_FLAGS_RELEASE /LTCG) |
|||
set_property(TARGET ${target_name} APPEND_STRING PROPERTY LINK_FLAGS_MINSIZEREL /LTCG) |
|||
set_property(TARGET ${target_name} APPEND_STRING PROPERTY LINK_FLAGS_RELWITHDEBINFO /LTCG) |
|||
endif() |
|||
endfunction() |
|||
|
|||
# Compile with compiler warnings turned on |
|||
function(pybind11_enable_warnings target_name) |
|||
if(MSVC) |
|||
target_compile_options(${target_name} PRIVATE /W4) |
|||
else() |
|||
target_compile_options(${target_name} PRIVATE -Wall -Wextra -Wconversion) |
|||
endif() |
|||
|
|||
if(PYBIND11_WERROR) |
|||
if(MSVC) |
|||
target_compile_options(${target_name} PRIVATE /WX) |
|||
else() |
|||
target_compile_options(${target_name} PRIVATE -Werror) |
|||
endif() |
|||
endif() |
|||
endfunction() |
|||
|
|||
set(PYBIND11_HEADERS |
|||
include/pybind11/attr.h |
|||
include/pybind11/cast.h |
|||
include/pybind11/chrono.h |
|||
include/pybind11/common.h |
|||
include/pybind11/complex.h |
|||
include/pybind11/descr.h |
|||
include/pybind11/options.h |
|||
include/pybind11/eigen.h |
|||
include/pybind11/eval.h |
|||
include/pybind11/functional.h |
|||
include/pybind11/numpy.h |
|||
include/pybind11/operators.h |
|||
include/pybind11/pybind11.h |
|||
include/pybind11/pytypes.h |
|||
include/pybind11/stl.h |
|||
include/pybind11/stl_bind.h |
|||
include/pybind11/typeid.h |
|||
) |
|||
string(REPLACE "include/" "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/include/" |
|||
PYBIND11_HEADERS "${PYBIND11_HEADERS}") |
|||
|
|||
if (PYBIND11_TEST) |
|||
add_subdirectory(tests) |
|||
endif() |
|||
|
|||
if (PYBIND11_INSTALL) |
|||
install(FILES ${PYBIND11_HEADERS} DESTINATION include/pybind11) |
|||
endif() |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@ |
|||
Thank you for your interest in this project! Please refer to the following |
|||
sections on how to contribute code and bug reports. |
|||
|
|||
### Reporting bugs |
|||
|
|||
At the moment, this project is run in the spare time of a single person |
|||
([Wenzel Jakob](http://rgl.epfl.ch/people/wjakob)) with very limited resources |
|||
for issue tracker tickets. Thus, before submitting a question or bug report, |
|||
please take a moment of your time and ensure that your issue isn't already |
|||
discussed in the project documentation provided at |
|||
[http://pybind11.readthedocs.org/en/latest](http://pybind11.readthedocs.org/en/latest). |
|||
|
|||
Assuming that you have identified a previously unknown problem or an important |
|||
question, it's essential that you submit a self-contained and minimal piece of |
|||
code that reproduces the problem. In other words: no external dependencies, |
|||
isolate the function(s) that cause breakage, submit matched and complete C++ |
|||
and Python snippets that can be easily compiled and run on my end. |
|||
|
|||
## Pull requests |
|||
Contributions are submitted, reviewed, and accepted using Github pull requests. |
|||
Please refer to [this |
|||
article](https://help.github.com/articles/using-pull-requests) for details and |
|||
adhere to the following rules to make the process as smooth as possible: |
|||
|
|||
* Make a new branch for every feature you're working on. |
|||
* Make small and clean pull requests that are easy to review but make sure they |
|||
do add value by themselves. |
|||
* Add tests for any new functionality and run the test suite (``make pytest``) |
|||
to ensure that no existing features break. |
|||
* This project has a strong focus on providing general solutions using a |
|||
minimal amount of code, thus small pull requests are greatly preferred. |
|||
|
|||
### License |
|||
|
|||
pybind11 is provided under a BSD-style license that can be found in the |
|||
``LICENSE`` file. By using, distributing, or contributing to this project, you |
|||
agree to the terms and conditions of this license. |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@ |
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch>, All rights reserved. |
|||
|
|||
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without |
|||
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met: |
|||
|
|||
1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this |
|||
list of conditions and the following disclaimer. |
|||
|
|||
2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, |
|||
this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation |
|||
and/or other materials provided with the distribution. |
|||
|
|||
3. Neither the name of the copyright holder nor the names of its contributors |
|||
may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software |
|||
without specific prior written permission. |
|||
|
|||
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND |
|||
ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED |
|||
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE |
|||
DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE |
|||
FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL |
|||
DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR |
|||
SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER |
|||
CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, |
|||
OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE |
|||
OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. |
|||
|
|||
You are under no obligation whatsoever to provide any bug fixes, patches, or |
|||
upgrades to the features, functionality or performance of the source code |
|||
("Enhancements") to anyone; however, if you choose to make your Enhancements |
|||
available either publicly, or directly to the author of this software, without |
|||
imposing a separate written license agreement for such Enhancements, then you |
|||
hereby grant the following license: a non-exclusive, royalty-free perpetual |
|||
license to install, use, modify, prepare derivative works, incorporate into |
|||
other computer software, distribute, and sublicense such enhancements or |
|||
derivative works thereof, in binary and source code form. |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@ |
|||
include include/pybind11/*.h |
|||
include LICENSE README.md CONTRIBUTING.md |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,123 @@ |
|||
 |
|||
|
|||
# pybind11 — Seamless operability between C++11 and Python |
|||
|
|||
[](http://pybind11.readthedocs.org/en/latest/?badge=latest) |
|||
[](https://travis-ci.org/pybind/pybind11) |
|||
[](https://ci.appveyor.com/project/wjakob/pybind11) |
|||
|
|||
**pybind11** is a lightweight header-only library that exposes C++ types in Python |
|||
and vice versa, mainly to create Python bindings of existing C++ code. Its |
|||
goals and syntax are similar to the excellent |
|||
[Boost.Python](http://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_58_0/libs/python/doc/) library |
|||
by David Abrahams: to minimize boilerplate code in traditional extension |
|||
modules by inferring type information using compile-time introspection. |
|||
|
|||
The main issue with Boost.Python—and the reason for creating such a similar |
|||
project—is Boost. Boost is an enormously large and complex suite of utility |
|||
libraries that works with almost every C++ compiler in existence. This |
|||
compatibility has its cost: arcane template tricks and workarounds are |
|||
necessary to support the oldest and buggiest of compiler specimens. Now that |
|||
C++11-compatible compilers are widely available, this heavy machinery has |
|||
become an excessively large and unnecessary dependency. |
|||
|
|||
Think of this library as a tiny self-contained version of Boost.Python with |
|||
everything stripped away that isn't relevant for binding generation. Without |
|||
comments, the core header files only require ~2.5K lines of code and depend on |
|||
Python (2.7 or 3.x) and the C++ standard library. This compact implementation |
|||
was possible thanks to some of the new C++11 language features (specifically: |
|||
tuples, lambda functions and variadic templates). Since its creation, this |
|||
library has grown beyond Boost.Python in many ways, leading to dramatically |
|||
simpler binding code in many common situations. |
|||
|
|||
Tutorial and reference documentation is provided at |
|||
[http://pybind11.readthedocs.org/en/latest](http://pybind11.readthedocs.org/en/latest). |
|||
A PDF version of the manual is available |
|||
[here](https://media.readthedocs.org/pdf/pybind11/latest/pybind11.pdf). |
|||
|
|||
## Core features |
|||
pybind11 can map the following core C++ features to Python |
|||
|
|||
- Functions accepting and returning custom data structures per value, reference, or pointer |
|||
- Instance methods and static methods |
|||
- Overloaded functions |
|||
- Instance attributes and static attributes |
|||
- Arbitrary exception types |
|||
- Enumerations |
|||
- Callbacks |
|||
- Iterators and ranges |
|||
- Custom operators |
|||
- Single and multiple inheritance |
|||
- STL data structures |
|||
- Iterators and ranges |
|||
- Smart pointers with reference counting like ``std::shared_ptr`` |
|||
- Internal references with correct reference counting |
|||
- C++ classes with virtual (and pure virtual) methods can be extended in Python |
|||
|
|||
## Goodies |
|||
In addition to the core functionality, pybind11 provides some extra goodies: |
|||
|
|||
- pybind11 uses C++11 move constructors and move assignment operators whenever |
|||
possible to efficiently transfer custom data types. |
|||
|
|||
- It is possible to bind C++11 lambda functions with captured variables. The |
|||
lambda capture data is stored inside the resulting Python function object. |
|||
|
|||
- It's easy to expose the internal storage of custom data types through |
|||
Pythons' buffer protocols. This is handy e.g. for fast conversion between |
|||
C++ matrix classes like Eigen and NumPy without expensive copy operations. |
|||
|
|||
- pybind11 can automatically vectorize functions so that they are transparently |
|||
applied to all entries of one or more NumPy array arguments. |
|||
|
|||
- Python's slice-based access and assignment operations can be supported with |
|||
just a few lines of code. |
|||
|
|||
- Everything is contained in just a few header files; there is no need to link |
|||
against any additional libraries. |
|||
|
|||
- Binaries are generally smaller by a factor of at least 2 compared to |
|||
equivalent bindings generated by Boost.Python. A recent pybind11 conversion |
|||
of PyRosetta, an enormous Boost.Python binding project, |
|||
[reported](http://graylab.jhu.edu/RosettaCon2016/PyRosetta-4.pdf) a binary |
|||
size reduction of **5.4x** and compile time reduction by **5.8x**. |
|||
|
|||
- When supported by the compiler, two new C++14 features (relaxed constexpr and |
|||
return value deduction) are used to precompute function signatures at compile |
|||
time, leading to smaller binaries. |
|||
|
|||
- With little extra effort, C++ types can be pickled and unpickled similar to |
|||
regular Python objects. |
|||
|
|||
## Supported compilers |
|||
|
|||
1. Clang/LLVM (any non-ancient version with C++11 support) |
|||
2. GCC (any non-ancient version with C++11 support) |
|||
3. Microsoft Visual Studio 2015 or newer |
|||
4. Intel C++ compiler 16 or newer (15 with a [workaround](https://github.com/pybind/pybind11/issues/276)) |
|||
5. Cygwin/GCC (tested on 2.5.1) |
|||
|
|||
## About |
|||
|
|||
This project was created by [Wenzel Jakob](https://www.mitsuba-renderer.org/~wenzel/). |
|||
Significant features and/or improvements to the code were contributed by |
|||
Jonas Adler, |
|||
Sylvain Corlay, |
|||
Trent Houliston, |
|||
Axel Huebl, |
|||
@hulucc, |
|||
Sergey Lyskov |
|||
Johan Mabille, |
|||
Tomasz Miąsko, |
|||
Dean Moldovan, |
|||
Ben Pritchard, |
|||
Jason Rhinelander, |
|||
Boris Schäling, |
|||
Pim Schellart, and |
|||
Ivan Smirnov. |
|||
|
|||
### License |
|||
|
|||
pybind11 is provided under a BSD-style license that can be found in the |
|||
``LICENSE`` file. By using, distributing, or contributing to this project, |
|||
you agree to the terms and conditions of this license. |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,11 @@ |
|||
.wy-table-responsive table td, |
|||
.wy-table-responsive table th { |
|||
white-space: initial !important; |
|||
} |
|||
.rst-content table.docutils td { |
|||
vertical-align: top !important; |
|||
} |
|||
div[class^='highlight'] pre { |
|||
white-space: pre; |
|||
white-space: pre-wrap; |
|||
} |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,81 @@ |
|||
Chrono |
|||
====== |
|||
|
|||
When including the additional header file :file:`pybind11/chrono.h` conversions |
|||
from C++11 chrono datatypes to python datetime objects are automatically enabled. |
|||
This header also enables conversions of python floats (often from sources such |
|||
as `time.monotonic()`, `time.perf_counter()` and `time.process_time()`) into |
|||
durations. |
|||
|
|||
An overview of clocks in C++11 |
|||
------------------------------ |
|||
|
|||
A point of confusion when using these conversions is the differences between |
|||
clocks provided in C++11. There are three clock types defined by the C++11 |
|||
standard and users can define their own if needed. Each of these clocks have |
|||
different properties and when converting to and from python will give different |
|||
results. |
|||
|
|||
The first clock defined by the standard is ``std::chrono::system_clock``. This |
|||
clock measures the current date and time. However, this clock changes with to |
|||
updates to the operating system time. For example, if your time is synchronised |
|||
with a time server this clock will change. This makes this clock a poor choice |
|||
for timing purposes but good for measuring the wall time. |
|||
|
|||
The second clock defined in the standard is ``std::chrono::steady_clock``. |
|||
This clock ticks at a steady rate and is never adjusted. This makes it excellent |
|||
for timing purposes, however the value in this clock does not correspond to the |
|||
current date and time. Often this clock will be the amount of time your system |
|||
has been on, although it does not have to be. This clock will never be the same |
|||
clock as the system clock as the system clock can change but steady clocks |
|||
cannot. |
|||
|
|||
The third clock defined in the standard is ``std::chrono::high_resolution_clock``. |
|||
This clock is the clock that has the highest resolution out of the clocks in the |
|||
system. It is normally a typedef to either the system clock or the steady clock |
|||
but can be its own independent clock. This is important as when using these |
|||
conversions as the types you get in python for this clock might be different |
|||
depending on the system. |
|||
If it is a typedef of the system clock, python will get datetime objects, but if |
|||
it is a different clock they will be timedelta objects. |
|||
|
|||
Provided conversions |
|||
-------------------- |
|||
|
|||
.. rubric:: C++ to Python |
|||
|
|||
- ``std::chrono::system_clock::time_point`` → ``datetime.datetime`` |
|||
System clock times are converted to python datetime instances. They are |
|||
in the local timezone, but do not have any timezone information attached |
|||
to them (they are naive datetime objects). |
|||
|
|||
- ``std::chrono::duration`` → ``datetime.timedelta`` |
|||
Durations are converted to timedeltas, any precision in the duration |
|||
greater than microseconds is lost by rounding towards zero. |
|||
|
|||
- ``std::chrono::[other_clocks]::time_point`` → ``datetime.timedelta`` |
|||
Any clock time that is not the system clock is converted to a time delta. |
|||
This timedelta measures the time from the clocks epoch to now. |
|||
|
|||
.. rubric:: Python to C++ |
|||
|
|||
- ``datetime.datetime`` → ``std::chrono::system_clock::time_point`` |
|||
Date/time objects are converted into system clock timepoints. Any |
|||
timezone information is ignored and the type is treated as a naive |
|||
object. |
|||
|
|||
- ``datetime.timedelta`` → ``std::chrono::duration`` |
|||
Time delta are converted into durations with microsecond precision. |
|||
|
|||
- ``datetime.timedelta`` → ``std::chrono::[other_clocks]::time_point`` |
|||
Time deltas that are converted into clock timepoints are treated as |
|||
the amount of time from the start of the clocks epoch. |
|||
|
|||
- ``float`` → ``std::chrono::duration`` |
|||
Floats that are passed to C++ as durations be interpreted as a number of |
|||
seconds. These will be converted to the duration using ``duration_cast`` |
|||
from the float. |
|||
|
|||
- ``float`` → ``std::chrono::[other_clocks]::time_point`` |
|||
Floats that are passed to C++ as time points will be interpreted as the |
|||
number of seconds from the start of the clocks epoch. |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,85 @@ |
|||
Custom type casters |
|||
=================== |
|||
|
|||
In very rare cases, applications may require custom type casters that cannot be |
|||
expressed using the abstractions provided by pybind11, thus requiring raw |
|||
Python C API calls. This is fairly advanced usage and should only be pursued by |
|||
experts who are familiar with the intricacies of Python reference counting. |
|||
|
|||
The following snippets demonstrate how this works for a very simple ``inty`` |
|||
type that that should be convertible from Python types that provide a |
|||
``__int__(self)`` method. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
struct inty { long long_value; }; |
|||
|
|||
void print(inty s) { |
|||
std::cout << s.long_value << std::endl; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
The following Python snippet demonstrates the intended usage from the Python side: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: python |
|||
|
|||
class A: |
|||
def __int__(self): |
|||
return 123 |
|||
|
|||
from example import print |
|||
print(A()) |
|||
|
|||
To register the necessary conversion routines, it is necessary to add |
|||
a partial overload to the ``pybind11::detail::type_caster<T>`` template. |
|||
Although this is an implementation detail, adding partial overloads to this |
|||
type is explicitly allowed. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
namespace pybind11 { namespace detail { |
|||
template <> struct type_caster<inty> { |
|||
public: |
|||
/** |
|||
* This macro establishes the name 'inty' in |
|||
* function signatures and declares a local variable |
|||
* 'value' of type inty |
|||
*/ |
|||
PYBIND11_TYPE_CASTER(inty, _("inty")); |
|||
|
|||
/** |
|||
* Conversion part 1 (Python->C++): convert a PyObject into a inty |
|||
* instance or return false upon failure. The second argument |
|||
* indicates whether implicit conversions should be applied. |
|||
*/ |
|||
bool load(handle src, bool) { |
|||
/* Extract PyObject from handle */ |
|||
PyObject *source = src.ptr(); |
|||
/* Try converting into a Python integer value */ |
|||
PyObject *tmp = PyNumber_Long(source); |
|||
if (!tmp) |
|||
return false; |
|||
/* Now try to convert into a C++ int */ |
|||
value.long_value = PyLong_AsLong(tmp); |
|||
Py_DECREF(tmp); |
|||
/* Ensure return code was OK (to avoid out-of-range errors etc) */ |
|||
return !(value.long_value == -1 && !PyErr_Occurred()); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
/** |
|||
* Conversion part 2 (C++ -> Python): convert an inty instance into |
|||
* a Python object. The second and third arguments are used to |
|||
* indicate the return value policy and parent object (for |
|||
* ``return_value_policy::reference_internal``) and are generally |
|||
* ignored by implicit casters. |
|||
*/ |
|||
static handle cast(inty src, return_value_policy /* policy */, handle /* parent */) { |
|||
return PyLong_FromLong(src.long_value); |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
}} // namespace pybind11::detail |
|||
|
|||
.. warning:: |
|||
|
|||
When using custom type casters, it's important to declare them consistently |
|||
in every compilation unit of the Python extension module. Otherwise, |
|||
undefined behavior can ensue. |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,50 @@ |
|||
Eigen |
|||
===== |
|||
|
|||
`Eigen <http://eigen.tuxfamily.org>`_ is C++ header-based library for dense and |
|||
sparse linear algebra. Due to its popularity and widespread adoption, pybind11 |
|||
provides transparent conversion support between Eigen and Scientific Python linear |
|||
algebra data types. |
|||
|
|||
Specifically, when including the optional header file :file:`pybind11/eigen.h`, |
|||
pybind11 will automatically and transparently convert |
|||
|
|||
1. Static and dynamic Eigen dense vectors and matrices to instances of |
|||
``numpy.ndarray`` (and vice versa). |
|||
|
|||
2. Returned matrix expressions such as blocks (including columns or rows) and |
|||
diagonals will be converted to ``numpy.ndarray`` of the expression |
|||
values. |
|||
|
|||
3. Returned matrix-like objects such as Eigen::DiagonalMatrix or |
|||
Eigen::SelfAdjointView will be converted to ``numpy.ndarray`` containing the |
|||
expressed value. |
|||
|
|||
4. Eigen sparse vectors and matrices to instances of |
|||
``scipy.sparse.csr_matrix``/``scipy.sparse.csc_matrix`` (and vice versa). |
|||
|
|||
This makes it possible to bind most kinds of functions that rely on these types. |
|||
One major caveat are functions that take Eigen matrices *by reference* and modify |
|||
them somehow, in which case the information won't be propagated to the caller. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
/* The Python bindings of these functions won't replicate |
|||
the intended effect of modifying the function arguments */ |
|||
void scale_by_2(Eigen::Vector3f &v) { |
|||
v *= 2; |
|||
} |
|||
void scale_by_2(Eigen::Ref<Eigen::MatrixXd> &v) { |
|||
v *= 2; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
To see why this is, refer to the section on :ref:`opaque` (although that |
|||
section specifically covers STL data types, the underlying issue is the same). |
|||
The :ref:`numpy` sections discuss an efficient alternative for exposing the |
|||
underlying native Eigen types as opaque objects in a way that still integrates |
|||
with NumPy and SciPy. |
|||
|
|||
.. seealso:: |
|||
|
|||
The file :file:`tests/test_eigen.cpp` contains a complete example that |
|||
shows how to pass Eigen sparse and dense data types in more detail. |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,113 @@ |
|||
Functional |
|||
########## |
|||
|
|||
The following features must be enabled by including :file:`pybind11/functional.h`. |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
Callbacks and passing anonymous functions |
|||
========================================= |
|||
|
|||
The C++11 standard brought lambda functions and the generic polymorphic |
|||
function wrapper ``std::function<>`` to the C++ programming language, which |
|||
enable powerful new ways of working with functions. Lambda functions come in |
|||
two flavors: stateless lambda function resemble classic function pointers that |
|||
link to an anonymous piece of code, while stateful lambda functions |
|||
additionally depend on captured variables that are stored in an anonymous |
|||
*lambda closure object*. |
|||
|
|||
Here is a simple example of a C++ function that takes an arbitrary function |
|||
(stateful or stateless) with signature ``int -> int`` as an argument and runs |
|||
it with the value 10. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
int func_arg(const std::function<int(int)> &f) { |
|||
return f(10); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
The example below is more involved: it takes a function of signature ``int -> int`` |
|||
and returns another function of the same kind. The return value is a stateful |
|||
lambda function, which stores the value ``f`` in the capture object and adds 1 to |
|||
its return value upon execution. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
std::function<int(int)> func_ret(const std::function<int(int)> &f) { |
|||
return [f](int i) { |
|||
return f(i) + 1; |
|||
}; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
This example demonstrates using python named parameters in C++ callbacks which |
|||
requires using ``py::cpp_function`` as a wrapper. Usage is similar to defining |
|||
methods of classes: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::cpp_function func_cpp() { |
|||
return py::cpp_function([](int i) { return i+1; }, |
|||
py::arg("number")); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
After including the extra header file :file:`pybind11/functional.h`, it is almost |
|||
trivial to generate binding code for all of these functions. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
#include <pybind11/functional.h> |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_PLUGIN(example) { |
|||
py::module m("example", "pybind11 example plugin"); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("func_arg", &func_arg); |
|||
m.def("func_ret", &func_ret); |
|||
m.def("func_cpp", &func_cpp); |
|||
|
|||
return m.ptr(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
The following interactive session shows how to call them from Python. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
$ python |
|||
>>> import example |
|||
>>> def square(i): |
|||
... return i * i |
|||
... |
|||
>>> example.func_arg(square) |
|||
100L |
|||
>>> square_plus_1 = example.func_ret(square) |
|||
>>> square_plus_1(4) |
|||
17L |
|||
>>> plus_1 = func_cpp() |
|||
>>> plus_1(number=43) |
|||
44L |
|||
|
|||
.. warning:: |
|||
|
|||
Keep in mind that passing a function from C++ to Python (or vice versa) |
|||
will instantiate a piece of wrapper code that translates function |
|||
invocations between the two languages. Naturally, this translation |
|||
increases the computational cost of each function call somewhat. A |
|||
problematic situation can arise when a function is copied back and forth |
|||
between Python and C++ many times in a row, in which case the underlying |
|||
wrappers will accumulate correspondingly. The resulting long sequence of |
|||
C++ -> Python -> C++ -> ... roundtrips can significantly decrease |
|||
performance. |
|||
|
|||
There is one exception: pybind11 detects case where a stateless function |
|||
(i.e. a function pointer or a lambda function without captured variables) |
|||
is passed as an argument to another C++ function exposed in Python. In this |
|||
case, there is no overhead. Pybind11 will extract the underlying C++ |
|||
function pointer from the wrapped function to sidestep a potential C++ -> |
|||
Python -> C++ roundtrip. This is demonstrated in :file:`tests/test_callbacks.cpp`. |
|||
|
|||
.. note:: |
|||
|
|||
This functionality is very useful when generating bindings for callbacks in |
|||
C++ libraries (e.g. GUI libraries, asynchronous networking libraries, etc.). |
|||
|
|||
The file :file:`tests/test_callbacks.cpp` contains a complete example |
|||
that demonstrates how to work with callbacks and anonymous functions in |
|||
more detail. |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@ |
|||
Type conversions |
|||
################ |
|||
|
|||
Apart from enabling cross-language function calls, a fundamental problem |
|||
that a binding tool like pybind11 must address is to provide access to |
|||
native Python types in C++ and vice versa. There are three fundamentally |
|||
different ways to do this—which approach is preferable for a particular type |
|||
depends on the situation at hand. |
|||
|
|||
1. Use a native C++ type everywhere. In this case, the type must be wrapped |
|||
using pybind11-generated bindings so that Python can interact with it. |
|||
|
|||
2. Use a native Python type everywhere. It will need to be wrapped so that |
|||
C++ functions can interact with it. |
|||
|
|||
3. Use a native C++ type on the C++ side and a native Python type on the |
|||
Python side. pybind11 refers to this as a *type conversion*. |
|||
|
|||
Type conversions are the most "natural" option in the sense that native |
|||
(non-wrapped) types are used everywhere. The main downside is that a copy |
|||
of the data must be made on every Python ↔ C++ transition: this is |
|||
needed since the C++ and Python versions of the same type generally won't |
|||
have the same memory layout. |
|||
|
|||
pybind11 can perform many kinds of conversions automatically. An overview |
|||
is provided in the table ":ref:`conversion_table`". |
|||
|
|||
The following subsections discuss the differences between these options in more |
|||
detail. The main focus in this section is on type conversions, which represent |
|||
the last case of the above list. |
|||
|
|||
.. toctree:: |
|||
:maxdepth: 1 |
|||
|
|||
overview |
|||
stl |
|||
functional |
|||
chrono |
|||
eigen |
|||
custom |
|||
|
|||
@ -0,0 +1,144 @@ |
|||
Overview |
|||
######## |
|||
|
|||
.. rubric:: 1. Native type in C++, wrapper in Python |
|||
|
|||
Exposing a custom C++ type using :class:`py::class_` was covered in detail |
|||
in the :doc:`/classes` section. There, the underlying data structure is |
|||
always the original C++ class while the :class:`py::class_` wrapper provides |
|||
a Python interface. Internally, when an object like this is sent from C++ to |
|||
Python, pybind11 will just add the outer wrapper layer over the native C++ |
|||
object. Getting it back from Python is just a matter of peeling off the |
|||
wrapper. |
|||
|
|||
.. rubric:: 2. Wrapper in C++, native type in Python |
|||
|
|||
This is the exact opposite situation. Now, we have a type which is native to |
|||
Python, like a ``tuple`` or a ``list``. One way to get this data into C++ is |
|||
with the :class:`py::object` family of wrappers. These are explained in more |
|||
detail in the :doc:`/advanced/pycpp/object` section. We'll just give a quick |
|||
example here: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
void print_list(py::list my_list) { |
|||
for (auto item : my_list) |
|||
std::cout << item << " "; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> print_list([1, 2, 3]) |
|||
1 2 3 |
|||
|
|||
The Python ``list`` is not converted in any way -- it's just wrapped in a C++ |
|||
:class:`py::list` class. At its core it's still a Python object. Copying a |
|||
:class:`py::list` will do the usual reference-counting like in Python. |
|||
Returning the object to Python will just remove the thin wrapper. |
|||
|
|||
.. rubric:: 3. Converting between native C++ and Python types |
|||
|
|||
In the previous two cases we had a native type in one language and a wrapper in |
|||
the other. Now, we have native types on both sides and we convert between them. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
void print_vector(const std::vector<int> &v) { |
|||
for (auto item : v) |
|||
std::cout << item << "\n"; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> print_vector([1, 2, 3]) |
|||
1 2 3 |
|||
|
|||
In this case, pybind11 will construct a new ``std::vector<int>`` and copy each |
|||
element from the Python ``list``. The newly constructed object will be passed |
|||
to ``print_vector``. The same thing happens in the other direction: a new |
|||
``list`` is made to match the value returned from C++. |
|||
|
|||
Lots of these conversions are supported out of the box, as shown in the table |
|||
below. They are very convenient, but keep in mind that these conversions are |
|||
fundamentally based on copying data. This is perfectly fine for small immutable |
|||
types but it may become quite expensive for large data structures. This can be |
|||
avoided by overriding the automatic conversion with a custom wrapper (i.e. the |
|||
above-mentioned approach 1). This requires some manual effort and more details |
|||
are available in the :ref:`opaque` section. |
|||
|
|||
.. _conversion_table: |
|||
|
|||
List of all builtin conversions |
|||
------------------------------- |
|||
|
|||
The following basic data types are supported out of the box (some may require |
|||
an additional extension header to be included). To pass other data structures |
|||
as arguments and return values, refer to the section on binding :ref:`classes`. |
|||
|
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| Data type | Description | Header file | |
|||
+====================================+===========================+===============================+ |
|||
| ``int8_t``, ``uint8_t`` | 8-bit integers | :file:`pybind11/pybind11.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``int16_t``, ``uint16_t`` | 16-bit integers | :file:`pybind11/pybind11.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``int32_t``, ``uint32_t`` | 32-bit integers | :file:`pybind11/pybind11.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``int64_t``, ``uint64_t`` | 64-bit integers | :file:`pybind11/pybind11.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``ssize_t``, ``size_t`` | Platform-dependent size | :file:`pybind11/pybind11.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``float``, ``double`` | Floating point types | :file:`pybind11/pybind11.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``bool`` | Two-state Boolean type | :file:`pybind11/pybind11.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``char`` | Character literal | :file:`pybind11/pybind11.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``wchar_t`` | Wide character literal | :file:`pybind11/pybind11.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``const char *`` | UTF-8 string literal | :file:`pybind11/pybind11.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``const wchar_t *`` | Wide string literal | :file:`pybind11/pybind11.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``std::string`` | STL dynamic UTF-8 string | :file:`pybind11/pybind11.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``std::wstring`` | STL dynamic wide string | :file:`pybind11/pybind11.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``std::pair<T1, T2>`` | Pair of two custom types | :file:`pybind11/pybind11.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``std::tuple<...>`` | Arbitrary tuple of types | :file:`pybind11/pybind11.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``std::reference_wrapper<...>`` | Reference type wrapper | :file:`pybind11/pybind11.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``std::complex<T>`` | Complex numbers | :file:`pybind11/complex.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``std::array<T, Size>`` | STL static array | :file:`pybind11/stl.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``std::vector<T>`` | STL dynamic array | :file:`pybind11/stl.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``std::list<T>`` | STL linked list | :file:`pybind11/stl.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``std::map<T1, T2>`` | STL ordered map | :file:`pybind11/stl.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``std::unordered_map<T1, T2>`` | STL unordered map | :file:`pybind11/stl.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``std::set<T>`` | STL ordered set | :file:`pybind11/stl.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``std::unordered_set<T>`` | STL unordered set | :file:`pybind11/stl.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``std::optional<T>`` | STL optional type (C++17) | :file:`pybind11/stl.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``std::experimental::optional<T>`` | STL optional type (exp.) | :file:`pybind11/stl.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``std::function<...>`` | STL polymorphic function | :file:`pybind11/functional.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``std::chrono::duration<...>`` | STL time duration | :file:`pybind11/chrono.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``std::chrono::time_point<...>`` | STL date/time | :file:`pybind11/chrono.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``Eigen::Matrix<...>`` | Eigen: dense matrix | :file:`pybind11/eigen.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``Eigen::Map<...>`` | Eigen: mapped memory | :file:`pybind11/eigen.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
| ``Eigen::SparseMatrix<...>`` | Eigen: sparse matrix | :file:`pybind11/eigen.h` | |
|||
+------------------------------------+---------------------------+-------------------------------+ |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,154 @@ |
|||
STL containers |
|||
############## |
|||
|
|||
Automatic conversion |
|||
==================== |
|||
|
|||
When including the additional header file :file:`pybind11/stl.h`, conversions |
|||
between ``std::vector<>``, ``std::list<>``, ``std::set<>``, and ``std::map<>`` |
|||
and the Python ``list``, ``set`` and ``dict`` data structures are automatically |
|||
enabled. The types ``std::pair<>`` and ``std::tuple<>`` are already supported |
|||
out of the box with just the core :file:`pybind11/pybind11.h` header. |
|||
|
|||
The major downside of these implicit conversions is that containers must be |
|||
converted (i.e. copied) on every Python->C++ and C++->Python transition, which |
|||
can have implications on the program semantics and performance. Please read the |
|||
next sections for more details and alternative approaches that avoid this. |
|||
|
|||
.. note:: |
|||
|
|||
Arbitrary nesting of any of these types is possible. |
|||
|
|||
.. seealso:: |
|||
|
|||
The file :file:`tests/test_python_types.cpp` contains a complete |
|||
example that demonstrates how to pass STL data types in more detail. |
|||
|
|||
.. _opaque: |
|||
|
|||
Making opaque types |
|||
=================== |
|||
|
|||
pybind11 heavily relies on a template matching mechanism to convert parameters |
|||
and return values that are constructed from STL data types such as vectors, |
|||
linked lists, hash tables, etc. This even works in a recursive manner, for |
|||
instance to deal with lists of hash maps of pairs of elementary and custom |
|||
types, etc. |
|||
|
|||
However, a fundamental limitation of this approach is that internal conversions |
|||
between Python and C++ types involve a copy operation that prevents |
|||
pass-by-reference semantics. What does this mean? |
|||
|
|||
Suppose we bind the following function |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
void append_1(std::vector<int> &v) { |
|||
v.push_back(1); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
and call it from Python, the following happens: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> v = [5, 6] |
|||
>>> append_1(v) |
|||
>>> print(v) |
|||
[5, 6] |
|||
|
|||
As you can see, when passing STL data structures by reference, modifications |
|||
are not propagated back the Python side. A similar situation arises when |
|||
exposing STL data structures using the ``def_readwrite`` or ``def_readonly`` |
|||
functions: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
/* ... definition ... */ |
|||
|
|||
class MyClass { |
|||
std::vector<int> contents; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/* ... binding code ... */ |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<MyClass>(m, "MyClass") |
|||
.def(py::init<>) |
|||
.def_readwrite("contents", &MyClass::contents); |
|||
|
|||
In this case, properties can be read and written in their entirety. However, an |
|||
``append`` operation involving such a list type has no effect: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> m = MyClass() |
|||
>>> m.contents = [5, 6] |
|||
>>> print(m.contents) |
|||
[5, 6] |
|||
>>> m.contents.append(7) |
|||
>>> print(m.contents) |
|||
[5, 6] |
|||
|
|||
Finally, the involved copy operations can be costly when dealing with very |
|||
large lists. To deal with all of the above situations, pybind11 provides a |
|||
macro named ``PYBIND11_MAKE_OPAQUE(T)`` that disables the template-based |
|||
conversion machinery of types, thus rendering them *opaque*. The contents of |
|||
opaque objects are never inspected or extracted, hence they *can* be passed by |
|||
reference. For instance, to turn ``std::vector<int>`` into an opaque type, add |
|||
the declaration |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_MAKE_OPAQUE(std::vector<int>); |
|||
|
|||
before any binding code (e.g. invocations to ``class_::def()``, etc.). This |
|||
macro must be specified at the top level (and outside of any namespaces), since |
|||
it instantiates a partial template overload. If your binding code consists of |
|||
multiple compilation units, it must be present in every file preceding any |
|||
usage of ``std::vector<int>``. Opaque types must also have a corresponding |
|||
``class_`` declaration to associate them with a name in Python, and to define a |
|||
set of available operations, e.g.: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<std::vector<int>>(m, "IntVector") |
|||
.def(py::init<>()) |
|||
.def("clear", &std::vector<int>::clear) |
|||
.def("pop_back", &std::vector<int>::pop_back) |
|||
.def("__len__", [](const std::vector<int> &v) { return v.size(); }) |
|||
.def("__iter__", [](std::vector<int> &v) { |
|||
return py::make_iterator(v.begin(), v.end()); |
|||
}, py::keep_alive<0, 1>()) /* Keep vector alive while iterator is used */ |
|||
// .... |
|||
|
|||
The ability to expose STL containers as native Python objects is a fairly |
|||
common request, hence pybind11 also provides an optional header file named |
|||
:file:`pybind11/stl_bind.h` that does exactly this. The mapped containers try |
|||
to match the behavior of their native Python counterparts as much as possible. |
|||
|
|||
The following example showcases usage of :file:`pybind11/stl_bind.h`: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
// Don't forget this |
|||
#include <pybind11/stl_bind.h> |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_MAKE_OPAQUE(std::vector<int>); |
|||
PYBIND11_MAKE_OPAQUE(std::map<std::string, double>); |
|||
|
|||
// ... |
|||
|
|||
// later in binding code: |
|||
py::bind_vector<std::vector<int>>(m, "VectorInt"); |
|||
py::bind_map<std::map<std::string, double>>(m, "MapStringDouble"); |
|||
|
|||
Please take a look at the :ref:`macro_notes` before using the |
|||
``PYBIND11_MAKE_OPAQUE`` macro. |
|||
|
|||
.. seealso:: |
|||
|
|||
The file :file:`tests/test_opaque_types.cpp` contains a complete |
|||
example that demonstrates how to create and expose opaque types using |
|||
pybind11 in more detail. |
|||
|
|||
The file :file:`tests/test_stl_binders.cpp` shows how to use the |
|||
convenience STL container wrappers. |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,634 @@ |
|||
Classes |
|||
####### |
|||
|
|||
This section presents advanced binding code for classes and it is assumed |
|||
that you are already familiar with the basics from :doc:`/classes`. |
|||
|
|||
.. _overriding_virtuals: |
|||
|
|||
Overriding virtual functions in Python |
|||
====================================== |
|||
|
|||
Suppose that a C++ class or interface has a virtual function that we'd like to |
|||
to override from within Python (we'll focus on the class ``Animal``; ``Dog`` is |
|||
given as a specific example of how one would do this with traditional C++ |
|||
code). |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
class Animal { |
|||
public: |
|||
virtual ~Animal() { } |
|||
virtual std::string go(int n_times) = 0; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
class Dog : public Animal { |
|||
public: |
|||
std::string go(int n_times) override { |
|||
std::string result; |
|||
for (int i=0; i<n_times; ++i) |
|||
result += "woof! "; |
|||
return result; |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
Let's also suppose that we are given a plain function which calls the |
|||
function ``go()`` on an arbitrary ``Animal`` instance. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
std::string call_go(Animal *animal) { |
|||
return animal->go(3); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
Normally, the binding code for these classes would look as follows: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_PLUGIN(example) { |
|||
py::module m("example", "pybind11 example plugin"); |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Animal> animal(m, "Animal"); |
|||
animal |
|||
.def("go", &Animal::go); |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Dog>(m, "Dog", animal) |
|||
.def(py::init<>()); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("call_go", &call_go); |
|||
|
|||
return m.ptr(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
However, these bindings are impossible to extend: ``Animal`` is not |
|||
constructible, and we clearly require some kind of "trampoline" that |
|||
redirects virtual calls back to Python. |
|||
|
|||
Defining a new type of ``Animal`` from within Python is possible but requires a |
|||
helper class that is defined as follows: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
class PyAnimal : public Animal { |
|||
public: |
|||
/* Inherit the constructors */ |
|||
using Animal::Animal; |
|||
|
|||
/* Trampoline (need one for each virtual function) */ |
|||
std::string go(int n_times) override { |
|||
PYBIND11_OVERLOAD_PURE( |
|||
std::string, /* Return type */ |
|||
Animal, /* Parent class */ |
|||
go, /* Name of function */ |
|||
n_times /* Argument(s) */ |
|||
); |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
The macro :func:`PYBIND11_OVERLOAD_PURE` should be used for pure virtual |
|||
functions, and :func:`PYBIND11_OVERLOAD` should be used for functions which have |
|||
a default implementation. There are also two alternate macros |
|||
:func:`PYBIND11_OVERLOAD_PURE_NAME` and :func:`PYBIND11_OVERLOAD_NAME` which |
|||
take a string-valued name argument between the *Parent class* and *Name of the |
|||
function* slots. This is useful when the C++ and Python versions of the |
|||
function have different names, e.g. ``operator()`` vs ``__call__``. |
|||
|
|||
The binding code also needs a few minor adaptations (highlighted): |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
:emphasize-lines: 4,6,7 |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_PLUGIN(example) { |
|||
py::module m("example", "pybind11 example plugin"); |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Animal, PyAnimal /* <--- trampoline*/> animal(m, "Animal"); |
|||
animal |
|||
.def(py::init<>()) |
|||
.def("go", &Animal::go); |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Dog>(m, "Dog", animal) |
|||
.def(py::init<>()); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("call_go", &call_go); |
|||
|
|||
return m.ptr(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
Importantly, pybind11 is made aware of the trampoline helper class by |
|||
specifying it as an extra template argument to :class:`class_`. (This can also |
|||
be combined with other template arguments such as a custom holder type; the |
|||
order of template types does not matter). Following this, we are able to |
|||
define a constructor as usual. |
|||
|
|||
Note, however, that the above is sufficient for allowing python classes to |
|||
extend ``Animal``, but not ``Dog``: see ref:`virtual_and_inheritance` for the |
|||
necessary steps required to providing proper overload support for inherited |
|||
classes. |
|||
|
|||
The Python session below shows how to override ``Animal::go`` and invoke it via |
|||
a virtual method call. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> from example import * |
|||
>>> d = Dog() |
|||
>>> call_go(d) |
|||
u'woof! woof! woof! ' |
|||
>>> class Cat(Animal): |
|||
... def go(self, n_times): |
|||
... return "meow! " * n_times |
|||
... |
|||
>>> c = Cat() |
|||
>>> call_go(c) |
|||
u'meow! meow! meow! ' |
|||
|
|||
Please take a look at the :ref:`macro_notes` before using this feature. |
|||
|
|||
.. note:: |
|||
|
|||
When the overridden type returns a reference or pointer to a type that |
|||
pybind11 converts from Python (for example, numeric values, std::string, |
|||
and other built-in value-converting types), there are some limitations to |
|||
be aware of: |
|||
|
|||
- because in these cases there is no C++ variable to reference (the value |
|||
is stored in the referenced Python variable), pybind11 provides one in |
|||
the PYBIND11_OVERLOAD macros (when needed) with static storage duration. |
|||
Note that this means that invoking the overloaded method on *any* |
|||
instance will change the referenced value stored in *all* instances of |
|||
that type. |
|||
|
|||
- Attempts to modify a non-const reference will not have the desired |
|||
effect: it will change only the static cache variable, but this change |
|||
will not propagate to underlying Python instance, and the change will be |
|||
replaced the next time the overload is invoked. |
|||
|
|||
.. seealso:: |
|||
|
|||
The file :file:`tests/test_virtual_functions.cpp` contains a complete |
|||
example that demonstrates how to override virtual functions using pybind11 |
|||
in more detail. |
|||
|
|||
.. _virtual_and_inheritance: |
|||
|
|||
Combining virtual functions and inheritance |
|||
=========================================== |
|||
|
|||
When combining virtual methods with inheritance, you need to be sure to provide |
|||
an override for each method for which you want to allow overrides from derived |
|||
python classes. For example, suppose we extend the above ``Animal``/``Dog`` |
|||
example as follows: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
class Animal { |
|||
public: |
|||
virtual std::string go(int n_times) = 0; |
|||
virtual std::string name() { return "unknown"; } |
|||
}; |
|||
class Dog : public class Animal { |
|||
public: |
|||
std::string go(int n_times) override { |
|||
std::string result; |
|||
for (int i=0; i<n_times; ++i) |
|||
result += bark() + " "; |
|||
return result; |
|||
} |
|||
virtual std::string bark() { return "woof!"; } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
then the trampoline class for ``Animal`` must, as described in the previous |
|||
section, override ``go()`` and ``name()``, but in order to allow python code to |
|||
inherit properly from ``Dog``, we also need a trampoline class for ``Dog`` that |
|||
overrides both the added ``bark()`` method *and* the ``go()`` and ``name()`` |
|||
methods inherited from ``Animal`` (even though ``Dog`` doesn't directly |
|||
override the ``name()`` method): |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
class PyAnimal : public Animal { |
|||
public: |
|||
using Animal::Animal; // Inherit constructors |
|||
std::string go(int n_times) override { PYBIND11_OVERLOAD_PURE(std::string, Animal, go, n_times); } |
|||
std::string name() override { PYBIND11_OVERLOAD(std::string, Animal, name, ); } |
|||
}; |
|||
class PyDog : public Dog { |
|||
public: |
|||
using Dog::Dog; // Inherit constructors |
|||
std::string go(int n_times) override { PYBIND11_OVERLOAD_PURE(std::string, Dog, go, n_times); } |
|||
std::string name() override { PYBIND11_OVERLOAD(std::string, Dog, name, ); } |
|||
std::string bark() override { PYBIND11_OVERLOAD(std::string, Dog, bark, ); } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
A registered class derived from a pybind11-registered class with virtual |
|||
methods requires a similar trampoline class, *even if* it doesn't explicitly |
|||
declare or override any virtual methods itself: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
class Husky : public Dog {}; |
|||
class PyHusky : public Husky { |
|||
using Dog::Dog; // Inherit constructors |
|||
std::string go(int n_times) override { PYBIND11_OVERLOAD_PURE(std::string, Husky, go, n_times); } |
|||
std::string name() override { PYBIND11_OVERLOAD(std::string, Husky, name, ); } |
|||
std::string bark() override { PYBIND11_OVERLOAD(std::string, Husky, bark, ); } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
There is, however, a technique that can be used to avoid this duplication |
|||
(which can be especially helpful for a base class with several virtual |
|||
methods). The technique involves using template trampoline classes, as |
|||
follows: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
template <class AnimalBase = Animal> class PyAnimal : public AnimalBase { |
|||
using AnimalBase::AnimalBase; // Inherit constructors |
|||
std::string go(int n_times) override { PYBIND11_OVERLOAD_PURE(std::string, AnimalBase, go, n_times); } |
|||
std::string name() override { PYBIND11_OVERLOAD(std::string, AnimalBase, name, ); } |
|||
}; |
|||
template <class DogBase = Dog> class PyDog : public PyAnimal<DogBase> { |
|||
using PyAnimal<DogBase>::PyAnimal; // Inherit constructors |
|||
// Override PyAnimal's pure virtual go() with a non-pure one: |
|||
std::string go(int n_times) override { PYBIND11_OVERLOAD(std::string, DogBase, go, n_times); } |
|||
std::string bark() override { PYBIND11_OVERLOAD(std::string, DogBase, bark, ); } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
This technique has the advantage of requiring just one trampoline method to be |
|||
declared per virtual method and pure virtual method override. It does, |
|||
however, require the compiler to generate at least as many methods (and |
|||
possibly more, if both pure virtual and overridden pure virtual methods are |
|||
exposed, as above). |
|||
|
|||
The classes are then registered with pybind11 using: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Animal, PyAnimal<>> animal(m, "Animal"); |
|||
py::class_<Dog, PyDog<>> dog(m, "Dog"); |
|||
py::class_<Husky, PyDog<Husky>> husky(m, "Husky"); |
|||
// ... add animal, dog, husky definitions |
|||
|
|||
Note that ``Husky`` did not require a dedicated trampoline template class at |
|||
all, since it neither declares any new virtual methods nor provides any pure |
|||
virtual method implementations. |
|||
|
|||
With either the repeated-virtuals or templated trampoline methods in place, you |
|||
can now create a python class that inherits from ``Dog``: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: python |
|||
|
|||
class ShihTzu(Dog): |
|||
def bark(self): |
|||
return "yip!" |
|||
|
|||
.. seealso:: |
|||
|
|||
See the file :file:`tests/test_virtual_functions.cpp` for complete examples |
|||
using both the duplication and templated trampoline approaches. |
|||
|
|||
Extended trampoline class functionality |
|||
======================================= |
|||
|
|||
The trampoline classes described in the previous sections are, by default, only |
|||
initialized when needed. More specifically, they are initialized when a python |
|||
class actually inherits from a registered type (instead of merely creating an |
|||
instance of the registered type), or when a registered constructor is only |
|||
valid for the trampoline class but not the registered class. This is primarily |
|||
for performance reasons: when the trampoline class is not needed for anything |
|||
except virtual method dispatching, not initializing the trampoline class |
|||
improves performance by avoiding needing to do a run-time check to see if the |
|||
inheriting python instance has an overloaded method. |
|||
|
|||
Sometimes, however, it is useful to always initialize a trampoline class as an |
|||
intermediate class that does more than just handle virtual method dispatching. |
|||
For example, such a class might perform extra class initialization, extra |
|||
destruction operations, and might define new members and methods to enable a |
|||
more python-like interface to a class. |
|||
|
|||
In order to tell pybind11 that it should *always* initialize the trampoline |
|||
class when creating new instances of a type, the class constructors should be |
|||
declared using ``py::init_alias<Args, ...>()`` instead of the usual |
|||
``py::init<Args, ...>()``. This forces construction via the trampoline class, |
|||
ensuring member initialization and (eventual) destruction. |
|||
|
|||
.. seealso:: |
|||
|
|||
See the file :file:`tests/test_alias_initialization.cpp` for complete examples |
|||
showing both normal and forced trampoline instantiation. |
|||
|
|||
.. _custom_constructors: |
|||
|
|||
Custom constructors |
|||
=================== |
|||
|
|||
The syntax for binding constructors was previously introduced, but it only |
|||
works when a constructor with the given parameters actually exists on the C++ |
|||
side. To extend this to more general cases, let's take a look at what actually |
|||
happens under the hood: the following statement |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Example>(m, "Example") |
|||
.def(py::init<int>()); |
|||
|
|||
is short hand notation for |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Example>(m, "Example") |
|||
.def("__init__", |
|||
[](Example &instance, int arg) { |
|||
new (&instance) Example(arg); |
|||
} |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
In other words, :func:`init` creates an anonymous function that invokes an |
|||
in-place constructor. Memory allocation etc. is already take care of beforehand |
|||
within pybind11. |
|||
|
|||
.. _classes_with_non_public_destructors: |
|||
|
|||
Non-public destructors |
|||
====================== |
|||
|
|||
If a class has a private or protected destructor (as might e.g. be the case in |
|||
a singleton pattern), a compile error will occur when creating bindings via |
|||
pybind11. The underlying issue is that the ``std::unique_ptr`` holder type that |
|||
is responsible for managing the lifetime of instances will reference the |
|||
destructor even if no deallocations ever take place. In order to expose classes |
|||
with private or protected destructors, it is possible to override the holder |
|||
type via a holder type argument to ``class_``. Pybind11 provides a helper class |
|||
``py::nodelete`` that disables any destructor invocations. In this case, it is |
|||
crucial that instances are deallocated on the C++ side to avoid memory leaks. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
/* ... definition ... */ |
|||
|
|||
class MyClass { |
|||
private: |
|||
~MyClass() { } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/* ... binding code ... */ |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<MyClass, std::unique_ptr<MyClass, py::nodelete>>(m, "MyClass") |
|||
.def(py::init<>) |
|||
|
|||
Implicit conversions |
|||
==================== |
|||
|
|||
Suppose that instances of two types ``A`` and ``B`` are used in a project, and |
|||
that an ``A`` can easily be converted into an instance of type ``B`` (examples of this |
|||
could be a fixed and an arbitrary precision number type). |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<A>(m, "A") |
|||
/// ... members ... |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<B>(m, "B") |
|||
.def(py::init<A>()) |
|||
/// ... members ... |
|||
|
|||
m.def("func", |
|||
[](const B &) { /* .... */ } |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
To invoke the function ``func`` using a variable ``a`` containing an ``A`` |
|||
instance, we'd have to write ``func(B(a))`` in Python. On the other hand, C++ |
|||
will automatically apply an implicit type conversion, which makes it possible |
|||
to directly write ``func(a)``. |
|||
|
|||
In this situation (i.e. where ``B`` has a constructor that converts from |
|||
``A``), the following statement enables similar implicit conversions on the |
|||
Python side: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::implicitly_convertible<A, B>(); |
|||
|
|||
.. note:: |
|||
|
|||
Implicit conversions from ``A`` to ``B`` only work when ``B`` is a custom |
|||
data type that is exposed to Python via pybind11. |
|||
|
|||
.. _static_properties: |
|||
|
|||
Static properties |
|||
================= |
|||
|
|||
The section on :ref:`properties` discussed the creation of instance properties |
|||
that are implemented in terms of C++ getters and setters. |
|||
|
|||
Static properties can also be created in a similar way to expose getters and |
|||
setters of static class attributes. It is important to note that the implicit |
|||
``self`` argument also exists in this case and is used to pass the Python |
|||
``type`` subclass instance. This parameter will often not be needed by the C++ |
|||
side, and the following example illustrates how to instantiate a lambda getter |
|||
function that ignores it: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Foo>(m, "Foo") |
|||
.def_property_readonly_static("foo", [](py::object /* self */) { return Foo(); }); |
|||
|
|||
Operator overloading |
|||
==================== |
|||
|
|||
Suppose that we're given the following ``Vector2`` class with a vector addition |
|||
and scalar multiplication operation, all implemented using overloaded operators |
|||
in C++. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
class Vector2 { |
|||
public: |
|||
Vector2(float x, float y) : x(x), y(y) { } |
|||
|
|||
Vector2 operator+(const Vector2 &v) const { return Vector2(x + v.x, y + v.y); } |
|||
Vector2 operator*(float value) const { return Vector2(x * value, y * value); } |
|||
Vector2& operator+=(const Vector2 &v) { x += v.x; y += v.y; return *this; } |
|||
Vector2& operator*=(float v) { x *= v; y *= v; return *this; } |
|||
|
|||
friend Vector2 operator*(float f, const Vector2 &v) { |
|||
return Vector2(f * v.x, f * v.y); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
std::string toString() const { |
|||
return "[" + std::to_string(x) + ", " + std::to_string(y) + "]"; |
|||
} |
|||
private: |
|||
float x, y; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
The following snippet shows how the above operators can be conveniently exposed |
|||
to Python. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
#include <pybind11/operators.h> |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_PLUGIN(example) { |
|||
py::module m("example", "pybind11 example plugin"); |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Vector2>(m, "Vector2") |
|||
.def(py::init<float, float>()) |
|||
.def(py::self + py::self) |
|||
.def(py::self += py::self) |
|||
.def(py::self *= float()) |
|||
.def(float() * py::self) |
|||
.def("__repr__", &Vector2::toString); |
|||
|
|||
return m.ptr(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
Note that a line like |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
.def(py::self * float()) |
|||
|
|||
is really just short hand notation for |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
.def("__mul__", [](const Vector2 &a, float b) { |
|||
return a * b; |
|||
}, py::is_operator()) |
|||
|
|||
This can be useful for exposing additional operators that don't exist on the |
|||
C++ side, or to perform other types of customization. The ``py::is_operator`` |
|||
flag marker is needed to inform pybind11 that this is an operator, which |
|||
returns ``NotImplemented`` when invoked with incompatible arguments rather than |
|||
throwing a type error. |
|||
|
|||
.. note:: |
|||
|
|||
To use the more convenient ``py::self`` notation, the additional |
|||
header file :file:`pybind11/operators.h` must be included. |
|||
|
|||
.. seealso:: |
|||
|
|||
The file :file:`tests/test_operator_overloading.cpp` contains a |
|||
complete example that demonstrates how to work with overloaded operators in |
|||
more detail. |
|||
|
|||
Pickling support |
|||
================ |
|||
|
|||
Python's ``pickle`` module provides a powerful facility to serialize and |
|||
de-serialize a Python object graph into a binary data stream. To pickle and |
|||
unpickle C++ classes using pybind11, two additional functions must be provided. |
|||
Suppose the class in question has the following signature: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
class Pickleable { |
|||
public: |
|||
Pickleable(const std::string &value) : m_value(value) { } |
|||
const std::string &value() const { return m_value; } |
|||
|
|||
void setExtra(int extra) { m_extra = extra; } |
|||
int extra() const { return m_extra; } |
|||
private: |
|||
std::string m_value; |
|||
int m_extra = 0; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
The binding code including the requisite ``__setstate__`` and ``__getstate__`` methods [#f3]_ |
|||
looks as follows: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Pickleable>(m, "Pickleable") |
|||
.def(py::init<std::string>()) |
|||
.def("value", &Pickleable::value) |
|||
.def("extra", &Pickleable::extra) |
|||
.def("setExtra", &Pickleable::setExtra) |
|||
.def("__getstate__", [](const Pickleable &p) { |
|||
/* Return a tuple that fully encodes the state of the object */ |
|||
return py::make_tuple(p.value(), p.extra()); |
|||
}) |
|||
.def("__setstate__", [](Pickleable &p, py::tuple t) { |
|||
if (t.size() != 2) |
|||
throw std::runtime_error("Invalid state!"); |
|||
|
|||
/* Invoke the in-place constructor. Note that this is needed even |
|||
when the object just has a trivial default constructor */ |
|||
new (&p) Pickleable(t[0].cast<std::string>()); |
|||
|
|||
/* Assign any additional state */ |
|||
p.setExtra(t[1].cast<int>()); |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
An instance can now be pickled as follows: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: python |
|||
|
|||
try: |
|||
import cPickle as pickle # Use cPickle on Python 2.7 |
|||
except ImportError: |
|||
import pickle |
|||
|
|||
p = Pickleable("test_value") |
|||
p.setExtra(15) |
|||
data = pickle.dumps(p, 2) |
|||
|
|||
Note that only the cPickle module is supported on Python 2.7. The second |
|||
argument to ``dumps`` is also crucial: it selects the pickle protocol version |
|||
2, since the older version 1 is not supported. Newer versions are also fine—for |
|||
instance, specify ``-1`` to always use the latest available version. Beware: |
|||
failure to follow these instructions will cause important pybind11 memory |
|||
allocation routines to be skipped during unpickling, which will likely lead to |
|||
memory corruption and/or segmentation faults. |
|||
|
|||
.. seealso:: |
|||
|
|||
The file :file:`tests/test_pickling.cpp` contains a complete example |
|||
that demonstrates how to pickle and unpickle types using pybind11 in more |
|||
detail. |
|||
|
|||
.. [#f3] http://docs.python.org/3/library/pickle.html#pickling-class-instances |
|||
|
|||
Multiple Inheritance |
|||
==================== |
|||
|
|||
pybind11 can create bindings for types that derive from multiple base types |
|||
(aka. *multiple inheritance*). To do so, specify all bases in the template |
|||
arguments of the ``class_`` declaration: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<MyType, BaseType1, BaseType2, BaseType3>(m, "MyType") |
|||
... |
|||
|
|||
The base types can be specified in arbitrary order, and they can even be |
|||
interspersed with alias types and holder types (discussed earlier in this |
|||
document)---pybind11 will automatically find out which is which. The only |
|||
requirement is that the first template argument is the type to be declared. |
|||
|
|||
There are two caveats regarding the implementation of this feature: |
|||
|
|||
1. When only one base type is specified for a C++ type that actually has |
|||
multiple bases, pybind11 will assume that it does not participate in |
|||
multiple inheritance, which can lead to undefined behavior. In such cases, |
|||
add the tag ``multiple_inheritance``: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<MyType, BaseType2>(m, "MyType", py::multiple_inheritance()); |
|||
|
|||
The tag is redundant and does not need to be specified when multiple base |
|||
types are listed. |
|||
|
|||
2. As was previously discussed in the section on :ref:`overriding_virtuals`, it |
|||
is easy to create Python types that derive from C++ classes. It is even |
|||
possible to make use of multiple inheritance to declare a Python class which |
|||
has e.g. a C++ and a Python class as bases. However, any attempt to create a |
|||
type that has *two or more* C++ classes in its hierarchy of base types will |
|||
fail with a fatal error message: ``TypeError: multiple bases have instance |
|||
lay-out conflict``. Core Python types that are implemented in C (e.g. |
|||
``dict``, ``list``, ``Exception``, etc.) also fall under this combination |
|||
and cannot be combined with C++ types bound using pybind11 via multiple |
|||
inheritance. |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,142 @@ |
|||
Exceptions |
|||
########## |
|||
|
|||
Built-in exception translation |
|||
============================== |
|||
|
|||
When C++ code invoked from Python throws an ``std::exception``, it is |
|||
automatically converted into a Python ``Exception``. pybind11 defines multiple |
|||
special exception classes that will map to different types of Python |
|||
exceptions: |
|||
|
|||
.. tabularcolumns:: |p{0.5\textwidth}|p{0.45\textwidth}| |
|||
|
|||
+--------------------------------------+------------------------------+ |
|||
| C++ exception type | Python exception type | |
|||
+======================================+==============================+ |
|||
| :class:`std::exception` | ``RuntimeError`` | |
|||
+--------------------------------------+------------------------------+ |
|||
| :class:`std::bad_alloc` | ``MemoryError`` | |
|||
+--------------------------------------+------------------------------+ |
|||
| :class:`std::domain_error` | ``ValueError`` | |
|||
+--------------------------------------+------------------------------+ |
|||
| :class:`std::invalid_argument` | ``ValueError`` | |
|||
+--------------------------------------+------------------------------+ |
|||
| :class:`std::length_error` | ``ValueError`` | |
|||
+--------------------------------------+------------------------------+ |
|||
| :class:`std::out_of_range` | ``ValueError`` | |
|||
+--------------------------------------+------------------------------+ |
|||
| :class:`std::range_error` | ``ValueError`` | |
|||
+--------------------------------------+------------------------------+ |
|||
| :class:`pybind11::stop_iteration` | ``StopIteration`` (used to | |
|||
| | implement custom iterators) | |
|||
+--------------------------------------+------------------------------+ |
|||
| :class:`pybind11::index_error` | ``IndexError`` (used to | |
|||
| | indicate out of bounds | |
|||
| | accesses in ``__getitem__``, | |
|||
| | ``__setitem__``, etc.) | |
|||
+--------------------------------------+------------------------------+ |
|||
| :class:`pybind11::value_error` | ``ValueError`` (used to | |
|||
| | indicate wrong value passed | |
|||
| | in ``container.remove(...)`` | |
|||
+--------------------------------------+------------------------------+ |
|||
| :class:`pybind11::key_error` | ``KeyError`` (used to | |
|||
| | indicate out of bounds | |
|||
| | accesses in ``__getitem__``, | |
|||
| | ``__setitem__`` in dict-like | |
|||
| | objects, etc.) | |
|||
+--------------------------------------+------------------------------+ |
|||
| :class:`pybind11::error_already_set` | Indicates that the Python | |
|||
| | exception flag has already | |
|||
| | been initialized | |
|||
+--------------------------------------+------------------------------+ |
|||
|
|||
When a Python function invoked from C++ throws an exception, it is converted |
|||
into a C++ exception of type :class:`error_already_set` whose string payload |
|||
contains a textual summary. |
|||
|
|||
There is also a special exception :class:`cast_error` that is thrown by |
|||
:func:`handle::call` when the input arguments cannot be converted to Python |
|||
objects. |
|||
|
|||
Registering custom translators |
|||
============================== |
|||
|
|||
If the default exception conversion policy described above is insufficient, |
|||
pybind11 also provides support for registering custom exception translators. |
|||
To register a simple exception conversion that translates a C++ exception into |
|||
a new Python exception using the C++ exception's ``what()`` method, a helper |
|||
function is available: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::register_exception<CppExp>(module, "PyExp"); |
|||
|
|||
This call creates a Python exception class with the name ``PyExp`` in the given |
|||
module and automatically converts any encountered exceptions of type ``CppExp`` |
|||
into Python exceptions of type ``PyExp``. |
|||
|
|||
When more advanced exception translation is needed, the function |
|||
``py::register_exception_translator(translator)`` can be used to register |
|||
functions that can translate arbitrary exception types (and which may include |
|||
additional logic to do so). The function takes a stateless callable (e.g. a |
|||
function pointer or a lambda function without captured variables) with the call |
|||
signature ``void(std::exception_ptr)``. |
|||
|
|||
When a C++ exception is thrown, the registered exception translators are tried |
|||
in reverse order of registration (i.e. the last registered translator gets the |
|||
first shot at handling the exception). |
|||
|
|||
Inside the translator, ``std::rethrow_exception`` should be used within |
|||
a try block to re-throw the exception. One or more catch clauses to catch |
|||
the appropriate exceptions should then be used with each clause using |
|||
``PyErr_SetString`` to set a Python exception or ``ex(string)`` to set |
|||
the python exception to a custom exception type (see below). |
|||
|
|||
To declare a custom Python exception type, declare a ``py::exception`` variable |
|||
and use this in the associated exception translator (note: it is often useful |
|||
to make this a static declaration when using it inside a lambda expression |
|||
without requiring capturing). |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
The following example demonstrates this for a hypothetical exception classes |
|||
``MyCustomException`` and ``OtherException``: the first is translated to a |
|||
custom python exception ``MyCustomError``, while the second is translated to a |
|||
standard python RuntimeError: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
static py::exception<MyCustomException> exc(m, "MyCustomError"); |
|||
py::register_exception_translator([](std::exception_ptr p) { |
|||
try { |
|||
if (p) std::rethrow_exception(p); |
|||
} catch (const MyCustomException &e) { |
|||
exc(e.what()); |
|||
} catch (const OtherException &e) { |
|||
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_RuntimeError, e.what()); |
|||
} |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
Multiple exceptions can be handled by a single translator, as shown in the |
|||
example above. If the exception is not caught by the current translator, the |
|||
previously registered one gets a chance. |
|||
|
|||
If none of the registered exception translators is able to handle the |
|||
exception, it is handled by the default converter as described in the previous |
|||
section. |
|||
|
|||
.. seealso:: |
|||
|
|||
The file :file:`tests/test_exceptions.cpp` contains examples |
|||
of various custom exception translators and custom exception types. |
|||
|
|||
.. note:: |
|||
|
|||
You must call either ``PyErr_SetString`` or a custom exception's call |
|||
operator (``exc(string)``) for every exception caught in a custom exception |
|||
translator. Failure to do so will cause Python to crash with ``SystemError: |
|||
error return without exception set``. |
|||
|
|||
Exceptions that you do not plan to handle should simply not be caught, or |
|||
may be explicity (re-)thrown to delegate it to the other, |
|||
previously-declared existing exception translators. |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,311 @@ |
|||
Functions |
|||
######### |
|||
|
|||
Before proceeding with this section, make sure that you are already familiar |
|||
with the basics of binding functions and classes, as explained in :doc:`/basics` |
|||
and :doc:`/classes`. The following guide is applicable to both free and member |
|||
functions, i.e. *methods* in Python. |
|||
|
|||
Return value policies |
|||
===================== |
|||
|
|||
Python and C++ use fundamentally different ways of managing the memory and |
|||
lifetime of objects managed by them. This can lead to issues when creating |
|||
bindings for functions that return a non-trivial type. Just by looking at the |
|||
type information, it is not clear whether Python should take charge of the |
|||
returned value and eventually free its resources, or if this is handled on the |
|||
C++ side. For this reason, pybind11 provides a several `return value policy` |
|||
annotations that can be passed to the :func:`module::def` and |
|||
:func:`class_::def` functions. The default policy is |
|||
:enum:`return_value_policy::automatic`. |
|||
|
|||
Return value policies are tricky, and it's very important to get them right. |
|||
Just to illustrate what can go wrong, consider the following simple example: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
/* Function declaration */ |
|||
Data *get_data() { return _data; /* (pointer to a static data structure) */ } |
|||
... |
|||
|
|||
/* Binding code */ |
|||
m.def("get_data", &get_data); // <-- KABOOM, will cause crash when called from Python |
|||
|
|||
What's going on here? When ``get_data()`` is called from Python, the return |
|||
value (a native C++ type) must be wrapped to turn it into a usable Python type. |
|||
In this case, the default return value policy (:enum:`return_value_policy::automatic`) |
|||
causes pybind11 to assume ownership of the static ``_data`` instance. |
|||
|
|||
When Python's garbage collector eventually deletes the Python |
|||
wrapper, pybind11 will also attempt to delete the C++ instance (via ``operator |
|||
delete()``) due to the implied ownership. At this point, the entire application |
|||
will come crashing down, though errors could also be more subtle and involve |
|||
silent data corruption. |
|||
|
|||
In the above example, the policy :enum:`return_value_policy::reference` should have |
|||
been specified so that the global data instance is only *referenced* without any |
|||
implied transfer of ownership, i.e.: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
m.def("get_data", &get_data, return_value_policy::reference); |
|||
|
|||
On the other hand, this is not the right policy for many other situations, |
|||
where ignoring ownership could lead to resource leaks. |
|||
As a developer using pybind11, it's important to be familiar with the different |
|||
return value policies, including which situation calls for which one of them. |
|||
The following table provides an overview of available policies: |
|||
|
|||
.. tabularcolumns:: |p{0.5\textwidth}|p{0.45\textwidth}| |
|||
|
|||
+--------------------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
|||
| Return value policy | Description | |
|||
+==================================================+============================================================================+ |
|||
| :enum:`return_value_policy::take_ownership` | Reference an existing object (i.e. do not create a new copy) and take | |
|||
| | ownership. Python will call the destructor and delete operator when the | |
|||
| | object's reference count reaches zero. Undefined behavior ensues when the | |
|||
| | C++ side does the same, or when the data was not dynamically allocated. | |
|||
+--------------------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
|||
| :enum:`return_value_policy::copy` | Create a new copy of the returned object, which will be owned by Python. | |
|||
| | This policy is comparably safe because the lifetimes of the two instances | |
|||
| | are decoupled. | |
|||
+--------------------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
|||
| :enum:`return_value_policy::move` | Use ``std::move`` to move the return value contents into a new instance | |
|||
| | that will be owned by Python. This policy is comparably safe because the | |
|||
| | lifetimes of the two instances (move source and destination) are decoupled.| |
|||
+--------------------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
|||
| :enum:`return_value_policy::reference` | Reference an existing object, but do not take ownership. The C++ side is | |
|||
| | responsible for managing the object's lifetime and deallocating it when | |
|||
| | it is no longer used. Warning: undefined behavior will ensue when the C++ | |
|||
| | side deletes an object that is still referenced and used by Python. | |
|||
+--------------------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
|||
| :enum:`return_value_policy::reference_internal` | Indicates that the lifetime of the return value is tied to the lifetime | |
|||
| | of a parent object, namely the implicit ``this``, or ``self`` argument of | |
|||
| | the called method or property. Internally, this policy works just like | |
|||
| | :enum:`return_value_policy::reference` but additionally applies a | |
|||
| | ``keep_alive<0, 1>`` *call policy* (described in the next section) that | |
|||
| | prevents the parent object from being garbage collected as long as the | |
|||
| | return value is referenced by Python. This is the default policy for | |
|||
| | property getters created via ``def_property``, ``def_readwrite``, etc. | |
|||
+--------------------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
|||
| :enum:`return_value_policy::automatic` | This is the default return value policy, which falls back to the policy | |
|||
| | :enum:`return_value_policy::take_ownership` when the return value is a | |
|||
| | pointer. Otherwise, it uses :enum:`return_value::move` or | |
|||
| | :enum:`return_value::copy` for rvalue and lvalue references, respectively. | |
|||
| | See above for a description of what all of these different policies do. | |
|||
+--------------------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
|||
| :enum:`return_value_policy::automatic_reference` | As above, but use policy :enum:`return_value_policy::reference` when the | |
|||
| | return value is a pointer. This is the default conversion policy for | |
|||
| | function arguments when calling Python functions manually from C++ code | |
|||
| | (i.e. via handle::operator()). You probably won't need to use this. | |
|||
+--------------------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ |
|||
|
|||
Return value policies can also be applied to properties: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
class_<MyClass>(m, "MyClass") |
|||
.def_property("data", &MyClass::getData, &MyClass::setData, |
|||
py::return_value_policy::copy); |
|||
|
|||
Technically, the code above applies the policy to both the getter and the |
|||
setter function, however, the setter doesn't really care about *return* |
|||
value policies which makes this a convenient terse syntax. Alternatively, |
|||
targeted arguments can be passed through the :class:`cpp_function` constructor: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
class_<MyClass>(m, "MyClass") |
|||
.def_property("data" |
|||
py::cpp_function(&MyClass::getData, py::return_value_policy::copy), |
|||
py::cpp_function(&MyClass::setData) |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
.. warning:: |
|||
|
|||
Code with invalid return value policies might access unitialized memory or |
|||
free data structures multiple times, which can lead to hard-to-debug |
|||
non-determinism and segmentation faults, hence it is worth spending the |
|||
time to understand all the different options in the table above. |
|||
|
|||
.. note:: |
|||
|
|||
One important aspect of the above policies is that they only apply to |
|||
instances which pybind11 has *not* seen before, in which case the policy |
|||
clarifies essential questions about the return value's lifetime and |
|||
ownership. When pybind11 knows the instance already (as identified by its |
|||
type and address in memory), it will return the existing Python object |
|||
wrapper rather than creating a new copy. |
|||
|
|||
.. note:: |
|||
|
|||
The next section on :ref:`call_policies` discusses *call policies* that can be |
|||
specified *in addition* to a return value policy from the list above. Call |
|||
policies indicate reference relationships that can involve both return values |
|||
and parameters of functions. |
|||
|
|||
.. note:: |
|||
|
|||
As an alternative to elaborate call policies and lifetime management logic, |
|||
consider using smart pointers (see the section on :ref:`smart_pointers` for |
|||
details). Smart pointers can tell whether an object is still referenced from |
|||
C++ or Python, which generally eliminates the kinds of inconsistencies that |
|||
can lead to crashes or undefined behavior. For functions returning smart |
|||
pointers, it is not necessary to specify a return value policy. |
|||
|
|||
.. _call_policies: |
|||
|
|||
Additional call policies |
|||
======================== |
|||
|
|||
In addition to the above return value policies, further `call policies` can be |
|||
specified to indicate dependencies between parameters. There is currently just |
|||
one policy named ``keep_alive<Nurse, Patient>``, which indicates that the |
|||
argument with index ``Patient`` should be kept alive at least until the |
|||
argument with index ``Nurse`` is freed by the garbage collector. Argument |
|||
indices start at one, while zero refers to the return value. For methods, index |
|||
``1`` refers to the implicit ``this`` pointer, while regular arguments begin at |
|||
index ``2``. Arbitrarily many call policies can be specified. When a ``Nurse`` |
|||
with value ``None`` is detected at runtime, the call policy does nothing. |
|||
|
|||
This feature internally relies on the ability to create a *weak reference* to |
|||
the nurse object, which is permitted by all classes exposed via pybind11. When |
|||
the nurse object does not support weak references, an exception will be thrown. |
|||
|
|||
Consider the following example: here, the binding code for a list append |
|||
operation ties the lifetime of the newly added element to the underlying |
|||
container: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<List>(m, "List") |
|||
.def("append", &List::append, py::keep_alive<1, 2>()); |
|||
|
|||
.. note:: |
|||
|
|||
``keep_alive`` is analogous to the ``with_custodian_and_ward`` (if Nurse, |
|||
Patient != 0) and ``with_custodian_and_ward_postcall`` (if Nurse/Patient == |
|||
0) policies from Boost.Python. |
|||
|
|||
.. seealso:: |
|||
|
|||
The file :file:`tests/test_keep_alive.cpp` contains a complete example |
|||
that demonstrates using :class:`keep_alive` in more detail. |
|||
|
|||
.. _python_objects_as_args: |
|||
|
|||
Python objects as arguments |
|||
=========================== |
|||
|
|||
pybind11 exposes all major Python types using thin C++ wrapper classes. These |
|||
wrapper classes can also be used as parameters of functions in bindings, which |
|||
makes it possible to directly work with native Python types on the C++ side. |
|||
For instance, the following statement iterates over a Python ``dict``: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
void print_dict(py::dict dict) { |
|||
/* Easily interact with Python types */ |
|||
for (auto item : dict) |
|||
std::cout << "key=" << item.first << ", " |
|||
<< "value=" << item.second << std::endl; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
It can be exported: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
m.def("print_dict", &print_dict); |
|||
|
|||
And used in Python as usual: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> print_dict({'foo': 123, 'bar': 'hello'}) |
|||
key=foo, value=123 |
|||
key=bar, value=hello |
|||
|
|||
For more information on using Python objects in C++, see :doc:`/advanced/pycpp/index`. |
|||
|
|||
Accepting \*args and \*\*kwargs |
|||
=============================== |
|||
|
|||
Python provides a useful mechanism to define functions that accept arbitrary |
|||
numbers of arguments and keyword arguments: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: python |
|||
|
|||
def generic(*args, **kwargs): |
|||
... # do something with args and kwargs |
|||
|
|||
Such functions can also be created using pybind11: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
void generic(py::args args, py::kwargs kwargs) { |
|||
/// .. do something with args |
|||
if (kwargs) |
|||
/// .. do something with kwargs |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
/// Binding code |
|||
m.def("generic", &generic); |
|||
|
|||
The class ``py::args`` derives from ``py::tuple`` and ``py::kwargs`` derives |
|||
from ``py::dict``. Note that the ``kwargs`` argument is invalid if no keyword |
|||
arguments were actually provided. Please refer to the other examples for |
|||
details on how to iterate over these, and on how to cast their entries into |
|||
C++ objects. A demonstration is also available in |
|||
``tests/test_kwargs_and_defaults.cpp``. |
|||
|
|||
.. warning:: |
|||
|
|||
Unlike Python, pybind11 does not allow combining normal parameters with the |
|||
``args`` / ``kwargs`` special parameters. |
|||
|
|||
Default arguments revisited |
|||
=========================== |
|||
|
|||
The section on :ref:`default_args` previously discussed basic usage of default |
|||
arguments using pybind11. One noteworthy aspect of their implementation is that |
|||
default arguments are converted to Python objects right at declaration time. |
|||
Consider the following example: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<MyClass>("MyClass") |
|||
.def("myFunction", py::arg("arg") = SomeType(123)); |
|||
|
|||
In this case, pybind11 must already be set up to deal with values of the type |
|||
``SomeType`` (via a prior instantiation of ``py::class_<SomeType>``), or an |
|||
exception will be thrown. |
|||
|
|||
Another aspect worth highlighting is that the "preview" of the default argument |
|||
in the function signature is generated using the object's ``__repr__`` method. |
|||
If not available, the signature may not be very helpful, e.g.: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
FUNCTIONS |
|||
... |
|||
| myFunction(...) |
|||
| Signature : (MyClass, arg : SomeType = <SomeType object at 0x101b7b080>) -> NoneType |
|||
... |
|||
|
|||
The first way of addressing this is by defining ``SomeType.__repr__``. |
|||
Alternatively, it is possible to specify the human-readable preview of the |
|||
default argument manually using the ``arg_v`` notation: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<MyClass>("MyClass") |
|||
.def("myFunction", py::arg_v("arg", SomeType(123), "SomeType(123)")); |
|||
|
|||
Sometimes it may be necessary to pass a null pointer value as a default |
|||
argument. In this case, remember to cast it to the underlying type in question, |
|||
like so: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<MyClass>("MyClass") |
|||
.def("myFunction", py::arg("arg") = (SomeType *) nullptr); |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,229 @@ |
|||
Miscellaneous |
|||
############# |
|||
|
|||
.. _macro_notes: |
|||
|
|||
General notes regarding convenience macros |
|||
========================================== |
|||
|
|||
pybind11 provides a few convenience macros such as |
|||
:func:`PYBIND11_MAKE_OPAQUE` and :func:`PYBIND11_DECLARE_HOLDER_TYPE`, and |
|||
``PYBIND11_OVERLOAD_*``. Since these are "just" macros that are evaluated |
|||
in the preprocessor (which has no concept of types), they *will* get confused |
|||
by commas in a template argument such as ``PYBIND11_OVERLOAD(MyReturnValue<T1, |
|||
T2>, myFunc)``. In this case, the preprocessor assumes that the comma indicates |
|||
the beginning of the next parameter. Use a ``typedef`` to bind the template to |
|||
another name and use it in the macro to avoid this problem. |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) |
|||
============================= |
|||
|
|||
The classes :class:`gil_scoped_release` and :class:`gil_scoped_acquire` can be |
|||
used to acquire and release the global interpreter lock in the body of a C++ |
|||
function call. In this way, long-running C++ code can be parallelized using |
|||
multiple Python threads. Taking :ref:`overriding_virtuals` as an example, this |
|||
could be realized as follows (important changes highlighted): |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
:emphasize-lines: 8,9,33,34 |
|||
|
|||
class PyAnimal : public Animal { |
|||
public: |
|||
/* Inherit the constructors */ |
|||
using Animal::Animal; |
|||
|
|||
/* Trampoline (need one for each virtual function) */ |
|||
std::string go(int n_times) { |
|||
/* Acquire GIL before calling Python code */ |
|||
py::gil_scoped_acquire acquire; |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_OVERLOAD_PURE( |
|||
std::string, /* Return type */ |
|||
Animal, /* Parent class */ |
|||
go, /* Name of function */ |
|||
n_times /* Argument(s) */ |
|||
); |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_PLUGIN(example) { |
|||
py::module m("example", "pybind11 example plugin"); |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Animal, PyAnimal> animal(m, "Animal"); |
|||
animal |
|||
.def(py::init<>()) |
|||
.def("go", &Animal::go); |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Dog>(m, "Dog", animal) |
|||
.def(py::init<>()); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("call_go", [](Animal *animal) -> std::string { |
|||
/* Release GIL before calling into (potentially long-running) C++ code */ |
|||
py::gil_scoped_release release; |
|||
return call_go(animal); |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
return m.ptr(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
Binding sequence data types, iterators, the slicing protocol, etc. |
|||
================================================================== |
|||
|
|||
Please refer to the supplemental example for details. |
|||
|
|||
.. seealso:: |
|||
|
|||
The file :file:`tests/test_sequences_and_iterators.cpp` contains a |
|||
complete example that shows how to bind a sequence data type, including |
|||
length queries (``__len__``), iterators (``__iter__``), the slicing |
|||
protocol and other kinds of useful operations. |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
Partitioning code over multiple extension modules |
|||
================================================= |
|||
|
|||
It's straightforward to split binding code over multiple extension modules, |
|||
while referencing types that are declared elsewhere. Everything "just" works |
|||
without any special precautions. One exception to this rule occurs when |
|||
extending a type declared in another extension module. Recall the basic example |
|||
from Section :ref:`inheritance`. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Pet> pet(m, "Pet"); |
|||
pet.def(py::init<const std::string &>()) |
|||
.def_readwrite("name", &Pet::name); |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Dog>(m, "Dog", pet /* <- specify parent */) |
|||
.def(py::init<const std::string &>()) |
|||
.def("bark", &Dog::bark); |
|||
|
|||
Suppose now that ``Pet`` bindings are defined in a module named ``basic``, |
|||
whereas the ``Dog`` bindings are defined somewhere else. The challenge is of |
|||
course that the variable ``pet`` is not available anymore though it is needed |
|||
to indicate the inheritance relationship to the constructor of ``class_<Dog>``. |
|||
However, it can be acquired as follows: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::object pet = (py::object) py::module::import("basic").attr("Pet"); |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Dog>(m, "Dog", pet) |
|||
.def(py::init<const std::string &>()) |
|||
.def("bark", &Dog::bark); |
|||
|
|||
Alternatively, you can specify the base class as a template parameter option to |
|||
``class_``, which performs an automated lookup of the corresponding Python |
|||
type. Like the above code, however, this also requires invoking the ``import`` |
|||
function once to ensure that the pybind11 binding code of the module ``basic`` |
|||
has been executed: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::module::import("basic"); |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Dog, Pet>(m, "Dog") |
|||
.def(py::init<const std::string &>()) |
|||
.def("bark", &Dog::bark); |
|||
|
|||
Naturally, both methods will fail when there are cyclic dependencies. |
|||
|
|||
Note that compiling code which has its default symbol visibility set to |
|||
*hidden* (e.g. via the command line flag ``-fvisibility=hidden`` on GCC/Clang) can interfere with the |
|||
ability to access types defined in another extension module. Workarounds |
|||
include changing the global symbol visibility (not recommended, because it will |
|||
lead unnecessarily large binaries) or manually exporting types that are |
|||
accessed by multiple extension modules: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
#ifdef _WIN32 |
|||
# define EXPORT_TYPE __declspec(dllexport) |
|||
#else |
|||
# define EXPORT_TYPE __attribute__ ((visibility("default"))) |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
class EXPORT_TYPE Dog : public Animal { |
|||
... |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
Note also that it is possible (although would rarely be required) to share arbitrary |
|||
C++ objects between extension modules at runtime. Internal library data is shared |
|||
between modules using capsule machinery [#f6]_ which can be also utilized for |
|||
storing, modifying and accessing user-defined data. Note that an extension module |
|||
will "see" other extensions' data if and only if they were built with the same |
|||
pybind11 version. Consider the following example: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
auto data = (MyData *) py::get_shared_data("mydata"); |
|||
if (!data) |
|||
data = (MyData *) py::set_shared_data("mydata", new MyData(42)); |
|||
|
|||
If the above snippet was used in several separately compiled extension modules, |
|||
the first one to be imported would create a ``MyData`` instance and associate |
|||
a ``"mydata"`` key with a pointer to it. Extensions that are imported later |
|||
would be then able to access the data behind the same pointer. |
|||
|
|||
.. [#f6] https://docs.python.org/3/extending/extending.html#using-capsules |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
Generating documentation using Sphinx |
|||
===================================== |
|||
|
|||
Sphinx [#f4]_ has the ability to inspect the signatures and documentation |
|||
strings in pybind11-based extension modules to automatically generate beautiful |
|||
documentation in a variety formats. The python_example repository [#f5]_ contains a |
|||
simple example repository which uses this approach. |
|||
|
|||
There are two potential gotchas when using this approach: first, make sure that |
|||
the resulting strings do not contain any :kbd:`TAB` characters, which break the |
|||
docstring parsing routines. You may want to use C++11 raw string literals, |
|||
which are convenient for multi-line comments. Conveniently, any excess |
|||
indentation will be automatically be removed by Sphinx. However, for this to |
|||
work, it is important that all lines are indented consistently, i.e.: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
// ok |
|||
m.def("foo", &foo, R"mydelimiter( |
|||
The foo function |
|||
|
|||
Parameters |
|||
---------- |
|||
)mydelimiter"); |
|||
|
|||
// *not ok* |
|||
m.def("foo", &foo, R"mydelimiter(The foo function |
|||
|
|||
Parameters |
|||
---------- |
|||
)mydelimiter"); |
|||
|
|||
By default, pybind11 automatically generates and prepends a signature to the docstring of a function |
|||
registered with ``module::def()`` and ``class_::def()``. Sometimes this |
|||
behavior is not desirable, because you want to provide your own signature or remove |
|||
the docstring completely to exclude the function from the Sphinx documentation. |
|||
The class ``options`` allows you to selectively suppress auto-generated signatures: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_PLUGIN(example) { |
|||
py::module m("example", "pybind11 example plugin"); |
|||
|
|||
py::options options; |
|||
options.disable_function_signatures(); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("add", [](int a, int b) { return a + b; }, "A function which adds two numbers"); |
|||
|
|||
return m.ptr(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
Note that changes to the settings affect only function bindings created during the |
|||
lifetime of the ``options`` instance. When it goes out of scope at the end of the module's init function, |
|||
the default settings are restored to prevent unwanted side effects. |
|||
|
|||
.. [#f4] http://www.sphinx-doc.org |
|||
.. [#f5] http://github.com/pybind/python_example |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,13 @@ |
|||
Python C++ interface |
|||
#################### |
|||
|
|||
pybind11 exposes Python types and functions using thin C++ wrappers, which |
|||
makes it possible to conveniently call Python code from C++ without resorting |
|||
to Python's C API. |
|||
|
|||
.. toctree:: |
|||
:maxdepth: 2 |
|||
|
|||
object |
|||
numpy |
|||
utilities |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,299 @@ |
|||
.. _numpy: |
|||
|
|||
NumPy |
|||
##### |
|||
|
|||
Buffer protocol |
|||
=============== |
|||
|
|||
Python supports an extremely general and convenient approach for exchanging |
|||
data between plugin libraries. Types can expose a buffer view [#f2]_, which |
|||
provides fast direct access to the raw internal data representation. Suppose we |
|||
want to bind the following simplistic Matrix class: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
class Matrix { |
|||
public: |
|||
Matrix(size_t rows, size_t cols) : m_rows(rows), m_cols(cols) { |
|||
m_data = new float[rows*cols]; |
|||
} |
|||
float *data() { return m_data; } |
|||
size_t rows() const { return m_rows; } |
|||
size_t cols() const { return m_cols; } |
|||
private: |
|||
size_t m_rows, m_cols; |
|||
float *m_data; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
The following binding code exposes the ``Matrix`` contents as a buffer object, |
|||
making it possible to cast Matrices into NumPy arrays. It is even possible to |
|||
completely avoid copy operations with Python expressions like |
|||
``np.array(matrix_instance, copy = False)``. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Matrix>(m, "Matrix") |
|||
.def_buffer([](Matrix &m) -> py::buffer_info { |
|||
return py::buffer_info( |
|||
m.data(), /* Pointer to buffer */ |
|||
sizeof(float), /* Size of one scalar */ |
|||
py::format_descriptor<float>::format(), /* Python struct-style format descriptor */ |
|||
2, /* Number of dimensions */ |
|||
{ m.rows(), m.cols() }, /* Buffer dimensions */ |
|||
{ sizeof(float) * m.rows(), /* Strides (in bytes) for each index */ |
|||
sizeof(float) } |
|||
); |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
The snippet above binds a lambda function, which can create ``py::buffer_info`` |
|||
description records on demand describing a given matrix. The contents of |
|||
``py::buffer_info`` mirror the Python buffer protocol specification. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
struct buffer_info { |
|||
void *ptr; |
|||
size_t itemsize; |
|||
std::string format; |
|||
int ndim; |
|||
std::vector<size_t> shape; |
|||
std::vector<size_t> strides; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
To create a C++ function that can take a Python buffer object as an argument, |
|||
simply use the type ``py::buffer`` as one of its arguments. Buffers can exist |
|||
in a great variety of configurations, hence some safety checks are usually |
|||
necessary in the function body. Below, you can see an basic example on how to |
|||
define a custom constructor for the Eigen double precision matrix |
|||
(``Eigen::MatrixXd``) type, which supports initialization from compatible |
|||
buffer objects (e.g. a NumPy matrix). |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
/* Bind MatrixXd (or some other Eigen type) to Python */ |
|||
typedef Eigen::MatrixXd Matrix; |
|||
|
|||
typedef Matrix::Scalar Scalar; |
|||
constexpr bool rowMajor = Matrix::Flags & Eigen::RowMajorBit; |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Matrix>(m, "Matrix") |
|||
.def("__init__", [](Matrix &m, py::buffer b) { |
|||
typedef Eigen::Stride<Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic> Strides; |
|||
|
|||
/* Request a buffer descriptor from Python */ |
|||
py::buffer_info info = b.request(); |
|||
|
|||
/* Some sanity checks ... */ |
|||
if (info.format != py::format_descriptor<Scalar>::format()) |
|||
throw std::runtime_error("Incompatible format: expected a double array!"); |
|||
|
|||
if (info.ndim != 2) |
|||
throw std::runtime_error("Incompatible buffer dimension!"); |
|||
|
|||
auto strides = Strides( |
|||
info.strides[rowMajor ? 0 : 1] / sizeof(Scalar), |
|||
info.strides[rowMajor ? 1 : 0] / sizeof(Scalar)); |
|||
|
|||
auto map = Eigen::Map<Matrix, 0, Strides>( |
|||
static_cat<Scalar *>(info.ptr), info.shape[0], info.shape[1], strides); |
|||
|
|||
new (&m) Matrix(map); |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
For reference, the ``def_buffer()`` call for this Eigen data type should look |
|||
as follows: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
.def_buffer([](Matrix &m) -> py::buffer_info { |
|||
return py::buffer_info( |
|||
m.data(), /* Pointer to buffer */ |
|||
sizeof(Scalar), /* Size of one scalar */ |
|||
/* Python struct-style format descriptor */ |
|||
py::format_descriptor<Scalar>::format(), |
|||
/* Number of dimensions */ |
|||
2, |
|||
/* Buffer dimensions */ |
|||
{ (size_t) m.rows(), |
|||
(size_t) m.cols() }, |
|||
/* Strides (in bytes) for each index */ |
|||
{ sizeof(Scalar) * (rowMajor ? m.cols() : 1), |
|||
sizeof(Scalar) * (rowMajor ? 1 : m.rows()) } |
|||
); |
|||
}) |
|||
|
|||
For a much easier approach of binding Eigen types (although with some |
|||
limitations), refer to the section on :doc:`/advanced/cast/eigen`. |
|||
|
|||
.. seealso:: |
|||
|
|||
The file :file:`tests/test_buffers.cpp` contains a complete example |
|||
that demonstrates using the buffer protocol with pybind11 in more detail. |
|||
|
|||
.. [#f2] http://docs.python.org/3/c-api/buffer.html |
|||
|
|||
Arrays |
|||
====== |
|||
|
|||
By exchanging ``py::buffer`` with ``py::array`` in the above snippet, we can |
|||
restrict the function so that it only accepts NumPy arrays (rather than any |
|||
type of Python object satisfying the buffer protocol). |
|||
|
|||
In many situations, we want to define a function which only accepts a NumPy |
|||
array of a certain data type. This is possible via the ``py::array_t<T>`` |
|||
template. For instance, the following function requires the argument to be a |
|||
NumPy array containing double precision values. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
void f(py::array_t<double> array); |
|||
|
|||
When it is invoked with a different type (e.g. an integer or a list of |
|||
integers), the binding code will attempt to cast the input into a NumPy array |
|||
of the requested type. Note that this feature requires the |
|||
:file:``pybind11/numpy.h`` header to be included. |
|||
|
|||
Data in NumPy arrays is not guaranteed to packed in a dense manner; |
|||
furthermore, entries can be separated by arbitrary column and row strides. |
|||
Sometimes, it can be useful to require a function to only accept dense arrays |
|||
using either the C (row-major) or Fortran (column-major) ordering. This can be |
|||
accomplished via a second template argument with values ``py::array::c_style`` |
|||
or ``py::array::f_style``. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
void f(py::array_t<double, py::array::c_style | py::array::forcecast> array); |
|||
|
|||
The ``py::array::forcecast`` argument is the default value of the second |
|||
template parameter, and it ensures that non-conforming arguments are converted |
|||
into an array satisfying the specified requirements instead of trying the next |
|||
function overload. |
|||
|
|||
Structured types |
|||
================ |
|||
|
|||
In order for ``py::array_t`` to work with structured (record) types, we first need |
|||
to register the memory layout of the type. This can be done via ``PYBIND11_NUMPY_DTYPE`` |
|||
macro which expects the type followed by field names: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
struct A { |
|||
int x; |
|||
double y; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
struct B { |
|||
int z; |
|||
A a; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_NUMPY_DTYPE(A, x, y); |
|||
PYBIND11_NUMPY_DTYPE(B, z, a); |
|||
|
|||
/* now both A and B can be used as template arguments to py::array_t */ |
|||
|
|||
Vectorizing functions |
|||
===================== |
|||
|
|||
Suppose we want to bind a function with the following signature to Python so |
|||
that it can process arbitrary NumPy array arguments (vectors, matrices, general |
|||
N-D arrays) in addition to its normal arguments: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
double my_func(int x, float y, double z); |
|||
|
|||
After including the ``pybind11/numpy.h`` header, this is extremely simple: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
m.def("vectorized_func", py::vectorize(my_func)); |
|||
|
|||
Invoking the function like below causes 4 calls to be made to ``my_func`` with |
|||
each of the array elements. The significant advantage of this compared to |
|||
solutions like ``numpy.vectorize()`` is that the loop over the elements runs |
|||
entirely on the C++ side and can be crunched down into a tight, optimized loop |
|||
by the compiler. The result is returned as a NumPy array of type |
|||
``numpy.dtype.float64``. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> x = np.array([[1, 3],[5, 7]]) |
|||
>>> y = np.array([[2, 4],[6, 8]]) |
|||
>>> z = 3 |
|||
>>> result = vectorized_func(x, y, z) |
|||
|
|||
The scalar argument ``z`` is transparently replicated 4 times. The input |
|||
arrays ``x`` and ``y`` are automatically converted into the right types (they |
|||
are of type ``numpy.dtype.int64`` but need to be ``numpy.dtype.int32`` and |
|||
``numpy.dtype.float32``, respectively) |
|||
|
|||
Sometimes we might want to explicitly exclude an argument from the vectorization |
|||
because it makes little sense to wrap it in a NumPy array. For instance, |
|||
suppose the function signature was |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
double my_func(int x, float y, my_custom_type *z); |
|||
|
|||
This can be done with a stateful Lambda closure: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
// Vectorize a lambda function with a capture object (e.g. to exclude some arguments from the vectorization) |
|||
m.def("vectorized_func", |
|||
[](py::array_t<int> x, py::array_t<float> y, my_custom_type *z) { |
|||
auto stateful_closure = [z](int x, float y) { return my_func(x, y, z); }; |
|||
return py::vectorize(stateful_closure)(x, y); |
|||
} |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
In cases where the computation is too complicated to be reduced to |
|||
``vectorize``, it will be necessary to create and access the buffer contents |
|||
manually. The following snippet contains a complete example that shows how this |
|||
works (the code is somewhat contrived, since it could have been done more |
|||
simply using ``vectorize``). |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
#include <pybind11/pybind11.h> |
|||
#include <pybind11/numpy.h> |
|||
|
|||
namespace py = pybind11; |
|||
|
|||
py::array_t<double> add_arrays(py::array_t<double> input1, py::array_t<double> input2) { |
|||
auto buf1 = input1.request(), buf2 = input2.request(); |
|||
|
|||
if (buf1.ndim != 1 || buf2.ndim != 1) |
|||
throw std::runtime_error("Number of dimensions must be one"); |
|||
|
|||
if (buf1.size != buf2.size) |
|||
throw std::runtime_error("Input shapes must match"); |
|||
|
|||
/* No pointer is passed, so NumPy will allocate the buffer */ |
|||
auto result = py::array_t<double>(buf1.size); |
|||
|
|||
auto buf3 = result.request(); |
|||
|
|||
double *ptr1 = (double *) buf1.ptr, |
|||
*ptr2 = (double *) buf2.ptr, |
|||
*ptr3 = (double *) buf3.ptr; |
|||
|
|||
for (size_t idx = 0; idx < buf1.shape[0]; idx++) |
|||
ptr3[idx] = ptr1[idx] + ptr2[idx]; |
|||
|
|||
return result; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_PLUGIN(test) { |
|||
py::module m("test"); |
|||
m.def("add_arrays", &add_arrays, "Add two NumPy arrays"); |
|||
return m.ptr(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
.. seealso:: |
|||
|
|||
The file :file:`tests/test_numpy_vectorize.cpp` contains a complete |
|||
example that demonstrates using :func:`vectorize` in more detail. |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,96 @@ |
|||
Python types |
|||
############ |
|||
|
|||
Available wrappers |
|||
================== |
|||
|
|||
All major Python types are available as thin C++ wrapper classes. These |
|||
can also be used as function parameters -- see :ref:`python_objects_as_args`. |
|||
|
|||
Available types include :class:`handle`, :class:`object`, :class:`bool_`, |
|||
:class:`int_`, :class:`float_`, :class:`str`, :class:`bytes`, :class:`tuple`, |
|||
:class:`list`, :class:`dict`, :class:`slice`, :class:`none`, :class:`capsule`, |
|||
:class:`iterable`, :class:`iterator`, :class:`function`, :class:`buffer`, |
|||
:class:`array`, and :class:`array_t`. |
|||
|
|||
Casting back and forth |
|||
====================== |
|||
|
|||
In this kind of mixed code, it is often necessary to convert arbitrary C++ |
|||
types to Python, which can be done using :func:`py::cast`: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
MyClass *cls = ..; |
|||
py::object obj = py::cast(cls); |
|||
|
|||
The reverse direction uses the following syntax: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::object obj = ...; |
|||
MyClass *cls = obj.cast<MyClass *>(); |
|||
|
|||
When conversion fails, both directions throw the exception :class:`cast_error`. |
|||
|
|||
Calling Python functions |
|||
======================== |
|||
|
|||
It is also possible to call python functions via ``operator()``. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::function f = <...>; |
|||
py::object result_py = f(1234, "hello", some_instance); |
|||
MyClass &result = result_py.cast<MyClass>(); |
|||
|
|||
Keyword arguments are also supported. In Python, there is the usual call syntax: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: python |
|||
|
|||
def f(number, say, to): |
|||
... # function code |
|||
|
|||
f(1234, say="hello", to=some_instance) # keyword call in Python |
|||
|
|||
In C++, the same call can be made using: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
using pybind11::literals; // to bring in the `_a` literal |
|||
f(1234, "say"_a="hello", "to"_a=some_instance); // keyword call in C++ |
|||
|
|||
Unpacking of ``*args`` and ``**kwargs`` is also possible and can be mixed with |
|||
other arguments: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
// * unpacking |
|||
py::tuple args = py::make_tuple(1234, "hello", some_instance); |
|||
f(*args); |
|||
|
|||
// ** unpacking |
|||
py::dict kwargs = py::dict("number"_a=1234, "say"_a="hello", "to"_a=some_instance); |
|||
f(**kwargs); |
|||
|
|||
// mixed keywords, * and ** unpacking |
|||
py::tuple args = py::make_tuple(1234); |
|||
py::dict kwargs = py::dict("to"_a=some_instance); |
|||
f(*args, "say"_a="hello", **kwargs); |
|||
|
|||
Generalized unpacking according to PEP448_ is also supported: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::dict kwargs1 = py::dict("number"_a=1234); |
|||
py::dict kwargs2 = py::dict("to"_a=some_instance); |
|||
f(**kwargs1, "say"_a="hello", **kwargs2); |
|||
|
|||
.. seealso:: |
|||
|
|||
The file :file:`tests/test_python_types.cpp` contains a complete |
|||
example that demonstrates passing native Python types in more detail. The |
|||
file :file:`tests/test_callbacks.cpp` presents a few examples of calling |
|||
Python functions from C++, including keywords arguments and unpacking. |
|||
|
|||
.. _PEP448: https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0448/ |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,57 @@ |
|||
Utilities |
|||
######### |
|||
|
|||
Using Python's print function in C++ |
|||
==================================== |
|||
|
|||
The usual way to write output in C++ is using ``std::cout`` while in Python one |
|||
would use ``print``. Since these methods use different buffers, mixing them can |
|||
lead to output order issues. To resolve this, pybind11 modules can use the |
|||
:func:`py::print` function which writes to Python's ``sys.stdout`` for consistency. |
|||
|
|||
Python's ``print`` function is replicated in the C++ API including optional |
|||
keyword arguments ``sep``, ``end``, ``file``, ``flush``. Everything works as |
|||
expected in Python: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::print(1, 2.0, "three"); // 1 2.0 three |
|||
py::print(1, 2.0, "three", "sep"_a="-"); // 1-2.0-three |
|||
|
|||
auto args = py::make_tuple("unpacked", true); |
|||
py::print("->", *args, "end"_a="<-"); // -> unpacked True <- |
|||
|
|||
Evaluating Python expressions from strings and files |
|||
==================================================== |
|||
|
|||
pybind11 provides the :func:`eval` and :func:`eval_file` functions to evaluate |
|||
Python expressions and statements. The following example illustrates how they |
|||
can be used. |
|||
|
|||
Both functions accept a template parameter that describes how the argument |
|||
should be interpreted. Possible choices include ``eval_expr`` (isolated |
|||
expression), ``eval_single_statement`` (a single statement, return value is |
|||
always ``none``), and ``eval_statements`` (sequence of statements, return value |
|||
is always ``none``). |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
// At beginning of file |
|||
#include <pybind11/eval.h> |
|||
|
|||
... |
|||
|
|||
// Evaluate in scope of main module |
|||
py::object scope = py::module::import("__main__").attr("__dict__"); |
|||
|
|||
// Evaluate an isolated expression |
|||
int result = py::eval("my_variable + 10", scope).cast<int>(); |
|||
|
|||
// Evaluate a sequence of statements |
|||
py::eval<py::eval_statements>( |
|||
"print('Hello')\n" |
|||
"print('world!');", |
|||
scope); |
|||
|
|||
// Evaluate the statements in an separate Python file on disk |
|||
py::eval_file("script.py", scope); |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,143 @@ |
|||
Smart pointers |
|||
############## |
|||
|
|||
std::unique_ptr |
|||
=============== |
|||
|
|||
Given a class ``Example`` with Python bindings, it's possible to return |
|||
instances wrapped in C++11 unique pointers, like so |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
std::unique_ptr<Example> create_example() { return std::unique_ptr<Example>(new Example()); } |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
m.def("create_example", &create_example); |
|||
|
|||
In other words, there is nothing special that needs to be done. While returning |
|||
unique pointers in this way is allowed, it is *illegal* to use them as function |
|||
arguments. For instance, the following function signature cannot be processed |
|||
by pybind11. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
void do_something_with_example(std::unique_ptr<Example> ex) { ... } |
|||
|
|||
The above signature would imply that Python needs to give up ownership of an |
|||
object that is passed to this function, which is generally not possible (for |
|||
instance, the object might be referenced elsewhere). |
|||
|
|||
std::shared_ptr |
|||
=============== |
|||
|
|||
The binding generator for classes, :class:`class_`, can be passed a template |
|||
type that denotes a special *holder* type that is used to manage references to |
|||
the object. If no such holder type template argument is given, the default for |
|||
a type named ``Type`` is ``std::unique_ptr<Type>``, which means that the object |
|||
is deallocated when Python's reference count goes to zero. |
|||
|
|||
It is possible to switch to other types of reference counting wrappers or smart |
|||
pointers, which is useful in codebases that rely on them. For instance, the |
|||
following snippet causes ``std::shared_ptr`` to be used instead. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Example, std::shared_ptr<Example> /* <- holder type */> obj(m, "Example"); |
|||
|
|||
Note that any particular class can only be associated with a single holder type. |
|||
|
|||
One potential stumbling block when using holder types is that they need to be |
|||
applied consistently. Can you guess what's broken about the following binding |
|||
code? |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
class Child { }; |
|||
|
|||
class Parent { |
|||
public: |
|||
Parent() : child(std::make_shared<Child>()) { } |
|||
Child *get_child() { return child.get(); } /* Hint: ** DON'T DO THIS ** */ |
|||
private: |
|||
std::shared_ptr<Child> child; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_PLUGIN(example) { |
|||
py::module m("example"); |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Child, std::shared_ptr<Child>>(m, "Child"); |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Parent, std::shared_ptr<Parent>>(m, "Parent") |
|||
.def(py::init<>()) |
|||
.def("get_child", &Parent::get_child); |
|||
|
|||
return m.ptr(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
The following Python code will cause undefined behavior (and likely a |
|||
segmentation fault). |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: python |
|||
|
|||
from example import Parent |
|||
print(Parent().get_child()) |
|||
|
|||
The problem is that ``Parent::get_child()`` returns a pointer to an instance of |
|||
``Child``, but the fact that this instance is already managed by |
|||
``std::shared_ptr<...>`` is lost when passing raw pointers. In this case, |
|||
pybind11 will create a second independent ``std::shared_ptr<...>`` that also |
|||
claims ownership of the pointer. In the end, the object will be freed **twice** |
|||
since these shared pointers have no way of knowing about each other. |
|||
|
|||
There are two ways to resolve this issue: |
|||
|
|||
1. For types that are managed by a smart pointer class, never use raw pointers |
|||
in function arguments or return values. In other words: always consistently |
|||
wrap pointers into their designated holder types (such as |
|||
``std::shared_ptr<...>``). In this case, the signature of ``get_child()`` |
|||
should be modified as follows: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
std::shared_ptr<Child> get_child() { return child; } |
|||
|
|||
2. Adjust the definition of ``Child`` by specifying |
|||
``std::enable_shared_from_this<T>`` (see cppreference_ for details) as a |
|||
base class. This adds a small bit of information to ``Child`` that allows |
|||
pybind11 to realize that there is already an existing |
|||
``std::shared_ptr<...>`` and communicate with it. In this case, the |
|||
declaration of ``Child`` should look as follows: |
|||
|
|||
.. _cppreference: http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/memory/enable_shared_from_this |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
class Child : public std::enable_shared_from_this<Child> { }; |
|||
|
|||
.. _smart_pointers: |
|||
|
|||
Custom smart pointers |
|||
===================== |
|||
|
|||
pybind11 supports ``std::unique_ptr`` and ``std::shared_ptr`` right out of the |
|||
box. For any other custom smart pointer, transparent conversions can be enabled |
|||
using a macro invocation similar to the following. It must be declared at the |
|||
level before any binding code: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_DECLARE_HOLDER_TYPE(T, SmartPtr<T>); |
|||
|
|||
The first argument of :func:`PYBIND11_DECLARE_HOLDER_TYPE` should be a |
|||
placeholder name that is used as a template parameter of the second argument. |
|||
Thus, feel free to use any identifier, but use it consistently on both sides; |
|||
also, don't use the name of a type that already exists in your codebase. |
|||
|
|||
Please take a look at the :ref:`macro_notes` before using this feature. |
|||
|
|||
.. seealso:: |
|||
|
|||
The file :file:`tests/test_smart_ptr.cpp` contains a complete example |
|||
that demonstrates how to work with custom reference-counting holder types |
|||
in more detail. |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,287 @@ |
|||
.. _basics: |
|||
|
|||
First steps |
|||
########### |
|||
|
|||
This sections demonstrates the basic features of pybind11. Before getting |
|||
started, make sure that development environment is set up to compile the |
|||
included set of test cases. |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
Compiling the test cases |
|||
======================== |
|||
|
|||
Linux/MacOS |
|||
----------- |
|||
|
|||
On Linux you'll need to install the **python-dev** or **python3-dev** packages as |
|||
well as **cmake**. On Mac OS, the included python version works out of the box, |
|||
but **cmake** must still be installed. |
|||
|
|||
After installing the prerequisites, run |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: bash |
|||
|
|||
mkdir build |
|||
cd build |
|||
cmake .. |
|||
make pytest -j 4 |
|||
|
|||
The last line will both compile and run the tests. |
|||
|
|||
Windows |
|||
------- |
|||
|
|||
On Windows, only **Visual Studio 2015** and newer are supported since pybind11 relies |
|||
on various C++11 language features that break older versions of Visual Studio. |
|||
|
|||
To compile and run the tests: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: batch |
|||
|
|||
mkdir build |
|||
cd build |
|||
cmake .. |
|||
cmake --build . --config Release --target pytest |
|||
|
|||
This will create a Visual Studio project, compile and run the target, all from the |
|||
command line. |
|||
|
|||
.. Note:: |
|||
|
|||
If all tests fail, make sure that the Python binary and the testcases are compiled |
|||
for the same processor type and bitness (i.e. either **i386** or **x86_64**). You |
|||
can specify **x86_64** as the target architecture for the generated Visual Studio |
|||
project using ``cmake -A x64 ..``. |
|||
|
|||
.. seealso:: |
|||
|
|||
Advanced users who are already familiar with Boost.Python may want to skip |
|||
the tutorial and look at the test cases in the :file:`tests` directory, |
|||
which exercise all features of pybind11. |
|||
|
|||
Header and namespace conventions |
|||
================================ |
|||
|
|||
For brevity, all code examples assume that the following two lines are present: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
#include <pybind11/pybind11.h> |
|||
|
|||
namespace py = pybind11; |
|||
|
|||
Some features may require additional headers, but those will be specified as needed. |
|||
|
|||
Creating bindings for a simple function |
|||
======================================= |
|||
|
|||
Let's start by creating Python bindings for an extremely simple function, which |
|||
adds two numbers and returns their result: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
int add(int i, int j) { |
|||
return i + j; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
For simplicity [#f1]_, we'll put both this function and the binding code into |
|||
a file named :file:`example.cpp` with the following contents: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
#include <pybind11/pybind11.h> |
|||
|
|||
int add(int i, int j) { |
|||
return i + j; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
namespace py = pybind11; |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_PLUGIN(example) { |
|||
py::module m("example", "pybind11 example plugin"); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("add", &add, "A function which adds two numbers"); |
|||
|
|||
return m.ptr(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
.. [#f1] In practice, implementation and binding code will generally be located |
|||
in separate files. |
|||
|
|||
The :func:`PYBIND11_PLUGIN` macro creates a function that will be called when an |
|||
``import`` statement is issued from within Python. The next line creates a |
|||
module named ``example`` (with the supplied docstring). The method |
|||
:func:`module::def` generates binding code that exposes the |
|||
``add()`` function to Python. The last line returns the internal Python object |
|||
associated with ``m`` to the Python interpreter. |
|||
|
|||
.. note:: |
|||
|
|||
Notice how little code was needed to expose our function to Python: all |
|||
details regarding the function's parameters and return value were |
|||
automatically inferred using template metaprogramming. This overall |
|||
approach and the used syntax are borrowed from Boost.Python, though the |
|||
underlying implementation is very different. |
|||
|
|||
pybind11 is a header-only-library, hence it is not necessary to link against |
|||
any special libraries (other than Python itself). On Windows, use the CMake |
|||
build file discussed in section :ref:`cmake`. On Linux and Mac OS, the above |
|||
example can be compiled using the following command |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: bash |
|||
|
|||
$ c++ -O3 -shared -std=c++11 -I <path-to-pybind11>/include `python-config --cflags --ldflags` example.cpp -o example.so |
|||
|
|||
In general, it is advisable to include several additional build parameters |
|||
that can considerably reduce the size of the created binary. Refer to section |
|||
:ref:`cmake` for a detailed example of a suitable cross-platform CMake-based |
|||
build system. |
|||
|
|||
Assuming that the created file :file:`example.so` (:file:`example.pyd` on Windows) |
|||
is located in the current directory, the following interactive Python session |
|||
shows how to load and execute the example. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
$ python |
|||
Python 2.7.10 (default, Aug 22 2015, 20:33:39) |
|||
[GCC 4.2.1 Compatible Apple LLVM 7.0.0 (clang-700.0.59.1)] on darwin |
|||
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. |
|||
>>> import example |
|||
>>> example.add(1, 2) |
|||
3L |
|||
>>> |
|||
|
|||
.. _keyword_args: |
|||
|
|||
Keyword arguments |
|||
================= |
|||
|
|||
With a simple modification code, it is possible to inform Python about the |
|||
names of the arguments ("i" and "j" in this case). |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
m.def("add", &add, "A function which adds two numbers", |
|||
py::arg("i"), py::arg("j")); |
|||
|
|||
:class:`arg` is one of several special tag classes which can be used to pass |
|||
metadata into :func:`module::def`. With this modified binding code, we can now |
|||
call the function using keyword arguments, which is a more readable alternative |
|||
particularly for functions taking many parameters: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> import example |
|||
>>> example.add(i=1, j=2) |
|||
3L |
|||
|
|||
The keyword names also appear in the function signatures within the documentation. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> help(example) |
|||
|
|||
.... |
|||
|
|||
FUNCTIONS |
|||
add(...) |
|||
Signature : (i: int, j: int) -> int |
|||
|
|||
A function which adds two numbers |
|||
|
|||
A shorter notation for named arguments is also available: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
// regular notation |
|||
m.def("add1", &add, py::arg("i"), py::arg("j")); |
|||
// shorthand |
|||
using namespace pybind11::literals; |
|||
m.def("add2", &add, "i"_a, "j"_a); |
|||
|
|||
The :var:`_a` suffix forms a C++11 literal which is equivalent to :class:`arg`. |
|||
Note that the literal operator must first be made visible with the directive |
|||
``using namespace pybind11::literals``. This does not bring in anything else |
|||
from the ``pybind11`` namespace except for literals. |
|||
|
|||
.. _default_args: |
|||
|
|||
Default arguments |
|||
================= |
|||
|
|||
Suppose now that the function to be bound has default arguments, e.g.: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
int add(int i = 1, int j = 2) { |
|||
return i + j; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
Unfortunately, pybind11 cannot automatically extract these parameters, since they |
|||
are not part of the function's type information. However, they are simple to specify |
|||
using an extension of :class:`arg`: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
m.def("add", &add, "A function which adds two numbers", |
|||
py::arg("i") = 1, py::arg("j") = 2); |
|||
|
|||
The default values also appear within the documentation. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> help(example) |
|||
|
|||
.... |
|||
|
|||
FUNCTIONS |
|||
add(...) |
|||
Signature : (i: int = 1, j: int = 2) -> int |
|||
|
|||
A function which adds two numbers |
|||
|
|||
The shorthand notation is also available for default arguments: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
// regular notation |
|||
m.def("add1", &add, py::arg("i") = 1, py::arg("j") = 2); |
|||
// shorthand |
|||
m.def("add2", &add, "i"_a=1, "j"_a=2); |
|||
|
|||
Exporting variables |
|||
=================== |
|||
|
|||
To expose a value from C++, use the ``attr`` function to register it in a module |
|||
as shown below. Built-in types and general objects (more on that later) can be |
|||
converted using the function ``py::cast``. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_PLUGIN(example) { |
|||
py::module m("example", "pybind11 example plugin"); |
|||
m.attr("the_answer") = py::cast(42); |
|||
m.attr("what") = py::cast("World"); |
|||
return m.ptr(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
These are then accessible from Python: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> import example |
|||
>>> example.the_answer |
|||
42 |
|||
>>> example.what |
|||
'World' |
|||
|
|||
.. _supported_types: |
|||
|
|||
Supported data types |
|||
==================== |
|||
|
|||
A large number of data types are supported out of the box and can be used |
|||
seamlessly as functions arguments, return values or with ``py::cast`` in general. |
|||
For a full overview, see the :doc:`advanced/cast/index` section. |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,90 @@ |
|||
import random |
|||
import os |
|||
import time |
|||
import datetime as dt |
|||
|
|||
nfns = 4 # Functions per class |
|||
nargs = 4 # Arguments per function |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def generate_dummy_code_pybind11(nclasses=10): |
|||
decl = "" |
|||
bindings = "" |
|||
|
|||
for cl in range(nclasses): |
|||
decl += "class cl%03i;\n" % cl |
|||
decl += '\n' |
|||
|
|||
for cl in range(nclasses): |
|||
decl += "class cl%03i {\n" % cl |
|||
decl += "public:\n" |
|||
bindings += ' py::class_<cl%03i>(m, "cl%03i")\n' % (cl, cl) |
|||
for fn in range(nfns): |
|||
ret = random.randint(0, nclasses - 1) |
|||
params = [random.randint(0, nclasses - 1) for i in range(nargs)] |
|||
decl += " cl%03i *fn_%03i(" % (ret, fn) |
|||
decl += ", ".join("cl%03i *" % p for p in params) |
|||
decl += ");\n" |
|||
bindings += ' .def("fn_%03i", &cl%03i::fn_%03i)\n' % \ |
|||
(fn, cl, fn) |
|||
decl += "};\n\n" |
|||
bindings += ' ;\n' |
|||
|
|||
result = "#include <pybind11/pybind11.h>\n\n" |
|||
result += "namespace py = pybind11;\n\n" |
|||
result += decl + '\n' |
|||
result += "PYBIND11_PLUGIN(example) {\n" |
|||
result += " py::module m(\"example\");" |
|||
result += bindings |
|||
result += " return m.ptr();" |
|||
result += "}" |
|||
return result |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def generate_dummy_code_boost(nclasses=10): |
|||
decl = "" |
|||
bindings = "" |
|||
|
|||
for cl in range(nclasses): |
|||
decl += "class cl%03i;\n" % cl |
|||
decl += '\n' |
|||
|
|||
for cl in range(nclasses): |
|||
decl += "class cl%03i {\n" % cl |
|||
decl += "public:\n" |
|||
bindings += ' py::class_<cl%03i>("cl%03i")\n' % (cl, cl) |
|||
for fn in range(nfns): |
|||
ret = random.randint(0, nclasses - 1) |
|||
params = [random.randint(0, nclasses - 1) for i in range(nargs)] |
|||
decl += " cl%03i *fn_%03i(" % (ret, fn) |
|||
decl += ", ".join("cl%03i *" % p for p in params) |
|||
decl += ");\n" |
|||
bindings += ' .def("fn_%03i", &cl%03i::fn_%03i, py::return_value_policy<py::manage_new_object>())\n' % \ |
|||
(fn, cl, fn) |
|||
decl += "};\n\n" |
|||
bindings += ' ;\n' |
|||
|
|||
result = "#include <boost/python.hpp>\n\n" |
|||
result += "namespace py = boost::python;\n\n" |
|||
result += decl + '\n' |
|||
result += "BOOST_PYTHON_MODULE(example) {\n" |
|||
result += bindings |
|||
result += "}" |
|||
return result |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
for codegen in [generate_dummy_code_pybind11, generate_dummy_code_boost]: |
|||
print ("{") |
|||
for i in range(0, 10): |
|||
nclasses = 2 ** i |
|||
with open("test.cpp", "w") as f: |
|||
f.write(codegen(nclasses)) |
|||
n1 = dt.datetime.now() |
|||
os.system("g++ -Os -shared -rdynamic -undefined dynamic_lookup " |
|||
"-fvisibility=hidden -std=c++14 test.cpp -I include " |
|||
"-I /System/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Headers -o test.so") |
|||
n2 = dt.datetime.now() |
|||
elapsed = (n2 - n1).total_seconds() |
|||
size = os.stat('test.so').st_size |
|||
print(" {%i, %f, %i}," % (nclasses * nfns, elapsed, size)) |
|||
print ("}") |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,99 @@ |
|||
Benchmark |
|||
========= |
|||
|
|||
The following is the result of a synthetic benchmark comparing both compilation |
|||
time and module size of pybind11 against Boost.Python. A detailed report about a |
|||
Boost.Python to pybind11 conversion of a real project is available here: [#f1]_. |
|||
|
|||
.. [#f1] http://graylab.jhu.edu/RosettaCon2016/PyRosetta-4.pdf |
|||
|
|||
Setup |
|||
----- |
|||
|
|||
A python script (see the ``docs/benchmark.py`` file) was used to generate a set |
|||
of files with dummy classes whose count increases for each successive benchmark |
|||
(between 1 and 2048 classes in powers of two). Each class has four methods with |
|||
a randomly generated signature with a return value and four arguments. (There |
|||
was no particular reason for this setup other than the desire to generate many |
|||
unique function signatures whose count could be controlled in a simple way.) |
|||
|
|||
Here is an example of the binding code for one class: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
... |
|||
class cl034 { |
|||
public: |
|||
cl279 *fn_000(cl084 *, cl057 *, cl065 *, cl042 *); |
|||
cl025 *fn_001(cl098 *, cl262 *, cl414 *, cl121 *); |
|||
cl085 *fn_002(cl445 *, cl297 *, cl145 *, cl421 *); |
|||
cl470 *fn_003(cl200 *, cl323 *, cl332 *, cl492 *); |
|||
}; |
|||
... |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_PLUGIN(example) { |
|||
py::module m("example"); |
|||
... |
|||
py::class_<cl034>(m, "cl034") |
|||
.def("fn_000", &cl034::fn_000) |
|||
.def("fn_001", &cl034::fn_001) |
|||
.def("fn_002", &cl034::fn_002) |
|||
.def("fn_003", &cl034::fn_003) |
|||
... |
|||
return m.ptr(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
The Boost.Python version looks almost identical except that a return value |
|||
policy had to be specified as an argument to ``def()``. For both libraries, |
|||
compilation was done with |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: bash |
|||
|
|||
Apple LLVM version 7.0.2 (clang-700.1.81) |
|||
|
|||
and the following compilation flags |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: bash |
|||
|
|||
g++ -Os -shared -rdynamic -undefined dynamic_lookup -fvisibility=hidden -std=c++14 |
|||
|
|||
Compilation time |
|||
---------------- |
|||
|
|||
The following log-log plot shows how the compilation time grows for an |
|||
increasing number of class and function declarations. pybind11 includes many |
|||
fewer headers, which initially leads to shorter compilation times, but the |
|||
performance is ultimately fairly similar (pybind11 is 19.8 seconds faster for |
|||
the largest largest file with 2048 classes and a total of 8192 methods -- a |
|||
modest **1.2x** speedup relative to Boost.Python, which required 116.35 |
|||
seconds). |
|||
|
|||
.. only:: not latex |
|||
|
|||
.. image:: pybind11_vs_boost_python1.svg |
|||
|
|||
.. only:: latex |
|||
|
|||
.. image:: pybind11_vs_boost_python1.png |
|||
|
|||
Module size |
|||
----------- |
|||
|
|||
Differences between the two libraries become much more pronounced when |
|||
considering the file size of the generated Python plugin: for the largest file, |
|||
the binary generated by Boost.Python required 16.8 MiB, which was **2.17 |
|||
times** / **9.1 megabytes** larger than the output generated by pybind11. For |
|||
very small inputs, Boost.Python has an edge in the plot below -- however, note |
|||
that it stores many definitions in an external library, whose size was not |
|||
included here, hence the comparison is slightly shifted in Boost.Python's |
|||
favor. |
|||
|
|||
.. only:: not latex |
|||
|
|||
.. image:: pybind11_vs_boost_python2.svg |
|||
|
|||
.. only:: latex |
|||
|
|||
.. image:: pybind11_vs_boost_python2.png |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
@ -0,0 +1,222 @@ |
|||
.. _changelog: |
|||
|
|||
Changelog |
|||
######### |
|||
|
|||
Starting with version 1.8, pybind11 releases use a |
|||
[semantic versioning](http://semver.org) policy. |
|||
|
|||
Breaking changes queued for v2.0.0 (Not yet released) |
|||
----------------------------------------------------- |
|||
* Redesigned virtual call mechanism and user-facing syntax (see |
|||
https://github.com/pybind/pybind11/commit/86d825f3302701d81414ddd3d38bcd09433076bc) |
|||
|
|||
* Remove ``handle.call()`` method |
|||
|
|||
1.9.0 (Not yet released) |
|||
------------------------ |
|||
* Queued changes: map indexing suite, documentation for indexing suites. |
|||
* Mapping a stateless C++ function to Python and back is now "for free" (i.e. no call overheads) |
|||
* Support for translation of arbitrary C++ exceptions to Python counterparts |
|||
* Added ``eval`` and ``eval_file`` functions for evaluating expressions and |
|||
statements from a string or file |
|||
* eigen.h type converter fixed for non-contiguous arrays (e.g. slices) |
|||
* Print more informative error messages when ``make_tuple()`` or ``cast()`` fail |
|||
* ``std::enable_shared_from_this<>`` now also works for ``const`` values |
|||
* A return value policy can now be passed to ``handle::operator()`` |
|||
* ``make_iterator()`` improvements for better compatibility with various types |
|||
(now uses prefix increment operator); it now also accepts iterators with |
|||
different begin/end types as long as they are equality comparable. |
|||
* ``arg()`` now accepts a wider range of argument types for default values |
|||
* Added ``py::repr()`` function which is equivalent to Python's builtin ``repr()``. |
|||
* Added support for registering structured dtypes via ``PYBIND11_NUMPY_DTYPE()`` macro. |
|||
* Added ``PYBIND11_STR_TYPE`` macro which maps to the ``builtins.str`` type. |
|||
* Added a simplified ``buffer_info`` constructor for 1-dimensional buffers. |
|||
* Format descriptor strings should now be accessed via ``format_descriptor::format()`` |
|||
(for compatibility purposes, the old syntax ``format_descriptor::value`` will still |
|||
work for non-structured data types). |
|||
* Added a class wrapping NumPy array descriptors: ``dtype``. |
|||
* Added buffer/NumPy support for ``char[N]`` and ``std::array<char, N>`` types. |
|||
* ``array`` gained new constructors accepting dtype objects. |
|||
* Added constructors for ``array`` and ``array_t`` explicitly accepting shape and |
|||
strides; if strides are not provided, they are deduced assuming C-contiguity. |
|||
Also added simplified constructors for 1-dimensional case. |
|||
* Added constructors for ``str`` from ``bytes`` and for ``bytes`` from ``str``. |
|||
This will do the UTF-8 decoding/encoding as required. |
|||
* Added constructors for ``str`` and ``bytes`` from zero-terminated char pointers, |
|||
and from char pointers and length. |
|||
* Added ``memoryview`` wrapper type which is constructible from ``buffer_info``. |
|||
* New syntax to call a Python function from C++ using keyword arguments and unpacking, |
|||
e.g. ``foo(1, 2, "z"_a=3)`` or ``bar(1, *args, "z"_a=3, **kwargs)``. |
|||
* Added ``py::print()`` function which replicates Python's API and writes to Python's |
|||
``sys.stdout`` by default (as opposed to C's ``stdout`` like ``std::cout``). |
|||
* Added ``py::dict`` keyword constructor:``auto d = dict("number"_a=42, "name"_a="World");`` |
|||
* Added ``py::str::format()`` method and ``_s`` literal: |
|||
``py::str s = "1 + 2 = {}"_s.format(3);`` |
|||
* Attribute and item accessors now have a more complete interface which makes it possible |
|||
to chain attributes ``obj.attr("a")[key].attr("b").attr("method")(1, 2, 3)```. |
|||
* Added built-in support for ``std::shared_ptr`` holder type. There is no more need |
|||
to do it manually via ``PYBIND11_DECLARE_HOLDER_TYPE(T, std::shared_ptr<T>)``. |
|||
* Default return values policy changes: non-static properties now use ``reference_internal`` |
|||
and static properties use ``reference`` (previous default was ``automatic``, i.e. ``copy``). |
|||
* Support for ``std::experimental::optional<T>`` and ``std::optional<T>`` (C++17). |
|||
* Various minor improvements of library internals (no user-visible changes) |
|||
|
|||
1.8.1 (July 12, 2016) |
|||
---------------------- |
|||
* Fixed a rare but potentially very severe issue when the garbage collector ran |
|||
during pybind11 type creation. |
|||
|
|||
1.8.0 (June 14, 2016) |
|||
---------------------- |
|||
* Redesigned CMake build system which exports a convenient |
|||
``pybind11_add_module`` function to parent projects. |
|||
* ``std::vector<>`` type bindings analogous to Boost.Python's ``indexing_suite`` |
|||
* Transparent conversion of sparse and dense Eigen matrices and vectors (``eigen.h``) |
|||
* Added an ``ExtraFlags`` template argument to the NumPy ``array_t<>`` wrapper |
|||
to disable an enforced cast that may lose precision, e.g. to create overloads |
|||
for different precisions and complex vs real-valued matrices. |
|||
* Prevent implicit conversion of floating point values to integral types in |
|||
function arguments |
|||
* Fixed incorrect default return value policy for functions returning a shared |
|||
pointer |
|||
* Don't allow registering a type via ``class_`` twice |
|||
* Don't allow casting a ``None`` value into a C++ lvalue reference |
|||
* Fixed a crash in ``enum_::operator==`` that was triggered by the ``help()`` command |
|||
* Improved detection of whether or not custom C++ types can be copy/move-constructed |
|||
* Extended ``str`` type to also work with ``bytes`` instances |
|||
* Added a ``"name"_a`` user defined string literal that is equivalent to ``py::arg("name")``. |
|||
* When specifying function arguments via ``py::arg``, the test that verifies |
|||
the number of arguments now runs at compile time. |
|||
* Added ``[[noreturn]]`` attribute to ``pybind11_fail()`` to quench some |
|||
compiler warnings |
|||
* List function arguments in exception text when the dispatch code cannot find |
|||
a matching overload |
|||
* Added ``PYBIND11_OVERLOAD_NAME`` and ``PYBIND11_OVERLOAD_PURE_NAME`` macros which |
|||
can be used to override virtual methods whose name differs in C++ and Python |
|||
(e.g. ``__call__`` and ``operator()``) |
|||
* Various minor ``iterator`` and ``make_iterator()`` improvements |
|||
* Transparently support ``__bool__`` on Python 2.x and Python 3.x |
|||
* Fixed issue with destructor of unpickled object not being called |
|||
* Minor CMake build system improvements on Windows |
|||
* New ``pybind11::args`` and ``pybind11::kwargs`` types to create functions which |
|||
take an arbitrary number of arguments and keyword arguments |
|||
* New syntax to call a Python function from C++ using ``*args`` and ``*kwargs`` |
|||
* The functions ``def_property_*`` now correctly process docstring arguments (these |
|||
formerly caused a segmentation fault) |
|||
* Many ``mkdoc.py`` improvements (enumerations, template arguments, ``DOC()`` |
|||
macro accepts more arguments) |
|||
* Cygwin support |
|||
* Documentation improvements (pickling support, ``keep_alive``, macro usage) |
|||
|
|||
1.7 (April 30, 2016) |
|||
---------------------- |
|||
* Added a new ``move`` return value policy that triggers C++11 move semantics. |
|||
The automatic return value policy falls back to this case whenever a rvalue |
|||
reference is encountered |
|||
* Significantly more general GIL state routines that are used instead of |
|||
Python's troublesome ``PyGILState_Ensure`` and ``PyGILState_Release`` API |
|||
* Redesign of opaque types that drastically simplifies their usage |
|||
* Extended ability to pass values of type ``[const] void *`` |
|||
* ``keep_alive`` fix: don't fail when there is no patient |
|||
* ``functional.h``: acquire the GIL before calling a Python function |
|||
* Added Python RAII type wrappers ``none`` and ``iterable`` |
|||
* Added ``*args`` and ``*kwargs`` pass-through parameters to |
|||
``pybind11.get_include()`` function |
|||
* Iterator improvements and fixes |
|||
* Documentation on return value policies and opaque types improved |
|||
|
|||
1.6 (April 30, 2016) |
|||
---------------------- |
|||
* Skipped due to upload to PyPI gone wrong and inability to recover |
|||
(https://github.com/pypa/packaging-problems/issues/74) |
|||
|
|||
1.5 (April 21, 2016) |
|||
---------------------- |
|||
* For polymorphic types, use RTTI to try to return the closest type registered with pybind11 |
|||
* Pickling support for serializing and unserializing C++ instances to a byte stream in Python |
|||
* Added a convenience routine ``make_iterator()`` which turns a range indicated |
|||
by a pair of C++ iterators into a iterable Python object |
|||
* Added ``len()`` and a variadic ``make_tuple()`` function |
|||
* Addressed a rare issue that could confuse the current virtual function |
|||
dispatcher and another that could lead to crashes in multi-threaded |
|||
applications |
|||
* Added a ``get_include()`` function to the Python module that returns the path |
|||
of the directory containing the installed pybind11 header files |
|||
* Documentation improvements: import issues, symbol visibility, pickling, limitations |
|||
* Added casting support for ``std::reference_wrapper<>`` |
|||
|
|||
1.4 (April 7, 2016) |
|||
-------------------------- |
|||
* Transparent type conversion for ``std::wstring`` and ``wchar_t`` |
|||
* Allow passing ``nullptr``-valued strings |
|||
* Transparent passing of ``void *`` pointers using capsules |
|||
* Transparent support for returning values wrapped in ``std::unique_ptr<>`` |
|||
* Improved docstring generation for compatibility with Sphinx |
|||
* Nicer debug error message when default parameter construction fails |
|||
* Support for "opaque" types that bypass the transparent conversion layer for STL containers |
|||
* Redesigned type casting interface to avoid ambiguities that could occasionally cause compiler errors |
|||
* Redesigned property implementation; fixes crashes due to an unfortunate default return value policy |
|||
* Anaconda package generation support |
|||
|
|||
1.3 (March 8, 2016) |
|||
-------------------------- |
|||
|
|||
* Added support for the Intel C++ compiler (v15+) |
|||
* Added support for the STL unordered set/map data structures |
|||
* Added support for the STL linked list data structure |
|||
* NumPy-style broadcasting support in ``pybind11::vectorize`` |
|||
* pybind11 now displays more verbose error messages when ``arg::operator=()`` fails |
|||
* pybind11 internal data structures now live in a version-dependent namespace to avoid ABI issues |
|||
* Many, many bugfixes involving corner cases and advanced usage |
|||
|
|||
1.2 (February 7, 2016) |
|||
-------------------------- |
|||
|
|||
* Optional: efficient generation of function signatures at compile time using C++14 |
|||
* Switched to a simpler and more general way of dealing with function default |
|||
arguments. Unused keyword arguments in function calls are now detected and |
|||
cause errors as expected |
|||
* New ``keep_alive`` call policy analogous to Boost.Python's ``with_custodian_and_ward`` |
|||
* New ``pybind11::base<>`` attribute to indicate a subclass relationship |
|||
* Improved interface for RAII type wrappers in ``pytypes.h`` |
|||
* Use RAII type wrappers consistently within pybind11 itself. This |
|||
fixes various potential refcount leaks when exceptions occur |
|||
* Added new ``bytes`` RAII type wrapper (maps to ``string`` in Python 2.7) |
|||
* Made handle and related RAII classes const correct, using them more |
|||
consistently everywhere now |
|||
* Got rid of the ugly ``__pybind11__`` attributes on the Python side---they are |
|||
now stored in a C++ hash table that is not visible in Python |
|||
* Fixed refcount leaks involving NumPy arrays and bound functions |
|||
* Vastly improved handling of shared/smart pointers |
|||
* Removed an unnecessary copy operation in ``pybind11::vectorize`` |
|||
* Fixed naming clashes when both pybind11 and NumPy headers are included |
|||
* Added conversions for additional exception types |
|||
* Documentation improvements (using multiple extension modules, smart pointers, |
|||
other minor clarifications) |
|||
* unified infrastructure for parsing variadic arguments in ``class_`` and cpp_function |
|||
* Fixed license text (was: ZLIB, should have been: 3-clause BSD) |
|||
* Python 3.2 compatibility |
|||
* Fixed remaining issues when accessing types in another plugin module |
|||
* Added enum comparison and casting methods |
|||
* Improved SFINAE-based detection of whether types are copy-constructible |
|||
* Eliminated many warnings about unused variables and the use of ``offsetof()`` |
|||
* Support for ``std::array<>`` conversions |
|||
|
|||
1.1 (December 7, 2015) |
|||
-------------------------- |
|||
|
|||
* Documentation improvements (GIL, wrapping functions, casting, fixed many typos) |
|||
* Generalized conversion of integer types |
|||
* Improved support for casting function objects |
|||
* Improved support for ``std::shared_ptr<>`` conversions |
|||
* Initial support for ``std::set<>`` conversions |
|||
* Fixed type resolution issue for types defined in a separate plugin module |
|||
* Cmake build system improvements |
|||
* Factored out generic functionality to non-templated code (smaller code size) |
|||
* Added a code size / compile time benchmark vs Boost.Python |
|||
* Added an appveyor CI script |
|||
|
|||
1.0 (October 15, 2015) |
|||
------------------------ |
|||
* Initial release |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,410 @@ |
|||
.. _classes: |
|||
|
|||
Object-oriented code |
|||
#################### |
|||
|
|||
Creating bindings for a custom type |
|||
=================================== |
|||
|
|||
Let's now look at a more complex example where we'll create bindings for a |
|||
custom C++ data structure named ``Pet``. Its definition is given below: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
struct Pet { |
|||
Pet(const std::string &name) : name(name) { } |
|||
void setName(const std::string &name_) { name = name_; } |
|||
const std::string &getName() const { return name; } |
|||
|
|||
std::string name; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
The binding code for ``Pet`` looks as follows: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
#include <pybind11/pybind11.h> |
|||
|
|||
namespace py = pybind11; |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_PLUGIN(example) { |
|||
py::module m("example", "pybind11 example plugin"); |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Pet>(m, "Pet") |
|||
.def(py::init<const std::string &>()) |
|||
.def("setName", &Pet::setName) |
|||
.def("getName", &Pet::getName); |
|||
|
|||
return m.ptr(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
:class:`class_` creates bindings for a C++ `class` or `struct`-style data |
|||
structure. :func:`init` is a convenience function that takes the types of a |
|||
constructor's parameters as template arguments and wraps the corresponding |
|||
constructor (see the :ref:`custom_constructors` section for details). An |
|||
interactive Python session demonstrating this example is shown below: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
% python |
|||
>>> import example |
|||
>>> p = example.Pet('Molly') |
|||
>>> print(p) |
|||
<example.Pet object at 0x10cd98060> |
|||
>>> p.getName() |
|||
u'Molly' |
|||
>>> p.setName('Charly') |
|||
>>> p.getName() |
|||
u'Charly' |
|||
|
|||
.. seealso:: |
|||
|
|||
Static member functions can be bound in the same way using |
|||
:func:`class_::def_static`. |
|||
|
|||
Keyword and default arguments |
|||
============================= |
|||
It is possible to specify keyword and default arguments using the syntax |
|||
discussed in the previous chapter. Refer to the sections :ref:`keyword_args` |
|||
and :ref:`default_args` for details. |
|||
|
|||
Binding lambda functions |
|||
======================== |
|||
|
|||
Note how ``print(p)`` produced a rather useless summary of our data structure in the example above: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> print(p) |
|||
<example.Pet object at 0x10cd98060> |
|||
|
|||
To address this, we could bind an utility function that returns a human-readable |
|||
summary to the special method slot named ``__repr__``. Unfortunately, there is no |
|||
suitable functionality in the ``Pet`` data structure, and it would be nice if |
|||
we did not have to change it. This can easily be accomplished by binding a |
|||
Lambda function instead: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Pet>(m, "Pet") |
|||
.def(py::init<const std::string &>()) |
|||
.def("setName", &Pet::setName) |
|||
.def("getName", &Pet::getName) |
|||
.def("__repr__", |
|||
[](const Pet &a) { |
|||
return "<example.Pet named '" + a.name + "'>"; |
|||
} |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
Both stateless [#f1]_ and stateful lambda closures are supported by pybind11. |
|||
With the above change, the same Python code now produces the following output: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> print(p) |
|||
<example.Pet named 'Molly'> |
|||
|
|||
.. _properties: |
|||
|
|||
Instance and static fields |
|||
========================== |
|||
|
|||
We can also directly expose the ``name`` field using the |
|||
:func:`class_::def_readwrite` method. A similar :func:`class_::def_readonly` |
|||
method also exists for ``const`` fields. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Pet>(m, "Pet") |
|||
.def(py::init<const std::string &>()) |
|||
.def_readwrite("name", &Pet::name) |
|||
// ... remainder ... |
|||
|
|||
This makes it possible to write |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> p = example.Pet('Molly') |
|||
>>> p.name |
|||
u'Molly' |
|||
>>> p.name = 'Charly' |
|||
>>> p.name |
|||
u'Charly' |
|||
|
|||
Now suppose that ``Pet::name`` was a private internal variable |
|||
that can only be accessed via setters and getters. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
class Pet { |
|||
public: |
|||
Pet(const std::string &name) : name(name) { } |
|||
void setName(const std::string &name_) { name = name_; } |
|||
const std::string &getName() const { return name; } |
|||
private: |
|||
std::string name; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
In this case, the method :func:`class_::def_property` |
|||
(:func:`class_::def_property_readonly` for read-only data) can be used to |
|||
provide a field-like interface within Python that will transparently call |
|||
the setter and getter functions: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Pet>(m, "Pet") |
|||
.def(py::init<const std::string &>()) |
|||
.def_property("name", &Pet::getName, &Pet::setName) |
|||
// ... remainder ... |
|||
|
|||
.. seealso:: |
|||
|
|||
Similar functions :func:`class_::def_readwrite_static`, |
|||
:func:`class_::def_readonly_static` :func:`class_::def_property_static`, |
|||
and :func:`class_::def_property_readonly_static` are provided for binding |
|||
static variables and properties. Please also see the section on |
|||
:ref:`static_properties` in the advanced part of the documentation. |
|||
|
|||
Dynamic attributes |
|||
================== |
|||
|
|||
Native Python classes can pick up new attributes dynamically: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> class Pet: |
|||
... name = 'Molly' |
|||
... |
|||
>>> p = Pet() |
|||
>>> p.name = 'Charly' # overwrite existing |
|||
>>> p.age = 2 # dynamically add a new attribute |
|||
|
|||
By default, classes exported from C++ do not support this and the only writable |
|||
attributes are the ones explicitly defined using :func:`class_::def_readwrite` |
|||
or :func:`class_::def_property`. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Pet>(m, "Pet") |
|||
.def(py::init<>()) |
|||
.def_readwrite("name", &Pet::name); |
|||
|
|||
Trying to set any other attribute results in an error: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> p = example.Pet() |
|||
>>> p.name = 'Charly' # OK, attribute defined in C++ |
|||
>>> p.age = 2 # fail |
|||
AttributeError: 'Pet' object has no attribute 'age' |
|||
|
|||
To enable dynamic attributes for C++ classes, the :class:`py::dynamic_attr` tag |
|||
must be added to the :class:`py::class_` constructor: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Pet>(m, "Pet", py::dynamic_attr()) |
|||
.def(py::init<>()) |
|||
.def_readwrite("name", &Pet::name); |
|||
|
|||
Now everything works as expected: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> p = example.Pet() |
|||
>>> p.name = 'Charly' # OK, overwrite value in C++ |
|||
>>> p.age = 2 # OK, dynamically add a new attribute |
|||
>>> p.__dict__ # just like a native Python class |
|||
{'age': 2} |
|||
|
|||
Note that there is a small runtime cost for a class with dynamic attributes. |
|||
Not only because of the addition of a ``__dict__``, but also because of more |
|||
expensive garbage collection tracking which must be activated to resolve |
|||
possible circular references. Native Python classes incur this same cost by |
|||
default, so this is not anything to worry about. By default, pybind11 classes |
|||
are more efficient than native Python classes. Enabling dynamic attributes |
|||
just brings them on par. |
|||
|
|||
.. _inheritance: |
|||
|
|||
Inheritance |
|||
=========== |
|||
|
|||
Suppose now that the example consists of two data structures with an |
|||
inheritance relationship: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
struct Pet { |
|||
Pet(const std::string &name) : name(name) { } |
|||
std::string name; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
struct Dog : Pet { |
|||
Dog(const std::string &name) : Pet(name) { } |
|||
std::string bark() const { return "woof!"; } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
There are two different ways of indicating a hierarchical relationship to |
|||
pybind11: the first specifies the C++ base class as an extra template |
|||
parameter of the :class:`class_`: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Pet>(m, "Pet") |
|||
.def(py::init<const std::string &>()) |
|||
.def_readwrite("name", &Pet::name); |
|||
|
|||
// Method 1: template parameter: |
|||
py::class_<Dog, Pet /* <- specify C++ parent type */>(m, "Dog") |
|||
.def(py::init<const std::string &>()) |
|||
.def("bark", &Dog::bark); |
|||
|
|||
Alternatively, we can also assign a name to the previously bound ``Pet`` |
|||
:class:`class_` object and reference it when binding the ``Dog`` class: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Pet> pet(m, "Pet"); |
|||
pet.def(py::init<const std::string &>()) |
|||
.def_readwrite("name", &Pet::name); |
|||
|
|||
// Method 2: pass parent class_ object: |
|||
py::class_<Dog>(m, "Dog", pet /* <- specify Python parent type */) |
|||
.def(py::init<const std::string &>()) |
|||
.def("bark", &Dog::bark); |
|||
|
|||
Functionality-wise, both approaches are equivalent. Afterwards, instances will |
|||
expose fields and methods of both types: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> p = example.Dog('Molly') |
|||
>>> p.name |
|||
u'Molly' |
|||
>>> p.bark() |
|||
u'woof!' |
|||
|
|||
Overloaded methods |
|||
================== |
|||
|
|||
Sometimes there are several overloaded C++ methods with the same name taking |
|||
different kinds of input arguments: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
struct Pet { |
|||
Pet(const std::string &name, int age) : name(name), age(age) { } |
|||
|
|||
void set(int age) { age = age; } |
|||
void set(const std::string &name) { name = name; } |
|||
|
|||
std::string name; |
|||
int age; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
Attempting to bind ``Pet::set`` will cause an error since the compiler does not |
|||
know which method the user intended to select. We can disambiguate by casting |
|||
them to function pointers. Binding multiple functions to the same Python name |
|||
automatically creates a chain of function overloads that will be tried in |
|||
sequence. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Pet>(m, "Pet") |
|||
.def(py::init<const std::string &, int>()) |
|||
.def("set", (void (Pet::*)(int)) &Pet::set, "Set the pet's age") |
|||
.def("set", (void (Pet::*)(const std::string &)) &Pet::set, "Set the pet's name"); |
|||
|
|||
The overload signatures are also visible in the method's docstring: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> help(example.Pet) |
|||
|
|||
class Pet(__builtin__.object) |
|||
| Methods defined here: |
|||
| |
|||
| __init__(...) |
|||
| Signature : (Pet, str, int) -> NoneType |
|||
| |
|||
| set(...) |
|||
| 1. Signature : (Pet, int) -> NoneType |
|||
| |
|||
| Set the pet's age |
|||
| |
|||
| 2. Signature : (Pet, str) -> NoneType |
|||
| |
|||
| Set the pet's name |
|||
|
|||
.. note:: |
|||
|
|||
To define multiple overloaded constructors, simply declare one after the |
|||
other using the ``.def(py::init<...>())`` syntax. The existing machinery |
|||
for specifying keyword and default arguments also works. |
|||
|
|||
Enumerations and internal types |
|||
=============================== |
|||
|
|||
Let's now suppose that the example class contains an internal enumeration type, |
|||
e.g.: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
struct Pet { |
|||
enum Kind { |
|||
Dog = 0, |
|||
Cat |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
Pet(const std::string &name, Kind type) : name(name), type(type) { } |
|||
|
|||
std::string name; |
|||
Kind type; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
The binding code for this example looks as follows: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<Pet> pet(m, "Pet"); |
|||
|
|||
pet.def(py::init<const std::string &, Pet::Kind>()) |
|||
.def_readwrite("name", &Pet::name) |
|||
.def_readwrite("type", &Pet::type); |
|||
|
|||
py::enum_<Pet::Kind>(pet, "Kind") |
|||
.value("Dog", Pet::Kind::Dog) |
|||
.value("Cat", Pet::Kind::Cat) |
|||
.export_values(); |
|||
|
|||
To ensure that the ``Kind`` type is created within the scope of ``Pet``, the |
|||
``pet`` :class:`class_` instance must be supplied to the :class:`enum_`. |
|||
constructor. The :func:`enum_::export_values` function exports the enum entries |
|||
into the parent scope, which should be skipped for newer C++11-style strongly |
|||
typed enums. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> p = Pet('Lucy', Pet.Cat) |
|||
>>> p.type |
|||
Kind.Cat |
|||
>>> int(p.type) |
|||
1L |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
.. note:: |
|||
|
|||
When the special tag ``py::arithmetic()`` is specified to the ``enum_`` |
|||
constructor, pybind11 creates an enumeration that also supports rudimentary |
|||
arithmetic and bit-level operations like comparisons, and, or, xor, negation, |
|||
etc. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
py::enum_<Pet::Kind>(pet, "Kind", py::arithmetic()) |
|||
... |
|||
|
|||
By default, these are omitted to conserve space. |
|||
|
|||
.. [#f1] Stateless closures are those with an empty pair of brackets ``[]`` as the capture object. |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,53 @@ |
|||
Build systems |
|||
############# |
|||
|
|||
Building with setuptools |
|||
======================== |
|||
|
|||
For projects on PyPI, building with setuptools is the way to go. Sylvain Corlay |
|||
has kindly provided an example project which shows how to set up everything, |
|||
including automatic generation of documentation using Sphinx. Please refer to |
|||
the [python_example]_ repository. |
|||
|
|||
.. [python_example] https://github.com/pybind/python_example |
|||
|
|||
Building with cppimport |
|||
======================== |
|||
|
|||
cppimport is a small Python import hook that determines whether there is a C++ |
|||
source file whose name matches the requested module. If there is, the file is |
|||
compiled as a Python extension using pybind11 and placed in the same folder as |
|||
the C++ source file. Python is then able to find the module and load it. |
|||
|
|||
.. [cppimport] https://github.com/tbenthompson/cppimport |
|||
|
|||
.. _cmake: |
|||
|
|||
Building with CMake |
|||
=================== |
|||
|
|||
For C++ codebases that have an existing CMake-based build system, a Python |
|||
extension module can be created with just a few lines of code: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cmake |
|||
|
|||
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8.12) |
|||
project(example) |
|||
|
|||
add_subdirectory(pybind11) |
|||
pybind11_add_module(example example.cpp) |
|||
|
|||
This assumes that the pybind11 repository is located in a subdirectory named |
|||
:file:`pybind11` and that the code is located in a file named :file:`example.cpp`. |
|||
The CMake command ``add_subdirectory`` will import a function with the signature |
|||
``pybind11_add_module(<name> source1 [source2 ...])``. It will take care of all |
|||
the details needed to build a Python extension module on any platform. |
|||
|
|||
The target Python version can be selected by setting the ``PYBIND11_PYTHON_VERSION`` |
|||
variable before adding the pybind11 subdirectory. Alternatively, an exact Python |
|||
installation can be specified by setting ``PYTHON_EXECUTABLE``. |
|||
|
|||
A working sample project, including a way to invoke CMake from :file:`setup.py` for |
|||
PyPI integration, can be found in the [cmake_example]_ repository. |
|||
|
|||
.. [cmake_example] https://github.com/pybind/cmake_example |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,308 @@ |
|||
#!/usr/bin/env python3 |
|||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- |
|||
# |
|||
# pybind11 documentation build configuration file, created by |
|||
# sphinx-quickstart on Sun Oct 11 19:23:48 2015. |
|||
# |
|||
# This file is execfile()d with the current directory set to its |
|||
# containing dir. |
|||
# |
|||
# Note that not all possible configuration values are present in this |
|||
# autogenerated file. |
|||
# |
|||
# All configuration values have a default; values that are commented out |
|||
# serve to show the default. |
|||
|
|||
import sys |
|||
import os |
|||
import shlex |
|||
|
|||
# If extensions (or modules to document with autodoc) are in another directory, |
|||
# add these directories to sys.path here. If the directory is relative to the |
|||
# documentation root, use os.path.abspath to make it absolute, like shown here. |
|||
#sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath('.')) |
|||
|
|||
# -- General configuration ------------------------------------------------ |
|||
|
|||
# If your documentation needs a minimal Sphinx version, state it here. |
|||
#needs_sphinx = '1.0' |
|||
|
|||
# Add any Sphinx extension module names here, as strings. They can be |
|||
# extensions coming with Sphinx (named 'sphinx.ext.*') or your custom |
|||
# ones. |
|||
extensions = [] |
|||
|
|||
# Add any paths that contain templates here, relative to this directory. |
|||
templates_path = ['.templates'] |
|||
|
|||
# The suffix(es) of source filenames. |
|||
# You can specify multiple suffix as a list of string: |
|||
# source_suffix = ['.rst', '.md'] |
|||
source_suffix = '.rst' |
|||
|
|||
# The encoding of source files. |
|||
#source_encoding = 'utf-8-sig' |
|||
|
|||
# The master toctree document. |
|||
master_doc = 'index' |
|||
|
|||
# General information about the project. |
|||
project = 'pybind11' |
|||
copyright = '2015, Wenzel Jakob' |
|||
author = 'Wenzel Jakob' |
|||
|
|||
# The version info for the project you're documenting, acts as replacement for |
|||
# |version| and |release|, also used in various other places throughout the |
|||
# built documents. |
|||
# |
|||
# The short X.Y version. |
|||
version = '1.9' |
|||
# The full version, including alpha/beta/rc tags. |
|||
release = '1.9.dev0' |
|||
|
|||
# The language for content autogenerated by Sphinx. Refer to documentation |
|||
# for a list of supported languages. |
|||
# |
|||
# This is also used if you do content translation via gettext catalogs. |
|||
# Usually you set "language" from the command line for these cases. |
|||
language = None |
|||
|
|||
# There are two options for replacing |today|: either, you set today to some |
|||
# non-false value, then it is used: |
|||
#today = '' |
|||
# Else, today_fmt is used as the format for a strftime call. |
|||
#today_fmt = '%B %d, %Y' |
|||
|
|||
# List of patterns, relative to source directory, that match files and |
|||
# directories to ignore when looking for source files. |
|||
exclude_patterns = ['.build', 'release.rst'] |
|||
|
|||
# The reST default role (used for this markup: `text`) to use for all |
|||
# documents. |
|||
#default_role = None |
|||
|
|||
# If true, '()' will be appended to :func: etc. cross-reference text. |
|||
#add_function_parentheses = True |
|||
|
|||
# If true, the current module name will be prepended to all description |
|||
# unit titles (such as .. function::). |
|||
#add_module_names = True |
|||
|
|||
# If true, sectionauthor and moduleauthor directives will be shown in the |
|||
# output. They are ignored by default. |
|||
#show_authors = False |
|||
|
|||
# The name of the Pygments (syntax highlighting) style to use. |
|||
#pygments_style = 'monokai' |
|||
|
|||
# A list of ignored prefixes for module index sorting. |
|||
#modindex_common_prefix = [] |
|||
|
|||
# If true, keep warnings as "system message" paragraphs in the built documents. |
|||
#keep_warnings = False |
|||
|
|||
# If true, `todo` and `todoList` produce output, else they produce nothing. |
|||
todo_include_todos = False |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
# -- Options for HTML output ---------------------------------------------- |
|||
|
|||
# The theme to use for HTML and HTML Help pages. See the documentation for |
|||
# a list of builtin themes. |
|||
|
|||
on_rtd = os.environ.get('READTHEDOCS', None) == 'True' |
|||
|
|||
if not on_rtd: # only import and set the theme if we're building docs locally |
|||
import sphinx_rtd_theme |
|||
html_theme = 'sphinx_rtd_theme' |
|||
html_theme_path = [sphinx_rtd_theme.get_html_theme_path()] |
|||
|
|||
html_context = { |
|||
'css_files': [ |
|||
'_static/theme_overrides.css' |
|||
] |
|||
} |
|||
else: |
|||
html_context = { |
|||
'css_files': [ |
|||
'//media.readthedocs.org/css/sphinx_rtd_theme.css', |
|||
'//media.readthedocs.org/css/readthedocs-doc-embed.css', |
|||
'_static/theme_overrides.css' |
|||
] |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
# Theme options are theme-specific and customize the look and feel of a theme |
|||
# further. For a list of options available for each theme, see the |
|||
# documentation. |
|||
#html_theme_options = {} |
|||
|
|||
# Add any paths that contain custom themes here, relative to this directory. |
|||
#html_theme_path = [] |
|||
|
|||
# The name for this set of Sphinx documents. If None, it defaults to |
|||
# "<project> v<release> documentation". |
|||
#html_title = None |
|||
|
|||
# A shorter title for the navigation bar. Default is the same as html_title. |
|||
#html_short_title = None |
|||
|
|||
# The name of an image file (relative to this directory) to place at the top |
|||
# of the sidebar. |
|||
#html_logo = None |
|||
|
|||
# The name of an image file (within the static path) to use as favicon of the |
|||
# docs. This file should be a Windows icon file (.ico) being 16x16 or 32x32 |
|||
# pixels large. |
|||
#html_favicon = None |
|||
|
|||
# Add any paths that contain custom static files (such as style sheets) here, |
|||
# relative to this directory. They are copied after the builtin static files, |
|||
# so a file named "default.css" will overwrite the builtin "default.css". |
|||
html_static_path = ['_static'] |
|||
|
|||
# Add any extra paths that contain custom files (such as robots.txt or |
|||
# .htaccess) here, relative to this directory. These files are copied |
|||
# directly to the root of the documentation. |
|||
#html_extra_path = [] |
|||
|
|||
# If not '', a 'Last updated on:' timestamp is inserted at every page bottom, |
|||
# using the given strftime format. |
|||
#html_last_updated_fmt = '%b %d, %Y' |
|||
|
|||
# If true, SmartyPants will be used to convert quotes and dashes to |
|||
# typographically correct entities. |
|||
#html_use_smartypants = True |
|||
|
|||
# Custom sidebar templates, maps document names to template names. |
|||
#html_sidebars = {} |
|||
|
|||
# Additional templates that should be rendered to pages, maps page names to |
|||
# template names. |
|||
#html_additional_pages = {} |
|||
|
|||
# If false, no module index is generated. |
|||
#html_domain_indices = True |
|||
|
|||
# If false, no index is generated. |
|||
#html_use_index = True |
|||
|
|||
# If true, the index is split into individual pages for each letter. |
|||
#html_split_index = False |
|||
|
|||
# If true, links to the reST sources are added to the pages. |
|||
#html_show_sourcelink = True |
|||
|
|||
# If true, "Created using Sphinx" is shown in the HTML footer. Default is True. |
|||
#html_show_sphinx = True |
|||
|
|||
# If true, "(C) Copyright ..." is shown in the HTML footer. Default is True. |
|||
#html_show_copyright = True |
|||
|
|||
# If true, an OpenSearch description file will be output, and all pages will |
|||
# contain a <link> tag referring to it. The value of this option must be the |
|||
# base URL from which the finished HTML is served. |
|||
#html_use_opensearch = '' |
|||
|
|||
# This is the file name suffix for HTML files (e.g. ".xhtml"). |
|||
#html_file_suffix = None |
|||
|
|||
# Language to be used for generating the HTML full-text search index. |
|||
# Sphinx supports the following languages: |
|||
# 'da', 'de', 'en', 'es', 'fi', 'fr', 'h', 'it', 'ja' |
|||
# 'nl', 'no', 'pt', 'ro', 'r', 'sv', 'tr' |
|||
#html_search_language = 'en' |
|||
|
|||
# A dictionary with options for the search language support, empty by default. |
|||
# Now only 'ja' uses this config value |
|||
#html_search_options = {'type': 'default'} |
|||
|
|||
# The name of a javascript file (relative to the configuration directory) that |
|||
# implements a search results scorer. If empty, the default will be used. |
|||
#html_search_scorer = 'scorer.js' |
|||
|
|||
# Output file base name for HTML help builder. |
|||
htmlhelp_basename = 'pybind11doc' |
|||
|
|||
# -- Options for LaTeX output --------------------------------------------- |
|||
|
|||
latex_elements = { |
|||
# The paper size ('letterpaper' or 'a4paper'). |
|||
#'papersize': 'letterpaper', |
|||
|
|||
# The font size ('10pt', '11pt' or '12pt'). |
|||
#'pointsize': '10pt', |
|||
|
|||
# Additional stuff for the LaTeX preamble. |
|||
'preamble': '\DeclareUnicodeCharacter{00A0}{}', |
|||
|
|||
# Latex figure (float) alignment |
|||
#'figure_align': 'htbp', |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
# Grouping the document tree into LaTeX files. List of tuples |
|||
# (source start file, target name, title, |
|||
# author, documentclass [howto, manual, or own class]). |
|||
latex_documents = [ |
|||
(master_doc, 'pybind11.tex', 'pybind11 Documentation', |
|||
'Wenzel Jakob', 'manual'), |
|||
] |
|||
|
|||
# The name of an image file (relative to this directory) to place at the top of |
|||
# the title page. |
|||
# latex_logo = 'pybind11-logo.png' |
|||
|
|||
# For "manual" documents, if this is true, then toplevel headings are parts, |
|||
# not chapters. |
|||
#latex_use_parts = False |
|||
|
|||
# If true, show page references after internal links. |
|||
#latex_show_pagerefs = False |
|||
|
|||
# If true, show URL addresses after external links. |
|||
#latex_show_urls = False |
|||
|
|||
# Documents to append as an appendix to all manuals. |
|||
#latex_appendices = [] |
|||
|
|||
# If false, no module index is generated. |
|||
#latex_domain_indices = True |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
# -- Options for manual page output --------------------------------------- |
|||
|
|||
# One entry per manual page. List of tuples |
|||
# (source start file, name, description, authors, manual section). |
|||
man_pages = [ |
|||
(master_doc, 'pybind11', 'pybind11 Documentation', |
|||
[author], 1) |
|||
] |
|||
|
|||
# If true, show URL addresses after external links. |
|||
#man_show_urls = False |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
# -- Options for Texinfo output ------------------------------------------- |
|||
|
|||
# Grouping the document tree into Texinfo files. List of tuples |
|||
# (source start file, target name, title, author, |
|||
# dir menu entry, description, category) |
|||
texinfo_documents = [ |
|||
(master_doc, 'pybind11', 'pybind11 Documentation', |
|||
author, 'pybind11', 'One line description of project.', |
|||
'Miscellaneous'), |
|||
] |
|||
|
|||
# Documents to append as an appendix to all manuals. |
|||
#texinfo_appendices = [] |
|||
|
|||
# If false, no module index is generated. |
|||
#texinfo_domain_indices = True |
|||
|
|||
# How to display URL addresses: 'footnote', 'no', or 'inline'. |
|||
#texinfo_show_urls = 'footnote' |
|||
|
|||
# If true, do not generate a @detailmenu in the "Top" node's menu. |
|||
#texinfo_no_detailmenu = False |
|||
|
|||
primary_domain = 'cpp' |
|||
highlight_language = 'cpp' |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,251 @@ |
|||
Frequently asked questions |
|||
########################## |
|||
|
|||
"ImportError: dynamic module does not define init function" |
|||
=========================================================== |
|||
|
|||
1. Make sure that the name specified in ``pybind::module`` and |
|||
``PYBIND11_PLUGIN`` is consistent and identical to the filename of the |
|||
extension library. The latter should not contain any extra prefixes (e.g. |
|||
``test.so`` instead of ``libtest.so``). |
|||
|
|||
2. If the above did not fix your issue, then you are likely using an |
|||
incompatible version of Python (for instance, the extension library was |
|||
compiled against Python 2, while the interpreter is running on top of some |
|||
version of Python 3, or vice versa) |
|||
|
|||
"Symbol not found: ``__Py_ZeroStruct`` / ``_PyInstanceMethod_Type``" |
|||
======================================================================== |
|||
|
|||
See item 2 of the first answer. |
|||
|
|||
"SystemError: dynamic module not initialized properly" |
|||
====================================================== |
|||
|
|||
See item 2 of the first answer. |
|||
|
|||
The Python interpreter immediately crashes when importing my module |
|||
=================================================================== |
|||
|
|||
See item 2 of the first answer. |
|||
|
|||
CMake doesn't detect the right Python version |
|||
============================================= |
|||
|
|||
The CMake-based build system will try to automatically detect the installed |
|||
version of Python and link against that. When this fails, or when there are |
|||
multiple versions of Python and it finds the wrong one, delete |
|||
``CMakeCache.txt`` and then invoke CMake as follows: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: bash |
|||
|
|||
cmake -DPYTHON_EXECUTABLE:FILEPATH=<path-to-python-executable> . |
|||
|
|||
Limitations involving reference arguments |
|||
========================================= |
|||
|
|||
In C++, it's fairly common to pass arguments using mutable references or |
|||
mutable pointers, which allows both read and write access to the value |
|||
supplied by the caller. This is sometimes done for efficiency reasons, or to |
|||
realize functions that have multiple return values. Here are two very basic |
|||
examples: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
void increment(int &i) { i++; } |
|||
void increment_ptr(int *i) { (*i)++; } |
|||
|
|||
In Python, all arguments are passed by reference, so there is no general |
|||
issue in binding such code from Python. |
|||
|
|||
However, certain basic Python types (like ``str``, ``int``, ``bool``, |
|||
``float``, etc.) are **immutable**. This means that the following attempt |
|||
to port the function to Python doesn't have the same effect on the value |
|||
provided by the caller -- in fact, it does nothing at all. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: python |
|||
|
|||
def increment(i): |
|||
i += 1 # nope.. |
|||
|
|||
pybind11 is also affected by such language-level conventions, which means that |
|||
binding ``increment`` or ``increment_ptr`` will also create Python functions |
|||
that don't modify their arguments. |
|||
|
|||
Although inconvenient, one workaround is to encapsulate the immutable types in |
|||
a custom type that does allow modifications. |
|||
|
|||
An other alternative involves binding a small wrapper lambda function that |
|||
returns a tuple with all output arguments (see the remainder of the |
|||
documentation for examples on binding lambda functions). An example: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
int foo(int &i) { i++; return 123; } |
|||
|
|||
and the binding code |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
m.def("foo", [](int i) { int rv = foo(i); return std::make_tuple(rv, i); }); |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
How can I reduce the build time? |
|||
================================ |
|||
|
|||
It's good practice to split binding code over multiple files, as in the |
|||
following example: |
|||
|
|||
:file:`example.cpp`: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
void init_ex1(py::module &); |
|||
void init_ex2(py::module &); |
|||
/* ... */ |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_PLUGIN(example) { |
|||
py::module m("example", "pybind example plugin"); |
|||
|
|||
init_ex1(m); |
|||
init_ex2(m); |
|||
/* ... */ |
|||
|
|||
return m.ptr(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
:file:`ex1.cpp`: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
void init_ex1(py::module &m) { |
|||
m.def("add", [](int a, int b) { return a + b; }); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
:file:`ex2.cpp`: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
void init_ex1(py::module &m) { |
|||
m.def("sub", [](int a, int b) { return a - b; }); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
:command:`python`: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: pycon |
|||
|
|||
>>> import example |
|||
>>> example.add(1, 2) |
|||
3 |
|||
>>> example.sub(1, 1) |
|||
0 |
|||
|
|||
As shown above, the various ``init_ex`` functions should be contained in |
|||
separate files that can be compiled independently from one another, and then |
|||
linked together into the same final shared object. Following this approach |
|||
will: |
|||
|
|||
1. reduce memory requirements per compilation unit. |
|||
|
|||
2. enable parallel builds (if desired). |
|||
|
|||
3. allow for faster incremental builds. For instance, when a single class |
|||
definition is changed, only a subset of the binding code will generally need |
|||
to be recompiled. |
|||
|
|||
"recursive template instantiation exceeded maximum depth of 256" |
|||
================================================================ |
|||
|
|||
If you receive an error about excessive recursive template evaluation, try |
|||
specifying a larger value, e.g. ``-ftemplate-depth=1024`` on GCC/Clang. The |
|||
culprit is generally the generation of function signatures at compile time |
|||
using C++14 template metaprogramming. |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
How can I create smaller binaries? |
|||
================================== |
|||
|
|||
To do its job, pybind11 extensively relies on a programming technique known as |
|||
*template metaprogramming*, which is a way of performing computation at compile |
|||
time using type information. Template metaprogamming usually instantiates code |
|||
involving significant numbers of deeply nested types that are either completely |
|||
removed or reduced to just a few instructions during the compiler's optimization |
|||
phase. However, due to the nested nature of these types, the resulting symbol |
|||
names in the compiled extension library can be extremely long. For instance, |
|||
the included test suite contains the following symbol: |
|||
|
|||
.. only:: html |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: none |
|||
|
|||
__ZN8pybind1112cpp_functionC1Iv8Example2JRNSt3__16vectorINS3_12basic_stringIwNS3_11char_traitsIwEENS3_9allocatorIwEEEENS8_ISA_EEEEEJNS_4nameENS_7siblingENS_9is_methodEA28_cEEEMT0_FT_DpT1_EDpRKT2_ |
|||
|
|||
.. only:: not html |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
__ZN8pybind1112cpp_functionC1Iv8Example2JRNSt3__16vectorINS3_12basic_stringIwNS3_11char_traitsIwEENS3_9allocatorIwEEEENS8_ISA_EEEEEJNS_4nameENS_7siblingENS_9is_methodEA28_cEEEMT0_FT_DpT1_EDpRKT2_ |
|||
|
|||
which is the mangled form of the following function type: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
pybind11::cpp_function::cpp_function<void, Example2, std::__1::vector<std::__1::basic_string<wchar_t, std::__1::char_traits<wchar_t>, std::__1::allocator<wchar_t> >, std::__1::allocator<std::__1::basic_string<wchar_t, std::__1::char_traits<wchar_t>, std::__1::allocator<wchar_t> > > >&, pybind11::name, pybind11::sibling, pybind11::is_method, char [28]>(void (Example2::*)(std::__1::vector<std::__1::basic_string<wchar_t, std::__1::char_traits<wchar_t>, std::__1::allocator<wchar_t> >, std::__1::allocator<std::__1::basic_string<wchar_t, std::__1::char_traits<wchar_t>, std::__1::allocator<wchar_t> > > >&), pybind11::name const&, pybind11::sibling const&, pybind11::is_method const&, char const (&) [28]) |
|||
|
|||
The memory needed to store just the mangled name of this function (196 bytes) |
|||
is larger than the actual piece of code (111 bytes) it represents! On the other |
|||
hand, it's silly to even give this function a name -- after all, it's just a |
|||
tiny cog in a bigger piece of machinery that is not exposed to the outside |
|||
world. So we'll generally only want to export symbols for those functions which |
|||
are actually called from the outside. |
|||
|
|||
This can be achieved by specifying the parameter ``-fvisibility=hidden`` to GCC |
|||
and Clang, which sets the default symbol visibility to *hidden*. It's best to |
|||
do this only for release builds, since the symbol names can be helpful in |
|||
debugging sessions. On Visual Studio, symbols are already hidden by default, so |
|||
nothing needs to be done there. Needless to say, this has a tremendous impact |
|||
on the final binary size of the resulting extension library. |
|||
|
|||
Another aspect that can require a fair bit of code are function signature |
|||
descriptions. pybind11 automatically generates human-readable function |
|||
signatures for docstrings, e.g.: |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: none |
|||
|
|||
| __init__(...) |
|||
| __init__(*args, **kwargs) |
|||
| Overloaded function. |
|||
| |
|||
| 1. __init__(example.Example1) -> NoneType |
|||
| |
|||
| Docstring for overload #1 goes here |
|||
| |
|||
| 2. __init__(example.Example1, int) -> NoneType |
|||
| |
|||
| Docstring for overload #2 goes here |
|||
| |
|||
| 3. __init__(example.Example1, example.Example1) -> NoneType |
|||
| |
|||
| Docstring for overload #3 goes here |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
In C++11 mode, these are generated at run time using string concatenation, |
|||
which can amount to 10-20% of the size of the resulting binary. If you can, |
|||
enable C++14 language features (using ``-std=c++14`` for GCC/Clang), in which |
|||
case signatures are efficiently pre-generated at compile time. Unfortunately, |
|||
Visual Studio's C++14 support (``constexpr``) is not good enough as of April |
|||
2016, so it always uses the more expensive run-time approach. |
|||
|
|||
Working with ancient Visual Studio 2009 builds on Windows |
|||
========================================================= |
|||
|
|||
The official Windows distributions of Python are compiled using truly |
|||
ancient versions of Visual Studio that lack good C++11 support. Some users |
|||
implicitly assume that it would be impossible to load a plugin built with |
|||
Visual Studio 2015 into a Python distribution that was compiled using Visual |
|||
Studio 2009. However, no such issue exists: it's perfectly legitimate to |
|||
interface DLLs that are built with different compilers and/or C libraries. |
|||
Common gotchas to watch out for involve not ``free()``-ing memory region |
|||
that that were ``malloc()``-ed in another shared library, using data |
|||
structures with incompatible ABIs, and so on. pybind11 is very careful not |
|||
to make these types of mistakes. |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@ |
|||
.. only: not latex |
|||
|
|||
.. image:: pybind11-logo.png |
|||
|
|||
pybind11 --- Seamless operability between C++11 and Python |
|||
========================================================== |
|||
|
|||
.. only: not latex |
|||
|
|||
Contents: |
|||
|
|||
.. toctree:: |
|||
:maxdepth: 1 |
|||
|
|||
intro |
|||
changelog |
|||
|
|||
.. toctree:: |
|||
:caption: The Basics |
|||
:maxdepth: 2 |
|||
|
|||
basics |
|||
classes |
|||
compiling |
|||
|
|||
.. toctree:: |
|||
:caption: Advanced Topics |
|||
:maxdepth: 2 |
|||
|
|||
advanced/functions |
|||
advanced/classes |
|||
advanced/exceptions |
|||
advanced/smart_ptrs |
|||
advanced/cast/index |
|||
advanced/pycpp/index |
|||
advanced/misc |
|||
|
|||
.. toctree:: |
|||
:caption: Extra Information |
|||
:maxdepth: 1 |
|||
|
|||
faq |
|||
benchmark |
|||
limitations |
|||
reference |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,93 @@ |
|||
.. image:: pybind11-logo.png |
|||
|
|||
About this project |
|||
================== |
|||
**pybind11** is a lightweight header-only library that exposes C++ types in Python |
|||
and vice versa, mainly to create Python bindings of existing C++ code. Its |
|||
goals and syntax are similar to the excellent `Boost.Python`_ library by David |
|||
Abrahams: to minimize boilerplate code in traditional extension modules by |
|||
inferring type information using compile-time introspection. |
|||
|
|||
.. _Boost.Python: http://www.boost.org/doc/libs/release/libs/python/doc/index.html |
|||
|
|||
The main issue with Boost.Python—and the reason for creating such a similar |
|||
project—is Boost. Boost is an enormously large and complex suite of utility |
|||
libraries that works with almost every C++ compiler in existence. This |
|||
compatibility has its cost: arcane template tricks and workarounds are |
|||
necessary to support the oldest and buggiest of compiler specimens. Now that |
|||
C++11-compatible compilers are widely available, this heavy machinery has |
|||
become an excessively large and unnecessary dependency. |
|||
|
|||
Think of this library as a tiny self-contained version of Boost.Python with |
|||
everything stripped away that isn't relevant for binding generation. Without |
|||
comments, the core header files only require ~2.5K lines of code and depend on |
|||
Python (2.7 or 3.x) and the C++ standard library. This compact implementation |
|||
was possible thanks to some of the new C++11 language features (specifically: |
|||
tuples, lambda functions and variadic templates). Since its creation, this |
|||
library has grown beyond Boost.Python in many ways, leading to dramatically |
|||
simpler binding code in many common situations. |
|||
|
|||
Core features |
|||
************* |
|||
The following core C++ features can be mapped to Python |
|||
|
|||
- Functions accepting and returning custom data structures per value, reference, or pointer |
|||
- Instance methods and static methods |
|||
- Overloaded functions |
|||
- Instance attributes and static attributes |
|||
- Arbitrary exception types |
|||
- Enumerations |
|||
- Callbacks |
|||
- Iterators and ranges |
|||
- Custom operators |
|||
- Single and multiple inheritance |
|||
- STL data structures |
|||
- Iterators and ranges |
|||
- Smart pointers with reference counting like ``std::shared_ptr`` |
|||
- Internal references with correct reference counting |
|||
- C++ classes with virtual (and pure virtual) methods can be extended in Python |
|||
|
|||
Goodies |
|||
******* |
|||
In addition to the core functionality, pybind11 provides some extra goodies: |
|||
|
|||
- It is possible to bind C++11 lambda functions with captured variables. The |
|||
lambda capture data is stored inside the resulting Python function object. |
|||
|
|||
- pybind11 uses C++11 move constructors and move assignment operators whenever |
|||
possible to efficiently transfer custom data types. |
|||
|
|||
- It's easy to expose the internal storage of custom data types through |
|||
Pythons' buffer protocols. This is handy e.g. for fast conversion between |
|||
C++ matrix classes like Eigen and NumPy without expensive copy operations. |
|||
|
|||
- pybind11 can automatically vectorize functions so that they are transparently |
|||
applied to all entries of one or more NumPy array arguments. |
|||
|
|||
- Python's slice-based access and assignment operations can be supported with |
|||
just a few lines of code. |
|||
|
|||
- Everything is contained in just a few header files; there is no need to link |
|||
against any additional libraries. |
|||
|
|||
- Binaries are generally smaller by a factor of at least 2 compared to |
|||
equivalent bindings generated by Boost.Python. A recent pybind11 conversion |
|||
of `PyRosetta`_, an enormous Boost.Python binding project, reported a binary |
|||
size reduction of **5.4x** and compile time reduction by **5.8x**. |
|||
|
|||
- When supported by the compiler, two new C++14 features (relaxed constexpr and |
|||
return value deduction) are used to precompute function signatures at compile |
|||
time, leading to smaller binaries. |
|||
|
|||
- With little extra effort, C++ types can be pickled and unpickled similar to |
|||
regular Python objects. |
|||
|
|||
.. _PyRosetta: http://graylab.jhu.edu/RosettaCon2016/PyRosetta-4.pdf |
|||
|
|||
Supported compilers |
|||
******************* |
|||
|
|||
1. Clang/LLVM (any non-ancient version with C++11 support) |
|||
2. GCC (any non-ancient version with C++11 support) |
|||
3. Microsoft Visual Studio 2015 or newer |
|||
4. Intel C++ compiler v15 or newer |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,20 @@ |
|||
Limitations |
|||
########### |
|||
|
|||
pybind11 strives to be a general solution to binding generation, but it also has |
|||
certain limitations: |
|||
|
|||
- pybind11 casts away ``const``-ness in function arguments and return values. |
|||
This is in line with the Python language, which has no concept of ``const`` |
|||
values. This means that some additional care is needed to avoid bugs that |
|||
would be caught by the type checker in a traditional C++ program. |
|||
|
|||
- The NumPy interface ``pybind11::array`` greatly simplifies accessing |
|||
numerical data from C++ (and vice versa), but it's not a full-blown array |
|||
class like ``Eigen::Array`` or ``boost.multi_array``. |
|||
|
|||
These features could be implemented but would lead to a significant increase in |
|||
complexity. I've decided to draw the line here to keep this project simple and |
|||
compact. Users who absolutely require these features are encouraged to fork |
|||
pybind11. |
|||
|
|||
|
After 
Width: 1131 | Height: 336 | Size: 57 KiB |
|
After 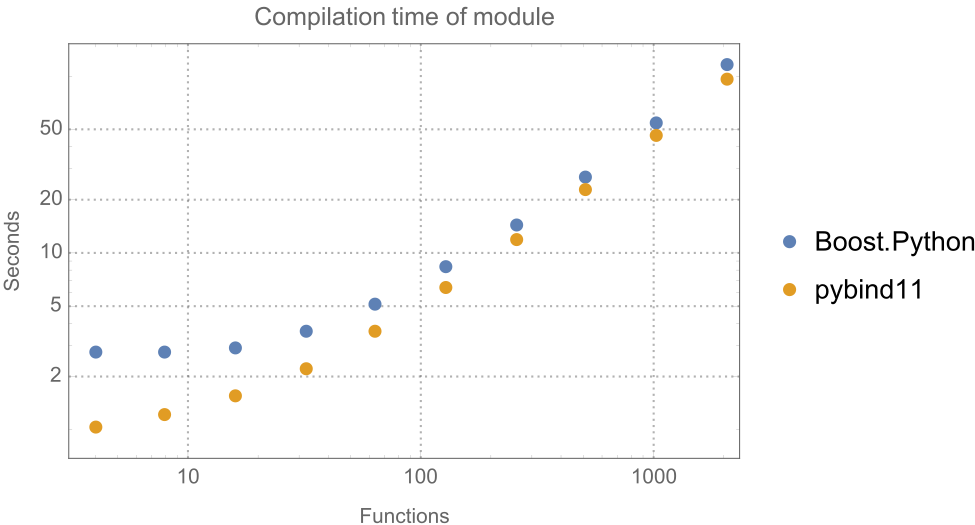
Width: 975 | Height: 525 | Size: 44 KiB |
@ -0,0 +1,427 @@ |
|||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> |
|||
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink" width="468pt" height="252pt" viewBox="0 0 468 252" version="1.1"> |
|||
<defs> |
|||
<g> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-0"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d=""/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-1"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 3.726562 0 L 2.847656 0 L 2.847656 -5.601562 C 2.636719 -5.398438 2.359375 -5.195312 2.015625 -4.996094 C 1.671875 -4.792969 1.363281 -4.640625 1.089844 -4.539062 L 1.089844 -5.390625 C 1.582031 -5.621094 2.011719 -5.902344 2.378906 -6.230469 C 2.746094 -6.558594 3.007812 -6.878906 3.160156 -7.1875 L 3.726562 -7.1875 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-2"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.414062 -3.53125 C 0.414062 -4.375 0.503906 -5.058594 0.675781 -5.574219 C 0.851562 -6.089844 1.109375 -6.488281 1.453125 -6.765625 C 1.796875 -7.046875 2.226562 -7.1875 2.75 -7.1875 C 3.132812 -7.1875 3.46875 -7.109375 3.757812 -6.957031 C 4.046875 -6.800781 4.289062 -6.578125 4.476562 -6.285156 C 4.664062 -5.996094 4.8125 -5.640625 4.921875 -5.222656 C 5.03125 -4.804688 5.082031 -4.238281 5.082031 -3.53125 C 5.082031 -2.691406 4.996094 -2.011719 4.824219 -1.496094 C 4.652344 -0.980469 4.394531 -0.582031 4.050781 -0.300781 C 3.707031 -0.0195312 3.273438 0.121094 2.75 0.121094 C 2.058594 0.121094 1.515625 -0.125 1.125 -0.621094 C 0.652344 -1.214844 0.414062 -2.1875 0.414062 -3.53125 Z M 1.320312 -3.53125 C 1.320312 -2.355469 1.457031 -1.574219 1.730469 -1.183594 C 2.007812 -0.796875 2.34375 -0.601562 2.75 -0.601562 C 3.152344 -0.601562 3.492188 -0.796875 3.765625 -1.1875 C 4.042969 -1.578125 4.179688 -2.359375 4.179688 -3.53125 C 4.179688 -4.710938 4.042969 -5.492188 3.765625 -5.878906 C 3.492188 -6.265625 3.148438 -6.460938 2.738281 -6.460938 C 2.335938 -6.460938 2.011719 -6.289062 1.773438 -5.945312 C 1.46875 -5.511719 1.320312 -4.707031 1.320312 -3.53125 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-3"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 5.035156 -0.84375 L 5.035156 0 L 0.304688 0 C 0.296875 -0.210938 0.332031 -0.414062 0.40625 -0.609375 C 0.527344 -0.933594 0.71875 -1.25 0.984375 -1.5625 C 1.25 -1.875 1.632812 -2.234375 2.132812 -2.648438 C 2.910156 -3.285156 3.4375 -3.789062 3.710938 -4.164062 C 3.984375 -4.535156 4.121094 -4.886719 4.121094 -5.21875 C 4.121094 -5.566406 3.996094 -5.863281 3.746094 -6.101562 C 3.5 -6.339844 3.171875 -6.460938 2.773438 -6.460938 C 2.351562 -6.460938 2.011719 -6.332031 1.757812 -6.078125 C 1.503906 -5.824219 1.375 -5.472656 1.371094 -5.023438 L 0.46875 -5.117188 C 0.53125 -5.789062 0.761719 -6.304688 1.167969 -6.65625 C 1.570312 -7.011719 2.113281 -7.1875 2.792969 -7.1875 C 3.480469 -7.1875 4.023438 -6.996094 4.421875 -6.617188 C 4.824219 -6.234375 5.023438 -5.761719 5.023438 -5.199219 C 5.023438 -4.914062 4.964844 -4.632812 4.847656 -4.355469 C 4.730469 -4.078125 4.535156 -3.789062 4.265625 -3.480469 C 3.992188 -3.175781 3.542969 -2.753906 2.910156 -2.222656 C 2.382812 -1.78125 2.042969 -1.480469 1.894531 -1.320312 C 1.746094 -1.164062 1.621094 -1.003906 1.523438 -0.84375 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-4"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.414062 -1.875 L 1.335938 -1.953125 C 1.40625 -1.503906 1.566406 -1.167969 1.8125 -0.941406 C 2.0625 -0.714844 2.363281 -0.601562 2.714844 -0.601562 C 3.136719 -0.601562 3.496094 -0.761719 3.789062 -1.078125 C 4.082031 -1.398438 4.226562 -1.820312 4.226562 -2.347656 C 4.226562 -2.851562 4.085938 -3.246094 3.804688 -3.535156 C 3.523438 -3.824219 3.15625 -3.96875 2.699219 -3.96875 C 2.417969 -3.96875 2.160156 -3.90625 1.933594 -3.777344 C 1.707031 -3.648438 1.527344 -3.480469 1.398438 -3.277344 L 0.570312 -3.382812 L 1.265625 -7.0625 L 4.824219 -7.0625 L 4.824219 -6.21875 L 1.96875 -6.21875 L 1.582031 -4.296875 C 2.011719 -4.597656 2.460938 -4.746094 2.933594 -4.746094 C 3.558594 -4.746094 4.085938 -4.53125 4.515625 -4.097656 C 4.945312 -3.664062 5.160156 -3.105469 5.160156 -2.425781 C 5.160156 -1.777344 4.972656 -1.21875 4.59375 -0.746094 C 4.136719 -0.167969 3.507812 0.121094 2.714844 0.121094 C 2.0625 0.121094 1.53125 -0.0585938 1.121094 -0.425781 C 0.710938 -0.789062 0.472656 -1.273438 0.414062 -1.875 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-5"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.820312 0 L 0.820312 -7.15625 L 5.648438 -7.15625 L 5.648438 -6.3125 L 1.765625 -6.3125 L 1.765625 -4.097656 L 5.125 -4.097656 L 5.125 -3.25 L 1.765625 -3.25 L 1.765625 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-6"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 4.058594 0 L 4.058594 -0.761719 C 3.65625 -0.175781 3.105469 0.117188 2.414062 0.117188 C 2.105469 0.117188 1.820312 0.0585938 1.554688 -0.0585938 C 1.289062 -0.175781 1.09375 -0.324219 0.964844 -0.5 C 0.835938 -0.679688 0.746094 -0.894531 0.695312 -1.152344 C 0.65625 -1.324219 0.640625 -1.597656 0.640625 -1.972656 L 0.640625 -5.1875 L 1.519531 -5.1875 L 1.519531 -2.308594 C 1.519531 -1.851562 1.535156 -1.542969 1.570312 -1.382812 C 1.625 -1.152344 1.746094 -0.96875 1.921875 -0.835938 C 2.101562 -0.703125 2.324219 -0.640625 2.585938 -0.640625 C 2.851562 -0.640625 3.097656 -0.707031 3.328125 -0.84375 C 3.5625 -0.976562 3.726562 -1.160156 3.820312 -1.394531 C 3.917969 -1.625 3.964844 -1.964844 3.964844 -2.40625 L 3.964844 -5.1875 L 4.84375 -5.1875 L 4.84375 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-7"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.660156 0 L 0.660156 -5.1875 L 1.449219 -5.1875 L 1.449219 -4.449219 C 1.832031 -5.019531 2.382812 -5.304688 3.101562 -5.304688 C 3.414062 -5.304688 3.699219 -5.246094 3.960938 -5.132812 C 4.222656 -5.023438 4.421875 -4.875 4.550781 -4.691406 C 4.679688 -4.507812 4.773438 -4.292969 4.824219 -4.042969 C 4.855469 -3.878906 4.875 -3.59375 4.875 -3.1875 L 4.875 0 L 3.992188 0 L 3.992188 -3.15625 C 3.992188 -3.511719 3.960938 -3.78125 3.890625 -3.957031 C 3.824219 -4.132812 3.703125 -4.277344 3.527344 -4.382812 C 3.351562 -4.488281 3.148438 -4.539062 2.914062 -4.539062 C 2.539062 -4.539062 2.21875 -4.421875 1.945312 -4.183594 C 1.671875 -3.945312 1.539062 -3.496094 1.539062 -2.832031 L 1.539062 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-8"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 4.042969 -1.898438 L 4.90625 -1.789062 C 4.8125 -1.191406 4.570312 -0.726562 4.183594 -0.386719 C 3.792969 -0.0507812 3.316406 0.117188 2.75 0.117188 C 2.039062 0.117188 1.46875 -0.113281 1.039062 -0.578125 C 0.605469 -1.042969 0.390625 -1.707031 0.390625 -2.574219 C 0.390625 -3.132812 0.484375 -3.625 0.667969 -4.042969 C 0.855469 -4.460938 1.136719 -4.777344 1.515625 -4.988281 C 1.894531 -5.199219 2.308594 -5.304688 2.753906 -5.304688 C 3.316406 -5.304688 3.777344 -5.160156 4.136719 -4.875 C 4.492188 -4.589844 4.722656 -4.1875 4.824219 -3.664062 L 3.96875 -3.53125 C 3.886719 -3.878906 3.746094 -4.140625 3.539062 -4.316406 C 3.332031 -4.492188 3.082031 -4.578125 2.789062 -4.578125 C 2.34375 -4.578125 1.984375 -4.421875 1.710938 -4.105469 C 1.433594 -3.789062 1.292969 -3.285156 1.292969 -2.597656 C 1.292969 -1.902344 1.425781 -1.394531 1.695312 -1.078125 C 1.960938 -0.761719 2.308594 -0.605469 2.738281 -0.605469 C 3.085938 -0.605469 3.371094 -0.710938 3.601562 -0.921875 C 3.835938 -1.132812 3.980469 -1.460938 4.042969 -1.898438 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-9"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 2.578125 -0.785156 L 2.703125 -0.0078125 C 2.457031 0.0429688 2.234375 0.0703125 2.039062 0.0703125 C 1.722656 0.0703125 1.476562 0.0195312 1.296875 -0.0820312 C 1.121094 -0.183594 1 -0.316406 0.929688 -0.480469 C 0.855469 -0.644531 0.820312 -0.992188 0.820312 -1.519531 L 0.820312 -4.5 L 0.175781 -4.5 L 0.175781 -5.1875 L 0.820312 -5.1875 L 0.820312 -6.46875 L 1.695312 -6.996094 L 1.695312 -5.1875 L 2.578125 -5.1875 L 2.578125 -4.5 L 1.695312 -4.5 L 1.695312 -1.46875 C 1.695312 -1.21875 1.710938 -1.058594 1.742188 -0.984375 C 1.773438 -0.914062 1.820312 -0.859375 1.890625 -0.816406 C 1.960938 -0.773438 2.0625 -0.75 2.191406 -0.75 C 2.289062 -0.75 2.417969 -0.761719 2.578125 -0.785156 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-10"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.664062 -6.148438 L 0.664062 -7.15625 L 1.542969 -7.15625 L 1.542969 -6.148438 Z M 0.664062 0 L 0.664062 -5.1875 L 1.542969 -5.1875 L 1.542969 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-11"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.332031 -2.59375 C 0.332031 -3.554688 0.597656 -4.265625 1.132812 -4.726562 C 1.578125 -5.109375 2.121094 -5.304688 2.765625 -5.304688 C 3.476562 -5.304688 4.058594 -5.070312 4.511719 -4.601562 C 4.964844 -4.132812 5.191406 -3.488281 5.191406 -2.664062 C 5.191406 -2 5.089844 -1.472656 4.890625 -1.089844 C 4.691406 -0.707031 4.398438 -0.410156 4.015625 -0.199219 C 3.632812 0.0117188 3.214844 0.117188 2.765625 0.117188 C 2.039062 0.117188 1.449219 -0.117188 1.003906 -0.582031 C 0.554688 -1.046875 0.332031 -1.71875 0.332031 -2.59375 Z M 1.234375 -2.59375 C 1.234375 -1.929688 1.378906 -1.429688 1.671875 -1.101562 C 1.960938 -0.769531 2.324219 -0.605469 2.765625 -0.605469 C 3.199219 -0.605469 3.5625 -0.773438 3.851562 -1.101562 C 4.140625 -1.433594 4.289062 -1.941406 4.289062 -2.621094 C 4.289062 -3.261719 4.140625 -3.75 3.851562 -4.078125 C 3.558594 -4.410156 3.195312 -4.574219 2.765625 -4.574219 C 2.324219 -4.574219 1.960938 -4.410156 1.671875 -4.082031 C 1.382812 -3.753906 1.234375 -3.257812 1.234375 -2.59375 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-12"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.308594 -1.546875 L 1.175781 -1.683594 C 1.226562 -1.335938 1.363281 -1.070312 1.585938 -0.882812 C 1.808594 -0.699219 2.117188 -0.605469 2.519531 -0.605469 C 2.921875 -0.605469 3.222656 -0.6875 3.417969 -0.851562 C 3.613281 -1.015625 3.710938 -1.210938 3.710938 -1.429688 C 3.710938 -1.628906 3.625 -1.785156 3.453125 -1.898438 C 3.332031 -1.976562 3.03125 -2.078125 2.554688 -2.195312 C 1.910156 -2.359375 1.460938 -2.5 1.214844 -2.621094 C 0.964844 -2.738281 0.777344 -2.902344 0.648438 -3.113281 C 0.519531 -3.324219 0.453125 -3.554688 0.453125 -3.808594 C 0.453125 -4.039062 0.507812 -4.253906 0.613281 -4.449219 C 0.71875 -4.648438 0.863281 -4.8125 1.046875 -4.941406 C 1.183594 -5.042969 1.367188 -5.128906 1.605469 -5.199219 C 1.839844 -5.269531 2.09375 -5.304688 2.363281 -5.304688 C 2.769531 -5.304688 3.128906 -5.242188 3.433594 -5.125 C 3.742188 -5.007812 3.96875 -4.851562 4.117188 -4.652344 C 4.261719 -4.453125 4.363281 -4.183594 4.417969 -3.847656 L 3.558594 -3.730469 C 3.519531 -3.996094 3.40625 -4.207031 3.21875 -4.355469 C 3.03125 -4.503906 2.769531 -4.578125 2.425781 -4.578125 C 2.023438 -4.578125 1.734375 -4.511719 1.5625 -4.378906 C 1.390625 -4.246094 1.304688 -4.089844 1.304688 -3.910156 C 1.304688 -3.796875 1.339844 -3.695312 1.410156 -3.601562 C 1.484375 -3.507812 1.59375 -3.429688 1.75 -3.367188 C 1.835938 -3.335938 2.09375 -3.261719 2.523438 -3.144531 C 3.144531 -2.976562 3.578125 -2.84375 3.824219 -2.738281 C 4.070312 -2.632812 4.265625 -2.476562 4.40625 -2.273438 C 4.546875 -2.074219 4.613281 -1.824219 4.613281 -1.523438 C 4.613281 -1.230469 4.527344 -0.953125 4.359375 -0.695312 C 4.1875 -0.4375 3.941406 -0.238281 3.617188 -0.09375 C 3.296875 0.046875 2.929688 0.117188 2.523438 0.117188 C 1.851562 0.117188 1.335938 -0.0234375 0.984375 -0.304688 C 0.632812 -0.582031 0.40625 -0.996094 0.308594 -1.546875 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph1-0"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d=""/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph1-1"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M -2.300781 -0.449219 L -2.378906 -1.34375 C -2.019531 -1.386719 -1.726562 -1.484375 -1.496094 -1.636719 C -1.265625 -1.792969 -1.082031 -2.03125 -0.941406 -2.359375 C -0.796875 -2.683594 -0.726562 -3.050781 -0.726562 -3.457031 C -0.726562 -3.820312 -0.78125 -4.136719 -0.890625 -4.414062 C -0.996094 -4.691406 -1.144531 -4.898438 -1.332031 -5.03125 C -1.519531 -5.167969 -1.722656 -5.234375 -1.945312 -5.234375 C -2.167969 -5.234375 -2.363281 -5.167969 -2.53125 -5.039062 C -2.699219 -4.910156 -2.839844 -4.695312 -2.953125 -4.394531 C -3.027344 -4.203125 -3.144531 -3.777344 -3.304688 -3.121094 C -3.460938 -2.460938 -3.609375 -2 -3.75 -1.738281 C -3.929688 -1.398438 -4.152344 -1.140625 -4.417969 -0.972656 C -4.683594 -0.804688 -4.980469 -0.722656 -5.308594 -0.722656 C -5.667969 -0.722656 -6.007812 -0.824219 -6.320312 -1.03125 C -6.632812 -1.234375 -6.875 -1.535156 -7.035156 -1.929688 C -7.199219 -2.324219 -7.28125 -2.761719 -7.28125 -3.242188 C -7.28125 -3.773438 -7.195312 -4.242188 -7.023438 -4.644531 C -6.851562 -5.050781 -6.601562 -5.363281 -6.269531 -5.582031 C -5.9375 -5.800781 -5.5625 -5.917969 -5.140625 -5.933594 L -5.074219 -5.023438 C -5.527344 -4.976562 -5.867188 -4.808594 -6.097656 -4.527344 C -6.328125 -4.246094 -6.445312 -3.832031 -6.445312 -3.28125 C -6.445312 -2.707031 -6.339844 -2.289062 -6.128906 -2.027344 C -5.921875 -1.765625 -5.667969 -1.636719 -5.371094 -1.636719 C -5.113281 -1.636719 -4.902344 -1.726562 -4.734375 -1.914062 C -4.570312 -2.097656 -4.398438 -2.574219 -4.226562 -3.34375 C -4.050781 -4.113281 -3.898438 -4.640625 -3.769531 -4.925781 C -3.578125 -5.34375 -3.335938 -5.652344 -3.039062 -5.851562 C -2.746094 -6.046875 -2.40625 -6.148438 -2.023438 -6.148438 C -1.640625 -6.148438 -1.28125 -6.039062 -0.945312 -5.820312 C -0.609375 -5.601562 -0.347656 -5.289062 -0.160156 -4.878906 C 0.0273438 -4.472656 0.121094 -4.011719 0.121094 -3.5 C 0.121094 -2.851562 0.0273438 -2.308594 -0.160156 -1.871094 C -0.351562 -1.433594 -0.632812 -1.089844 -1.011719 -0.84375 C -1.390625 -0.59375 -1.820312 -0.460938 -2.300781 -0.449219 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph1-2"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M -1.671875 -4.210938 L -1.558594 -5.117188 C -1.027344 -4.972656 -0.617188 -4.707031 -0.320312 -4.320312 C -0.0273438 -3.933594 0.117188 -3.4375 0.117188 -2.835938 C 0.117188 -2.078125 -0.117188 -1.476562 -0.582031 -1.03125 C -1.050781 -0.585938 -1.707031 -0.367188 -2.546875 -0.367188 C -3.421875 -0.367188 -4.097656 -0.589844 -4.578125 -1.039062 C -5.0625 -1.488281 -5.304688 -2.070312 -5.304688 -2.789062 C -5.304688 -3.480469 -5.066406 -4.046875 -4.59375 -4.488281 C -4.121094 -4.925781 -3.457031 -5.148438 -2.601562 -5.148438 C -2.550781 -5.148438 -2.472656 -5.144531 -2.367188 -5.140625 L -2.367188 -1.273438 C -1.796875 -1.304688 -1.363281 -1.46875 -1.058594 -1.757812 C -0.757812 -2.046875 -0.605469 -2.410156 -0.605469 -2.84375 C -0.605469 -3.164062 -0.691406 -3.4375 -0.859375 -3.667969 C -1.027344 -3.894531 -1.296875 -4.074219 -1.671875 -4.210938 Z M -3.089844 -1.324219 L -3.089844 -4.21875 C -3.527344 -4.179688 -3.855469 -4.070312 -4.070312 -3.886719 C -4.410156 -3.605469 -4.578125 -3.242188 -4.578125 -2.796875 C -4.578125 -2.394531 -4.445312 -2.054688 -4.175781 -1.78125 C -3.90625 -1.503906 -3.542969 -1.351562 -3.089844 -1.324219 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph1-3"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M -1.898438 -4.042969 L -1.789062 -4.90625 C -1.191406 -4.8125 -0.726562 -4.570312 -0.386719 -4.183594 C -0.0507812 -3.792969 0.117188 -3.316406 0.117188 -2.75 C 0.117188 -2.039062 -0.113281 -1.46875 -0.578125 -1.039062 C -1.042969 -0.605469 -1.707031 -0.390625 -2.574219 -0.390625 C -3.132812 -0.390625 -3.625 -0.484375 -4.042969 -0.667969 C -4.460938 -0.855469 -4.777344 -1.136719 -4.988281 -1.515625 C -5.199219 -1.894531 -5.304688 -2.308594 -5.304688 -2.753906 C -5.304688 -3.316406 -5.160156 -3.777344 -4.875 -4.136719 C -4.589844 -4.492188 -4.1875 -4.722656 -3.664062 -4.824219 L -3.53125 -3.96875 C -3.878906 -3.886719 -4.140625 -3.746094 -4.316406 -3.539062 C -4.492188 -3.332031 -4.578125 -3.082031 -4.578125 -2.789062 C -4.578125 -2.34375 -4.421875 -1.984375 -4.105469 -1.710938 C -3.789062 -1.433594 -3.285156 -1.292969 -2.597656 -1.292969 C -1.902344 -1.292969 -1.394531 -1.425781 -1.078125 -1.695312 C -0.761719 -1.960938 -0.605469 -2.308594 -0.605469 -2.738281 C -0.605469 -3.085938 -0.710938 -3.371094 -0.921875 -3.601562 C -1.132812 -3.835938 -1.460938 -3.980469 -1.898438 -4.042969 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph1-4"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M -2.59375 -0.332031 C -3.554688 -0.332031 -4.265625 -0.597656 -4.726562 -1.132812 C -5.109375 -1.578125 -5.304688 -2.121094 -5.304688 -2.765625 C -5.304688 -3.476562 -5.070312 -4.058594 -4.601562 -4.511719 C -4.132812 -4.964844 -3.488281 -5.191406 -2.664062 -5.191406 C -2 -5.191406 -1.472656 -5.089844 -1.089844 -4.890625 C -0.707031 -4.691406 -0.410156 -4.398438 -0.199219 -4.015625 C 0.0117188 -3.632812 0.117188 -3.214844 0.117188 -2.765625 C 0.117188 -2.039062 -0.117188 -1.449219 -0.582031 -1.003906 C -1.046875 -0.554688 -1.71875 -0.332031 -2.59375 -0.332031 Z M -2.59375 -1.234375 C -1.929688 -1.234375 -1.429688 -1.378906 -1.101562 -1.671875 C -0.769531 -1.960938 -0.605469 -2.324219 -0.605469 -2.765625 C -0.605469 -3.199219 -0.773438 -3.5625 -1.101562 -3.851562 C -1.433594 -4.140625 -1.941406 -4.289062 -2.621094 -4.289062 C -3.261719 -4.289062 -3.75 -4.140625 -4.078125 -3.851562 C -4.410156 -3.558594 -4.574219 -3.195312 -4.574219 -2.765625 C -4.574219 -2.324219 -4.410156 -1.960938 -4.082031 -1.671875 C -3.753906 -1.382812 -3.257812 -1.234375 -2.59375 -1.234375 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph1-5"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0 -0.660156 L -5.1875 -0.660156 L -5.1875 -1.449219 L -4.449219 -1.449219 C -5.019531 -1.832031 -5.304688 -2.382812 -5.304688 -3.101562 C -5.304688 -3.414062 -5.246094 -3.699219 -5.132812 -3.960938 C -5.023438 -4.222656 -4.875 -4.421875 -4.691406 -4.550781 C -4.507812 -4.679688 -4.292969 -4.773438 -4.042969 -4.824219 C -3.878906 -4.855469 -3.59375 -4.875 -3.1875 -4.875 L 0 -4.875 L 0 -3.992188 L -3.15625 -3.992188 C -3.511719 -3.992188 -3.78125 -3.960938 -3.957031 -3.890625 C -4.132812 -3.824219 -4.277344 -3.703125 -4.382812 -3.527344 C -4.488281 -3.351562 -4.539062 -3.148438 -4.539062 -2.914062 C -4.539062 -2.539062 -4.421875 -2.21875 -4.183594 -1.945312 C -3.945312 -1.671875 -3.496094 -1.539062 -2.832031 -1.539062 L 0 -1.539062 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph1-6"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0 -4.023438 L -0.65625 -4.023438 C -0.140625 -3.695312 0.117188 -3.210938 0.117188 -2.574219 C 0.117188 -2.160156 0.00390625 -1.78125 -0.226562 -1.433594 C -0.453125 -1.085938 -0.769531 -0.816406 -1.179688 -0.628906 C -1.585938 -0.4375 -2.058594 -0.34375 -2.585938 -0.34375 C -3.105469 -0.34375 -3.574219 -0.429688 -3.996094 -0.601562 C -4.417969 -0.773438 -4.742188 -1.03125 -4.964844 -1.375 C -5.191406 -1.722656 -5.304688 -2.109375 -5.304688 -2.535156 C -5.304688 -2.847656 -5.238281 -3.125 -5.105469 -3.367188 C -4.972656 -3.613281 -4.800781 -3.8125 -4.589844 -3.964844 L -7.15625 -3.964844 L -7.15625 -4.839844 L 0 -4.839844 Z M -2.585938 -1.246094 C -1.921875 -1.246094 -1.425781 -1.386719 -1.097656 -1.664062 C -0.769531 -1.945312 -0.605469 -2.273438 -0.605469 -2.65625 C -0.605469 -3.039062 -0.761719 -3.367188 -1.078125 -3.636719 C -1.390625 -3.90625 -1.871094 -4.039062 -2.515625 -4.039062 C -3.226562 -4.039062 -3.746094 -3.902344 -4.078125 -3.628906 C -4.410156 -3.355469 -4.574219 -3.015625 -4.574219 -2.617188 C -4.574219 -2.226562 -4.414062 -1.898438 -4.097656 -1.636719 C -3.777344 -1.375 -3.273438 -1.246094 -2.585938 -1.246094 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph1-7"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M -1.546875 -0.308594 L -1.683594 -1.175781 C -1.335938 -1.226562 -1.070312 -1.363281 -0.882812 -1.585938 C -0.699219 -1.808594 -0.605469 -2.117188 -0.605469 -2.519531 C -0.605469 -2.921875 -0.6875 -3.222656 -0.851562 -3.417969 C -1.015625 -3.613281 -1.210938 -3.710938 -1.429688 -3.710938 C -1.628906 -3.710938 -1.785156 -3.625 -1.898438 -3.453125 C -1.976562 -3.332031 -2.078125 -3.03125 -2.195312 -2.554688 C -2.359375 -1.910156 -2.5 -1.460938 -2.621094 -1.214844 C -2.738281 -0.964844 -2.902344 -0.777344 -3.113281 -0.648438 C -3.324219 -0.519531 -3.554688 -0.453125 -3.808594 -0.453125 C -4.039062 -0.453125 -4.253906 -0.507812 -4.449219 -0.613281 C -4.648438 -0.71875 -4.8125 -0.863281 -4.941406 -1.046875 C -5.042969 -1.183594 -5.128906 -1.367188 -5.199219 -1.605469 C -5.269531 -1.839844 -5.304688 -2.09375 -5.304688 -2.363281 C -5.304688 -2.769531 -5.242188 -3.128906 -5.125 -3.433594 C -5.007812 -3.742188 -4.851562 -3.96875 -4.652344 -4.117188 C -4.453125 -4.261719 -4.183594 -4.363281 -3.847656 -4.417969 L -3.730469 -3.558594 C -3.996094 -3.519531 -4.207031 -3.40625 -4.355469 -3.21875 C -4.503906 -3.03125 -4.578125 -2.769531 -4.578125 -2.425781 C -4.578125 -2.023438 -4.511719 -1.734375 -4.378906 -1.5625 C -4.246094 -1.390625 -4.089844 -1.304688 -3.910156 -1.304688 C -3.796875 -1.304688 -3.695312 -1.339844 -3.601562 -1.410156 C -3.507812 -1.484375 -3.429688 -1.59375 -3.367188 -1.75 C -3.335938 -1.835938 -3.261719 -2.09375 -3.144531 -2.523438 C -2.976562 -3.144531 -2.84375 -3.578125 -2.738281 -3.824219 C -2.632812 -4.070312 -2.476562 -4.265625 -2.273438 -4.40625 C -2.074219 -4.546875 -1.824219 -4.613281 -1.523438 -4.613281 C -1.230469 -4.613281 -0.953125 -4.527344 -0.695312 -4.359375 C -0.4375 -4.1875 -0.238281 -3.941406 -0.09375 -3.617188 C 0.046875 -3.296875 0.117188 -2.929688 0.117188 -2.523438 C 0.117188 -1.851562 -0.0234375 -1.335938 -0.304688 -0.984375 C -0.582031 -0.632812 -0.996094 -0.40625 -1.546875 -0.308594 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-0"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d=""/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-1"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 7.054688 -3.011719 L 8.191406 -2.726562 C 7.953125 -1.792969 7.523438 -1.078125 6.90625 -0.589844 C 6.285156 -0.0976562 5.53125 0.148438 4.632812 0.148438 C 3.707031 0.148438 2.957031 -0.0429688 2.375 -0.417969 C 1.796875 -0.796875 1.355469 -1.34375 1.050781 -2.054688 C 0.75 -2.769531 0.597656 -3.539062 0.597656 -4.359375 C 0.597656 -5.253906 0.769531 -6.035156 1.109375 -6.699219 C 1.453125 -7.367188 1.9375 -7.871094 2.570312 -8.21875 C 3.199219 -8.5625 3.894531 -8.734375 4.652344 -8.734375 C 5.511719 -8.734375 6.234375 -8.515625 6.820312 -8.078125 C 7.40625 -7.640625 7.8125 -7.027344 8.046875 -6.234375 L 6.925781 -5.96875 C 6.726562 -6.59375 6.4375 -7.050781 6.058594 -7.335938 C 5.679688 -7.621094 5.203125 -7.765625 4.628906 -7.765625 C 3.96875 -7.765625 3.417969 -7.605469 2.972656 -7.289062 C 2.53125 -6.972656 2.21875 -6.546875 2.039062 -6.015625 C 1.859375 -5.480469 1.769531 -4.929688 1.769531 -4.367188 C 1.769531 -3.636719 1.875 -2.996094 2.089844 -2.453125 C 2.300781 -1.90625 2.632812 -1.5 3.082031 -1.230469 C 3.53125 -0.960938 4.015625 -0.828125 4.539062 -0.828125 C 5.175781 -0.828125 5.71875 -1.007812 6.15625 -1.375 C 6.597656 -1.742188 6.898438 -2.289062 7.054688 -3.011719 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-2"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.398438 -3.109375 C 0.398438 -4.261719 0.71875 -5.117188 1.359375 -5.671875 C 1.894531 -6.132812 2.546875 -6.363281 3.316406 -6.363281 C 4.171875 -6.363281 4.871094 -6.082031 5.414062 -5.523438 C 5.957031 -4.960938 6.226562 -4.1875 6.226562 -3.199219 C 6.226562 -2.398438 6.109375 -1.769531 5.867188 -1.308594 C 5.628906 -0.851562 5.277344 -0.492188 4.820312 -0.242188 C 4.359375 0.0117188 3.859375 0.140625 3.316406 0.140625 C 2.445312 0.140625 1.742188 -0.140625 1.203125 -0.695312 C 0.667969 -1.253906 0.398438 -2.0625 0.398438 -3.109375 Z M 1.484375 -3.109375 C 1.484375 -2.3125 1.65625 -1.71875 2.003906 -1.320312 C 2.351562 -0.925781 2.789062 -0.726562 3.316406 -0.726562 C 3.839844 -0.726562 4.273438 -0.925781 4.625 -1.324219 C 4.972656 -1.722656 5.144531 -2.328125 5.144531 -3.148438 C 5.144531 -3.917969 4.96875 -4.5 4.621094 -4.894531 C 4.269531 -5.292969 3.835938 -5.492188 3.316406 -5.492188 C 2.789062 -5.492188 2.351562 -5.292969 2.003906 -4.898438 C 1.65625 -4.503906 1.484375 -3.90625 1.484375 -3.109375 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-3"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.789062 0 L 0.789062 -6.222656 L 1.734375 -6.222656 L 1.734375 -5.351562 C 1.929688 -5.65625 2.1875 -5.898438 2.515625 -6.085938 C 2.839844 -6.269531 3.207031 -6.363281 3.621094 -6.363281 C 4.082031 -6.363281 4.460938 -6.265625 4.753906 -6.078125 C 5.050781 -5.886719 5.257812 -5.617188 5.378906 -5.273438 C 5.871094 -6 6.511719 -6.363281 7.300781 -6.363281 C 7.917969 -6.363281 8.390625 -6.191406 8.726562 -5.851562 C 9.058594 -5.507812 9.222656 -4.984375 9.222656 -4.273438 L 9.222656 0 L 8.171875 0 L 8.171875 -3.921875 C 8.171875 -4.34375 8.140625 -4.644531 8.070312 -4.832031 C 8.003906 -5.015625 7.878906 -5.164062 7.699219 -5.28125 C 7.519531 -5.394531 7.308594 -5.449219 7.066406 -5.449219 C 6.628906 -5.449219 6.265625 -5.304688 5.976562 -5.011719 C 5.6875 -4.722656 5.542969 -4.257812 5.542969 -3.617188 L 5.542969 0 L 4.488281 0 L 4.488281 -4.042969 C 4.488281 -4.511719 4.402344 -4.863281 4.230469 -5.097656 C 4.058594 -5.332031 3.777344 -5.449219 3.386719 -5.449219 C 3.089844 -5.449219 2.816406 -5.371094 2.5625 -5.214844 C 2.3125 -5.058594 2.128906 -4.828125 2.015625 -4.53125 C 1.902344 -4.230469 1.84375 -3.796875 1.84375 -3.226562 L 1.84375 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-4"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.789062 2.382812 L 0.789062 -6.222656 L 1.75 -6.222656 L 1.75 -5.414062 C 1.976562 -5.730469 2.234375 -5.96875 2.519531 -6.125 C 2.804688 -6.285156 3.148438 -6.363281 3.554688 -6.363281 C 4.085938 -6.363281 4.554688 -6.226562 4.960938 -5.953125 C 5.367188 -5.679688 5.675781 -5.292969 5.882812 -4.796875 C 6.089844 -4.296875 6.195312 -3.75 6.195312 -3.15625 C 6.195312 -2.519531 6.078125 -1.949219 5.851562 -1.4375 C 5.621094 -0.929688 5.289062 -0.539062 4.855469 -0.265625 C 4.417969 0.00390625 3.960938 0.140625 3.480469 0.140625 C 3.128906 0.140625 2.8125 0.0664062 2.535156 -0.0820312 C 2.253906 -0.230469 2.023438 -0.417969 1.84375 -0.644531 L 1.84375 2.382812 Z M 1.746094 -3.078125 C 1.746094 -2.277344 1.90625 -1.683594 2.234375 -1.300781 C 2.558594 -0.917969 2.949219 -0.726562 3.410156 -0.726562 C 3.878906 -0.726562 4.28125 -0.925781 4.613281 -1.320312 C 4.949219 -1.71875 5.117188 -2.332031 5.117188 -3.164062 C 5.117188 -3.957031 4.953125 -4.550781 4.625 -4.945312 C 4.300781 -5.339844 3.910156 -5.539062 3.457031 -5.539062 C 3.007812 -5.539062 2.609375 -5.328125 2.265625 -4.90625 C 1.917969 -4.488281 1.746094 -3.875 1.746094 -3.078125 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-5"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.796875 -7.375 L 0.796875 -8.589844 L 1.851562 -8.589844 L 1.851562 -7.375 Z M 0.796875 0 L 0.796875 -6.222656 L 1.851562 -6.222656 L 1.851562 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-6"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.765625 0 L 0.765625 -8.589844 L 1.820312 -8.589844 L 1.820312 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-7"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 4.851562 -0.765625 C 4.460938 -0.433594 4.085938 -0.203125 3.722656 -0.0625 C 3.363281 0.0742188 2.976562 0.140625 2.5625 0.140625 C 1.878906 0.140625 1.351562 -0.0273438 0.984375 -0.359375 C 0.617188 -0.695312 0.433594 -1.121094 0.433594 -1.640625 C 0.433594 -1.945312 0.503906 -2.222656 0.640625 -2.476562 C 0.78125 -2.726562 0.960938 -2.929688 1.1875 -3.082031 C 1.410156 -3.234375 1.664062 -3.351562 1.945312 -3.429688 C 2.152344 -3.484375 2.464844 -3.535156 2.882812 -3.585938 C 3.734375 -3.6875 4.359375 -3.808594 4.765625 -3.949219 C 4.769531 -4.09375 4.769531 -4.1875 4.769531 -4.226562 C 4.769531 -4.65625 4.671875 -4.957031 4.46875 -5.132812 C 4.199219 -5.371094 3.800781 -5.492188 3.269531 -5.492188 C 2.773438 -5.492188 2.40625 -5.402344 2.171875 -5.230469 C 1.933594 -5.054688 1.757812 -4.75 1.648438 -4.304688 L 0.617188 -4.445312 C 0.710938 -4.886719 0.863281 -5.246094 1.078125 -5.515625 C 1.292969 -5.789062 1.601562 -5.996094 2.007812 -6.144531 C 2.414062 -6.289062 2.886719 -6.363281 3.421875 -6.363281 C 3.953125 -6.363281 4.382812 -6.300781 4.71875 -6.175781 C 5.050781 -6.050781 5.292969 -5.894531 5.449219 -5.703125 C 5.605469 -5.515625 5.714844 -5.273438 5.777344 -4.984375 C 5.8125 -4.804688 5.828125 -4.484375 5.828125 -4.015625 L 5.828125 -2.609375 C 5.828125 -1.628906 5.851562 -1.007812 5.898438 -0.746094 C 5.941406 -0.488281 6.03125 -0.238281 6.164062 0 L 5.0625 0 C 4.953125 -0.21875 4.882812 -0.476562 4.851562 -0.765625 Z M 4.765625 -3.125 C 4.382812 -2.96875 3.804688 -2.835938 3.039062 -2.726562 C 2.605469 -2.664062 2.300781 -2.59375 2.121094 -2.515625 C 1.941406 -2.4375 1.804688 -2.320312 1.703125 -2.171875 C 1.605469 -2.019531 1.558594 -1.851562 1.558594 -1.671875 C 1.558594 -1.390625 1.664062 -1.15625 1.878906 -0.96875 C 2.089844 -0.78125 2.402344 -0.6875 2.8125 -0.6875 C 3.21875 -0.6875 3.578125 -0.773438 3.898438 -0.953125 C 4.214844 -1.128906 4.445312 -1.375 4.59375 -1.679688 C 4.707031 -1.917969 4.765625 -2.273438 4.765625 -2.734375 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-8"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 3.09375 -0.945312 L 3.246094 -0.0117188 C 2.949219 0.0507812 2.683594 0.0820312 2.449219 0.0820312 C 2.066406 0.0820312 1.769531 0.0234375 1.558594 -0.101562 C 1.347656 -0.222656 1.199219 -0.378906 1.113281 -0.578125 C 1.027344 -0.773438 0.984375 -1.1875 0.984375 -1.820312 L 0.984375 -5.402344 L 0.210938 -5.402344 L 0.210938 -6.222656 L 0.984375 -6.222656 L 0.984375 -7.765625 L 2.03125 -8.398438 L 2.03125 -6.222656 L 3.09375 -6.222656 L 3.09375 -5.402344 L 2.03125 -5.402344 L 2.03125 -1.765625 C 2.03125 -1.464844 2.050781 -1.269531 2.089844 -1.183594 C 2.125 -1.097656 2.1875 -1.03125 2.269531 -0.976562 C 2.355469 -0.925781 2.476562 -0.902344 2.632812 -0.902344 C 2.75 -0.902344 2.902344 -0.914062 3.09375 -0.945312 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-9"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.789062 0 L 0.789062 -6.222656 L 1.742188 -6.222656 L 1.742188 -5.335938 C 2.199219 -6.019531 2.859375 -6.363281 3.71875 -6.363281 C 4.09375 -6.363281 4.441406 -6.296875 4.753906 -6.160156 C 5.070312 -6.027344 5.304688 -5.851562 5.460938 -5.632812 C 5.617188 -5.414062 5.726562 -5.152344 5.789062 -4.851562 C 5.828125 -4.65625 5.847656 -4.3125 5.847656 -3.828125 L 5.847656 0 L 4.792969 0 L 4.792969 -3.785156 C 4.792969 -4.214844 4.75 -4.535156 4.671875 -4.75 C 4.589844 -4.960938 4.441406 -5.132812 4.234375 -5.257812 C 4.023438 -5.386719 3.78125 -5.449219 3.5 -5.449219 C 3.050781 -5.449219 2.660156 -5.304688 2.335938 -5.023438 C 2.007812 -4.738281 1.84375 -4.195312 1.84375 -3.398438 L 1.84375 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-10"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 5.050781 -2.003906 L 6.140625 -1.867188 C 5.96875 -1.230469 5.648438 -0.738281 5.1875 -0.386719 C 4.722656 -0.0351562 4.125 0.140625 3.40625 0.140625 C 2.496094 0.140625 1.773438 -0.140625 1.238281 -0.699219 C 0.707031 -1.261719 0.4375 -2.046875 0.4375 -3.058594 C 0.4375 -4.105469 0.710938 -4.917969 1.25 -5.496094 C 1.789062 -6.074219 2.484375 -6.363281 3.34375 -6.363281 C 4.175781 -6.363281 4.859375 -6.078125 5.382812 -5.515625 C 5.910156 -4.949219 6.175781 -4.148438 6.175781 -3.125 C 6.175781 -3.0625 6.171875 -2.96875 6.171875 -2.84375 L 1.53125 -2.84375 C 1.570312 -2.160156 1.761719 -1.632812 2.109375 -1.273438 C 2.457031 -0.910156 2.890625 -0.726562 3.410156 -0.726562 C 3.796875 -0.726562 4.125 -0.828125 4.398438 -1.03125 C 4.671875 -1.234375 4.890625 -1.558594 5.050781 -2.003906 Z M 1.585938 -3.710938 L 5.0625 -3.710938 C 5.015625 -4.234375 4.882812 -4.625 4.664062 -4.886719 C 4.328125 -5.292969 3.890625 -5.496094 3.359375 -5.496094 C 2.875 -5.496094 2.464844 -5.335938 2.136719 -5.007812 C 1.804688 -4.683594 1.625 -4.25 1.585938 -3.710938 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-11"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 1.042969 0 L 1.042969 -5.402344 L 0.109375 -5.402344 L 0.109375 -6.222656 L 1.042969 -6.222656 L 1.042969 -6.882812 C 1.042969 -7.300781 1.078125 -7.613281 1.15625 -7.816406 C 1.257812 -8.089844 1.433594 -8.3125 1.691406 -8.480469 C 1.945312 -8.652344 2.304688 -8.734375 2.765625 -8.734375 C 3.0625 -8.734375 3.390625 -8.703125 3.75 -8.632812 L 3.59375 -7.710938 C 3.375 -7.75 3.164062 -7.769531 2.96875 -7.769531 C 2.648438 -7.769531 2.421875 -7.703125 2.289062 -7.5625 C 2.15625 -7.425781 2.09375 -7.171875 2.09375 -6.796875 L 2.09375 -6.222656 L 3.304688 -6.222656 L 3.304688 -5.402344 L 2.09375 -5.402344 L 2.09375 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-12"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 4.828125 0 L 4.828125 -0.785156 C 4.433594 -0.167969 3.851562 0.140625 3.085938 0.140625 C 2.589844 0.140625 2.136719 0.00390625 1.71875 -0.269531 C 1.304688 -0.542969 0.980469 -0.925781 0.753906 -1.414062 C 0.523438 -1.90625 0.410156 -2.46875 0.410156 -3.105469 C 0.410156 -3.726562 0.515625 -4.289062 0.71875 -4.796875 C 0.925781 -5.300781 1.238281 -5.6875 1.652344 -5.960938 C 2.066406 -6.230469 2.53125 -6.363281 3.039062 -6.363281 C 3.414062 -6.363281 3.75 -6.285156 4.042969 -6.125 C 4.335938 -5.96875 4.574219 -5.761719 4.757812 -5.507812 L 4.757812 -8.589844 L 5.804688 -8.589844 L 5.804688 0 Z M 1.492188 -3.105469 C 1.492188 -2.308594 1.664062 -1.710938 2 -1.320312 C 2.335938 -0.925781 2.730469 -0.726562 3.1875 -0.726562 C 3.648438 -0.726562 4.039062 -0.914062 4.363281 -1.292969 C 4.683594 -1.667969 4.84375 -2.242188 4.84375 -3.015625 C 4.84375 -3.867188 4.679688 -4.492188 4.351562 -4.890625 C 4.023438 -5.289062 3.621094 -5.492188 3.140625 -5.492188 C 2.671875 -5.492188 2.28125 -5.296875 1.964844 -4.914062 C 1.652344 -4.53125 1.492188 -3.929688 1.492188 -3.105469 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-13"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 4.867188 0 L 4.867188 -0.914062 C 4.382812 -0.210938 3.726562 0.140625 2.894531 0.140625 C 2.527344 0.140625 2.183594 0.0703125 1.867188 -0.0703125 C 1.546875 -0.210938 1.3125 -0.386719 1.15625 -0.601562 C 1.003906 -0.8125 0.894531 -1.074219 0.832031 -1.382812 C 0.789062 -1.589844 0.765625 -1.917969 0.765625 -2.367188 L 0.765625 -6.222656 L 1.820312 -6.222656 L 1.820312 -2.773438 C 1.820312 -2.222656 1.84375 -1.851562 1.886719 -1.65625 C 1.953125 -1.378906 2.09375 -1.164062 2.308594 -1.003906 C 2.523438 -0.847656 2.789062 -0.765625 3.105469 -0.765625 C 3.421875 -0.765625 3.71875 -0.847656 3.996094 -1.011719 C 4.273438 -1.171875 4.46875 -1.394531 4.585938 -1.671875 C 4.699219 -1.953125 4.757812 -2.359375 4.757812 -2.890625 L 4.757812 -6.222656 L 5.8125 -6.222656 L 5.8125 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-0"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d=""/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-1"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.953125 0 L 0.953125 -9.304688 L 4.445312 -9.304688 C 5.15625 -9.304688 5.722656 -9.210938 6.152344 -9.023438 C 6.582031 -8.835938 6.921875 -8.546875 7.164062 -8.152344 C 7.40625 -7.761719 7.527344 -7.351562 7.527344 -6.925781 C 7.527344 -6.527344 7.421875 -6.152344 7.203125 -5.800781 C 6.988281 -5.449219 6.664062 -5.167969 6.226562 -4.953125 C 6.789062 -4.785156 7.222656 -4.503906 7.523438 -4.105469 C 7.828125 -3.707031 7.980469 -3.238281 7.980469 -2.699219 C 7.980469 -2.261719 7.886719 -1.855469 7.703125 -1.480469 C 7.519531 -1.105469 7.292969 -0.820312 7.019531 -0.617188 C 6.75 -0.414062 6.410156 -0.257812 6 -0.15625 C 5.59375 -0.0507812 5.09375 0 4.5 0 Z M 2.183594 -5.394531 L 4.195312 -5.394531 C 4.742188 -5.394531 5.132812 -5.429688 5.371094 -5.503906 C 5.683594 -5.597656 5.917969 -5.75 6.078125 -5.96875 C 6.238281 -6.183594 6.316406 -6.453125 6.316406 -6.78125 C 6.316406 -7.089844 6.242188 -7.359375 6.09375 -7.59375 C 5.945312 -7.828125 5.734375 -7.992188 5.460938 -8.078125 C 5.183594 -8.164062 4.710938 -8.207031 4.042969 -8.207031 L 2.183594 -8.207031 Z M 2.183594 -1.097656 L 4.5 -1.097656 C 4.898438 -1.097656 5.175781 -1.113281 5.339844 -1.140625 C 5.621094 -1.191406 5.859375 -1.277344 6.050781 -1.398438 C 6.242188 -1.515625 6.394531 -1.6875 6.519531 -1.914062 C 6.640625 -2.140625 6.703125 -2.402344 6.703125 -2.699219 C 6.703125 -3.046875 6.613281 -3.347656 6.4375 -3.601562 C 6.257812 -3.859375 6.011719 -4.039062 5.695312 -4.140625 C 5.382812 -4.246094 4.929688 -4.296875 4.335938 -4.296875 L 2.183594 -4.296875 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-2"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.429688 -3.371094 C 0.429688 -4.617188 0.777344 -5.542969 1.472656 -6.144531 C 2.050781 -6.644531 2.757812 -6.894531 3.59375 -6.894531 C 4.519531 -6.894531 5.277344 -6.589844 5.867188 -5.984375 C 6.453125 -5.375 6.746094 -4.535156 6.746094 -3.464844 C 6.746094 -2.597656 6.617188 -1.914062 6.355469 -1.417969 C 6.097656 -0.921875 5.71875 -0.535156 5.222656 -0.261719 C 4.722656 0.015625 4.179688 0.152344 3.59375 0.152344 C 2.648438 0.152344 1.886719 -0.148438 1.304688 -0.753906 C 0.722656 -1.359375 0.429688 -2.230469 0.429688 -3.371094 Z M 1.605469 -3.371094 C 1.605469 -2.507812 1.792969 -1.859375 2.171875 -1.429688 C 2.546875 -1 3.023438 -0.789062 3.59375 -0.789062 C 4.160156 -0.789062 4.632812 -1.003906 5.007812 -1.433594 C 5.382812 -1.867188 5.574219 -2.523438 5.574219 -3.410156 C 5.574219 -4.242188 5.382812 -4.875 5.003906 -5.304688 C 4.625 -5.734375 4.15625 -5.949219 3.59375 -5.949219 C 3.023438 -5.949219 2.546875 -5.734375 2.171875 -5.304688 C 1.792969 -4.878906 1.605469 -4.234375 1.605469 -3.371094 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-3"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.398438 -2.011719 L 1.53125 -2.191406 C 1.59375 -1.738281 1.769531 -1.390625 2.058594 -1.148438 C 2.347656 -0.90625 2.753906 -0.789062 3.273438 -0.789062 C 3.800781 -0.789062 4.1875 -0.894531 4.445312 -1.109375 C 4.699219 -1.320312 4.824219 -1.570312 4.824219 -1.859375 C 4.824219 -2.117188 4.710938 -2.320312 4.488281 -2.46875 C 4.332031 -2.570312 3.941406 -2.699219 3.320312 -2.855469 C 2.480469 -3.066406 1.902344 -3.25 1.578125 -3.40625 C 1.253906 -3.558594 1.007812 -3.773438 0.839844 -4.046875 C 0.671875 -4.320312 0.589844 -4.621094 0.589844 -4.953125 C 0.589844 -5.253906 0.660156 -5.53125 0.796875 -5.785156 C 0.933594 -6.042969 1.121094 -6.253906 1.359375 -6.421875 C 1.535156 -6.554688 1.777344 -6.667969 2.085938 -6.757812 C 2.390625 -6.847656 2.722656 -6.894531 3.070312 -6.894531 C 3.601562 -6.894531 4.066406 -6.816406 4.464844 -6.664062 C 4.867188 -6.511719 5.160156 -6.304688 5.351562 -6.046875 C 5.542969 -5.785156 5.671875 -5.4375 5.746094 -5 L 4.628906 -4.851562 C 4.578125 -5.195312 4.429688 -5.46875 4.1875 -5.664062 C 3.945312 -5.859375 3.597656 -5.953125 3.15625 -5.953125 C 2.628906 -5.953125 2.253906 -5.867188 2.03125 -5.695312 C 1.808594 -5.519531 1.695312 -5.316406 1.695312 -5.085938 C 1.695312 -4.9375 1.742188 -4.804688 1.835938 -4.683594 C 1.929688 -4.5625 2.074219 -4.460938 2.273438 -4.378906 C 2.386719 -4.335938 2.722656 -4.242188 3.28125 -4.085938 C 4.089844 -3.871094 4.652344 -3.695312 4.972656 -3.558594 C 5.292969 -3.421875 5.542969 -3.21875 5.726562 -2.957031 C 5.90625 -2.695312 6 -2.371094 6 -1.980469 C 6 -1.601562 5.886719 -1.242188 5.664062 -0.90625 C 5.441406 -0.570312 5.121094 -0.308594 4.703125 -0.125 C 4.285156 0.0585938 3.8125 0.152344 3.28125 0.152344 C 2.40625 0.152344 1.738281 -0.03125 1.277344 -0.394531 C 0.820312 -0.757812 0.527344 -1.296875 0.398438 -2.011719 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-4"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 3.351562 -1.023438 L 3.515625 -0.0117188 C 3.195312 0.0546875 2.90625 0.0898438 2.652344 0.0898438 C 2.238281 0.0898438 1.917969 0.0234375 1.6875 -0.109375 C 1.460938 -0.238281 1.300781 -0.410156 1.207031 -0.625 C 1.113281 -0.839844 1.066406 -1.289062 1.066406 -1.972656 L 1.066406 -5.851562 L 0.226562 -5.851562 L 0.226562 -6.742188 L 1.066406 -6.742188 L 1.066406 -8.410156 L 2.203125 -9.097656 L 2.203125 -6.742188 L 3.351562 -6.742188 L 3.351562 -5.851562 L 2.203125 -5.851562 L 2.203125 -1.910156 C 2.203125 -1.585938 2.222656 -1.375 2.261719 -1.28125 C 2.304688 -1.1875 2.367188 -1.113281 2.460938 -1.058594 C 2.550781 -1.003906 2.679688 -0.976562 2.851562 -0.976562 C 2.976562 -0.976562 3.144531 -0.992188 3.351562 -1.023438 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-5"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 1.179688 0 L 1.179688 -1.300781 L 2.480469 -1.300781 L 2.480469 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-6"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 1.003906 0 L 1.003906 -9.304688 L 4.511719 -9.304688 C 5.128906 -9.304688 5.601562 -9.277344 5.929688 -9.21875 C 6.386719 -9.140625 6.769531 -8.996094 7.078125 -8.78125 C 7.386719 -8.566406 7.636719 -8.269531 7.824219 -7.882812 C 8.011719 -7.5 8.105469 -7.074219 8.105469 -6.613281 C 8.105469 -5.824219 7.855469 -5.152344 7.351562 -4.605469 C 6.847656 -4.058594 5.9375 -3.78125 4.621094 -3.78125 L 2.234375 -3.78125 L 2.234375 0 Z M 2.234375 -4.882812 L 4.640625 -4.882812 C 5.4375 -4.882812 6 -5.03125 6.335938 -5.324219 C 6.667969 -5.621094 6.835938 -6.039062 6.835938 -6.578125 C 6.835938 -6.964844 6.738281 -7.296875 6.542969 -7.574219 C 6.34375 -7.851562 6.085938 -8.035156 5.765625 -8.125 C 5.558594 -8.179688 5.171875 -8.207031 4.613281 -8.207031 L 2.234375 -8.207031 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-7"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.804688 2.597656 L 0.679688 1.523438 C 0.929688 1.589844 1.148438 1.625 1.332031 1.625 C 1.585938 1.625 1.789062 1.582031 1.941406 1.5 C 2.09375 1.414062 2.21875 1.296875 2.316406 1.140625 C 2.390625 1.027344 2.503906 0.746094 2.664062 0.292969 C 2.6875 0.230469 2.722656 0.136719 2.765625 0.0117188 L 0.210938 -6.742188 L 1.441406 -6.742188 L 2.84375 -2.835938 C 3.027344 -2.34375 3.1875 -1.820312 3.332031 -1.277344 C 3.464844 -1.800781 3.621094 -2.3125 3.800781 -2.8125 L 5.242188 -6.742188 L 6.386719 -6.742188 L 3.820312 0.113281 C 3.546875 0.855469 3.332031 1.363281 3.179688 1.644531 C 2.976562 2.019531 2.746094 2.296875 2.480469 2.472656 C 2.21875 2.648438 1.90625 2.734375 1.542969 2.734375 C 1.324219 2.734375 1.078125 2.6875 0.804688 2.597656 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-8"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.855469 0 L 0.855469 -9.304688 L 2 -9.304688 L 2 -5.96875 C 2.53125 -6.585938 3.207031 -6.894531 4.019531 -6.894531 C 4.519531 -6.894531 4.953125 -6.796875 5.320312 -6.597656 C 5.6875 -6.402344 5.949219 -6.128906 6.109375 -5.78125 C 6.269531 -5.433594 6.347656 -4.933594 6.347656 -4.273438 L 6.347656 0 L 5.203125 0 L 5.203125 -4.273438 C 5.203125 -4.84375 5.082031 -5.257812 4.832031 -5.519531 C 4.585938 -5.78125 4.234375 -5.910156 3.78125 -5.910156 C 3.445312 -5.910156 3.125 -5.820312 2.828125 -5.644531 C 2.53125 -5.46875 2.316406 -5.234375 2.191406 -4.933594 C 2.0625 -4.632812 2 -4.21875 2 -3.6875 L 2 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-9"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.855469 0 L 0.855469 -6.742188 L 1.886719 -6.742188 L 1.886719 -5.78125 C 2.382812 -6.523438 3.09375 -6.894531 4.03125 -6.894531 C 4.4375 -6.894531 4.808594 -6.820312 5.152344 -6.675781 C 5.492188 -6.527344 5.746094 -6.335938 5.914062 -6.101562 C 6.085938 -5.863281 6.203125 -5.582031 6.273438 -5.257812 C 6.3125 -5.046875 6.335938 -4.675781 6.335938 -4.144531 L 6.335938 0 L 5.191406 0 L 5.191406 -4.101562 C 5.191406 -4.566406 5.148438 -4.914062 5.058594 -5.144531 C 4.96875 -5.375 4.8125 -5.558594 4.585938 -5.695312 C 4.359375 -5.835938 4.09375 -5.902344 3.789062 -5.902344 C 3.304688 -5.902344 2.882812 -5.75 2.53125 -5.441406 C 2.175781 -5.132812 2 -4.546875 2 -3.679688 L 2 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-10"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.855469 2.582031 L 0.855469 -6.742188 L 1.898438 -6.742188 L 1.898438 -5.867188 C 2.144531 -6.207031 2.421875 -6.464844 2.730469 -6.636719 C 3.039062 -6.808594 3.414062 -6.894531 3.851562 -6.894531 C 4.429688 -6.894531 4.9375 -6.746094 5.375 -6.449219 C 5.816406 -6.152344 6.148438 -5.734375 6.375 -5.195312 C 6.597656 -4.65625 6.710938 -4.066406 6.710938 -3.421875 C 6.710938 -2.730469 6.585938 -2.109375 6.339844 -1.558594 C 6.089844 -1.007812 5.730469 -0.582031 5.257812 -0.289062 C 4.785156 0.00390625 4.289062 0.152344 3.769531 0.152344 C 3.390625 0.152344 3.046875 0.0703125 2.746094 -0.0898438 C 2.441406 -0.25 2.195312 -0.453125 2 -0.699219 L 2 2.582031 Z M 1.890625 -3.332031 C 1.890625 -2.464844 2.066406 -1.824219 2.417969 -1.410156 C 2.769531 -0.996094 3.195312 -0.789062 3.695312 -0.789062 C 4.203125 -0.789062 4.636719 -1 5 -1.429688 C 5.359375 -1.859375 5.542969 -2.527344 5.542969 -3.429688 C 5.542969 -4.289062 5.363281 -4.929688 5.011719 -5.359375 C 4.65625 -5.785156 4.234375 -6 3.746094 -6 C 3.257812 -6 2.828125 -5.769531 2.453125 -5.316406 C 2.078125 -4.859375 1.890625 -4.199219 1.890625 -3.332031 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-11"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 1.910156 0 L 0.851562 0 L 0.851562 -9.304688 L 1.992188 -9.304688 L 1.992188 -5.984375 C 2.476562 -6.589844 3.089844 -6.894531 3.839844 -6.894531 C 4.253906 -6.894531 4.648438 -6.808594 5.019531 -6.644531 C 5.390625 -6.476562 5.691406 -6.242188 5.933594 -5.9375 C 6.171875 -5.636719 6.359375 -5.269531 6.492188 -4.84375 C 6.628906 -4.414062 6.695312 -3.957031 6.695312 -3.472656 C 6.695312 -2.316406 6.410156 -1.425781 5.839844 -0.792969 C 5.269531 -0.164062 4.582031 0.152344 3.78125 0.152344 C 2.988281 0.152344 2.363281 -0.179688 1.910156 -0.84375 Z M 1.898438 -3.421875 C 1.898438 -2.613281 2.007812 -2.027344 2.226562 -1.667969 C 2.585938 -1.082031 3.074219 -0.789062 3.6875 -0.789062 C 4.1875 -0.789062 4.617188 -1.003906 4.984375 -1.4375 C 5.347656 -1.871094 5.527344 -2.519531 5.527344 -3.375 C 5.527344 -4.257812 5.355469 -4.90625 5.003906 -5.324219 C 4.65625 -5.742188 4.234375 -5.953125 3.738281 -5.953125 C 3.238281 -5.953125 2.808594 -5.738281 2.445312 -5.304688 C 2.082031 -4.871094 1.898438 -4.242188 1.898438 -3.421875 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-12"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.863281 -7.992188 L 0.863281 -9.304688 L 2.007812 -9.304688 L 2.007812 -7.992188 Z M 0.863281 0 L 0.863281 -6.742188 L 2.007812 -6.742188 L 2.007812 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-13"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 5.230469 0 L 5.230469 -0.851562 C 4.804688 -0.183594 4.175781 0.152344 3.34375 0.152344 C 2.808594 0.152344 2.3125 0.00390625 1.863281 -0.292969 C 1.414062 -0.589844 1.0625 -1 0.816406 -1.53125 C 0.570312 -2.0625 0.445312 -2.675781 0.445312 -3.363281 C 0.445312 -4.035156 0.554688 -4.648438 0.78125 -5.195312 C 1.003906 -5.742188 1.339844 -6.164062 1.789062 -6.457031 C 2.238281 -6.75 2.738281 -6.894531 3.292969 -6.894531 C 3.699219 -6.894531 4.0625 -6.808594 4.378906 -6.636719 C 4.695312 -6.464844 4.957031 -6.242188 5.15625 -5.96875 L 5.15625 -9.304688 L 6.289062 -9.304688 L 6.289062 0 Z M 1.617188 -3.363281 C 1.617188 -2.5 1.800781 -1.855469 2.164062 -1.429688 C 2.527344 -1 2.957031 -0.789062 3.453125 -0.789062 C 3.953125 -0.789062 4.375 -0.992188 4.726562 -1.398438 C 5.074219 -1.808594 5.25 -2.429688 5.25 -3.269531 C 5.25 -4.191406 5.070312 -4.867188 4.714844 -5.300781 C 4.359375 -5.730469 3.921875 -5.949219 3.402344 -5.949219 C 2.894531 -5.949219 2.46875 -5.742188 2.128906 -5.324219 C 1.789062 -4.910156 1.617188 -4.257812 1.617188 -3.363281 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-14"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 4.84375 0 L 3.699219 0 L 3.699219 -7.28125 C 3.425781 -7.019531 3.066406 -6.757812 2.617188 -6.492188 C 2.171875 -6.230469 1.769531 -6.035156 1.414062 -5.902344 L 1.414062 -7.007812 C 2.054688 -7.308594 2.613281 -7.671875 3.089844 -8.101562 C 3.570312 -8.527344 3.90625 -8.941406 4.105469 -9.34375 L 4.84375 -9.34375 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<clipPath id="clip1"> |
|||
<path d="M 89 21 L 91 21 L 91 221 L 89 221 Z "/> |
|||
</clipPath> |
|||
<clipPath id="clip2"> |
|||
<path d="M 201 21 L 203 21 L 203 221 L 201 221 Z "/> |
|||
</clipPath> |
|||
<clipPath id="clip3"> |
|||
<path d="M 313 21 L 315 21 L 315 221 L 313 221 Z "/> |
|||
</clipPath> |
|||
<clipPath id="clip4"> |
|||
<path d="M 33 180 L 355 180 L 355 182 L 33 182 Z "/> |
|||
</clipPath> |
|||
<clipPath id="clip5"> |
|||
<path d="M 33 146 L 355 146 L 355 148 L 33 148 Z "/> |
|||
</clipPath> |
|||
<clipPath id="clip6"> |
|||
<path d="M 33 120 L 355 120 L 355 122 L 33 122 Z "/> |
|||
</clipPath> |
|||
<clipPath id="clip7"> |
|||
<path d="M 33 95 L 355 95 L 355 97 L 33 97 Z "/> |
|||
</clipPath> |
|||
<clipPath id="clip8"> |
|||
<path d="M 33 61 L 355 61 L 355 63 L 33 63 Z "/> |
|||
</clipPath> |
|||
</defs> |
|||
<g id="surface11"> |
|||
<g clip-path="url(#clip1)" clip-rule="nonzero"> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:0.5;stroke-dasharray:1,2;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 90.226562 220.007812 L 90.226562 21 "/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g clip-path="url(#clip2)" clip-rule="nonzero"> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:0.5;stroke-dasharray:1,2;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 201.996094 220.007812 L 201.996094 21 "/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g clip-path="url(#clip3)" clip-rule="nonzero"> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:0.5;stroke-dasharray:1,2;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 313.761719 220.007812 L 313.761719 21 "/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g clip-path="url(#clip4)" clip-rule="nonzero"> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:0.5;stroke-dasharray:1,2;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 180.734375 L 355 180.734375 "/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g clip-path="url(#clip5)" clip-rule="nonzero"> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:0.5;stroke-dasharray:1,2;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 146.960938 L 355 146.960938 "/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g clip-path="url(#clip6)" clip-rule="nonzero"> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:0.5;stroke-dasharray:1,2;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 121.410156 L 355 121.410156 "/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g clip-path="url(#clip7)" clip-rule="nonzero"> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:0.5;stroke-dasharray:1,2;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 95.859375 L 355 95.859375 "/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g clip-path="url(#clip8)" clip-rule="nonzero"> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:0.5;stroke-dasharray:1,2;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 62.082031 L 355 62.082031 "/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 49.128906 169 C 49.128906 168.167969 48.800781 167.375 48.214844 166.785156 C 47.625 166.199219 46.832031 165.871094 46 165.871094 C 45.167969 165.871094 44.375 166.199219 43.785156 166.785156 C 43.199219 167.375 42.871094 168.167969 42.871094 169 C 42.871094 169.832031 43.199219 170.625 43.785156 171.214844 C 44.375 171.800781 45.167969 172.128906 46 172.128906 C 46.832031 172.128906 47.625 171.800781 48.214844 171.214844 C 48.800781 170.625 49.128906 169.832031 49.128906 169 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 82.128906 169 C 82.128906 168.167969 81.800781 167.375 81.214844 166.785156 C 80.625 166.199219 79.832031 165.871094 79 165.871094 C 78.167969 165.871094 77.375 166.199219 76.785156 166.785156 C 76.199219 167.375 75.871094 168.167969 75.871094 169 C 75.871094 169.832031 76.199219 170.625 76.785156 171.214844 C 77.375 171.800781 78.167969 172.128906 79 172.128906 C 79.832031 172.128906 80.625 171.800781 81.214844 171.214844 C 81.800781 170.625 82.128906 169.832031 82.128906 169 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 116.128906 167 C 116.128906 166.167969 115.800781 165.375 115.214844 164.785156 C 114.625 164.199219 113.832031 163.871094 113 163.871094 C 112.167969 163.871094 111.375 164.199219 110.785156 164.785156 C 110.199219 165.375 109.871094 166.167969 109.871094 167 C 109.871094 167.832031 110.199219 168.625 110.785156 169.214844 C 111.375 169.800781 112.167969 170.128906 113 170.128906 C 113.832031 170.128906 114.625 169.800781 115.214844 169.214844 C 115.800781 168.625 116.128906 167.832031 116.128906 167 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 150.128906 159 C 150.128906 158.167969 149.800781 157.375 149.214844 156.785156 C 148.625 156.199219 147.832031 155.871094 147 155.871094 C 146.167969 155.871094 145.375 156.199219 144.785156 156.785156 C 144.199219 157.375 143.871094 158.167969 143.871094 159 C 143.871094 159.832031 144.199219 160.625 144.785156 161.214844 C 145.375 161.800781 146.167969 162.128906 147 162.128906 C 147.832031 162.128906 148.625 161.800781 149.214844 161.214844 C 149.800781 160.625 150.128906 159.832031 150.128906 159 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 183.128906 146 C 183.128906 145.167969 182.800781 144.375 182.214844 143.785156 C 181.625 143.199219 180.832031 142.871094 180 142.871094 C 179.167969 142.871094 178.375 143.199219 177.785156 143.785156 C 177.199219 144.375 176.871094 145.167969 176.871094 146 C 176.871094 146.832031 177.199219 147.625 177.785156 148.214844 C 178.375 148.800781 179.167969 149.128906 180 149.128906 C 180.832031 149.128906 181.625 148.800781 182.214844 148.214844 C 182.800781 147.625 183.128906 146.832031 183.128906 146 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 217.128906 128 C 217.128906 127.167969 216.800781 126.375 216.214844 125.785156 C 215.625 125.199219 214.832031 124.871094 214 124.871094 C 213.167969 124.871094 212.375 125.199219 211.785156 125.785156 C 211.199219 126.375 210.871094 127.167969 210.871094 128 C 210.871094 128.832031 211.199219 129.625 211.785156 130.214844 C 212.375 130.800781 213.167969 131.128906 214 131.128906 C 214.832031 131.128906 215.625 130.800781 216.214844 130.214844 C 216.800781 129.625 217.128906 128.832031 217.128906 128 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 251.128906 108 C 251.128906 107.167969 250.800781 106.375 250.214844 105.785156 C 249.625 105.199219 248.832031 104.871094 248 104.871094 C 247.167969 104.871094 246.375 105.199219 245.785156 105.785156 C 245.199219 106.375 244.871094 107.167969 244.871094 108 C 244.871094 108.832031 245.199219 109.625 245.785156 110.214844 C 246.375 110.800781 247.167969 111.128906 248 111.128906 C 248.832031 111.128906 249.625 110.800781 250.214844 110.214844 C 250.800781 109.625 251.128906 108.832031 251.128906 108 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 284.128906 85 C 284.128906 84.167969 283.800781 83.375 283.214844 82.785156 C 282.625 82.199219 281.832031 81.871094 281 81.871094 C 280.167969 81.871094 279.375 82.199219 278.785156 82.785156 C 278.199219 83.375 277.871094 84.167969 277.871094 85 C 277.871094 85.832031 278.199219 86.625 278.785156 87.214844 C 279.375 87.800781 280.167969 88.128906 281 88.128906 C 281.832031 88.128906 282.625 87.800781 283.214844 87.214844 C 283.800781 86.625 284.128906 85.832031 284.128906 85 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 318.128906 59 C 318.128906 58.167969 317.800781 57.375 317.214844 56.785156 C 316.625 56.199219 315.832031 55.871094 315 55.871094 C 314.167969 55.871094 313.375 56.199219 312.785156 56.785156 C 312.199219 57.375 311.871094 58.167969 311.871094 59 C 311.871094 59.832031 312.199219 60.625 312.785156 61.214844 C 313.375 61.800781 314.167969 62.128906 315 62.128906 C 315.832031 62.128906 316.625 61.800781 317.214844 61.214844 C 317.800781 60.625 318.128906 59.832031 318.128906 59 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 352.128906 31 C 352.128906 30.167969 351.800781 29.375 351.214844 28.785156 C 350.625 28.199219 349.832031 27.871094 349 27.871094 C 348.167969 27.871094 347.375 28.199219 346.785156 28.785156 C 346.199219 29.375 345.871094 30.167969 345.871094 31 C 345.871094 31.832031 346.199219 32.625 346.785156 33.214844 C 347.375 33.800781 348.167969 34.128906 349 34.128906 C 349.832031 34.128906 350.625 33.800781 351.214844 33.214844 C 351.800781 32.625 352.128906 31.832031 352.128906 31 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 49.128906 205 C 49.128906 204.167969 48.800781 203.375 48.214844 202.785156 C 47.625 202.199219 46.832031 201.871094 46 201.871094 C 45.167969 201.871094 44.375 202.199219 43.785156 202.785156 C 43.199219 203.375 42.871094 204.167969 42.871094 205 C 42.871094 205.832031 43.199219 206.625 43.785156 207.214844 C 44.375 207.800781 45.167969 208.128906 46 208.128906 C 46.832031 208.128906 47.625 207.800781 48.214844 207.214844 C 48.800781 206.625 49.128906 205.832031 49.128906 205 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 82.128906 199 C 82.128906 198.167969 81.800781 197.375 81.214844 196.785156 C 80.625 196.199219 79.832031 195.871094 79 195.871094 C 78.167969 195.871094 77.375 196.199219 76.785156 196.785156 C 76.199219 197.375 75.871094 198.167969 75.871094 199 C 75.871094 199.832031 76.199219 200.625 76.785156 201.214844 C 77.375 201.800781 78.167969 202.128906 79 202.128906 C 79.832031 202.128906 80.625 201.800781 81.214844 201.214844 C 81.800781 200.625 82.128906 199.832031 82.128906 199 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 116.128906 190 C 116.128906 189.167969 115.800781 188.375 115.214844 187.785156 C 114.625 187.199219 113.832031 186.871094 113 186.871094 C 112.167969 186.871094 111.375 187.199219 110.785156 187.785156 C 110.199219 188.375 109.871094 189.167969 109.871094 190 C 109.871094 190.832031 110.199219 191.625 110.785156 192.214844 C 111.375 192.800781 112.167969 193.128906 113 193.128906 C 113.832031 193.128906 114.625 192.800781 115.214844 192.214844 C 115.800781 191.625 116.128906 190.832031 116.128906 190 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 150.128906 177 C 150.128906 176.167969 149.800781 175.375 149.214844 174.785156 C 148.625 174.199219 147.832031 173.871094 147 173.871094 C 146.167969 173.871094 145.375 174.199219 144.785156 174.785156 C 144.199219 175.375 143.871094 176.167969 143.871094 177 C 143.871094 177.832031 144.199219 178.625 144.785156 179.214844 C 145.375 179.800781 146.167969 180.128906 147 180.128906 C 147.832031 180.128906 148.625 179.800781 149.214844 179.214844 C 149.800781 178.625 150.128906 177.832031 150.128906 177 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 183.128906 159 C 183.128906 158.167969 182.800781 157.375 182.214844 156.785156 C 181.625 156.199219 180.832031 155.871094 180 155.871094 C 179.167969 155.871094 178.375 156.199219 177.785156 156.785156 C 177.199219 157.375 176.871094 158.167969 176.871094 159 C 176.871094 159.832031 177.199219 160.625 177.785156 161.214844 C 178.375 161.800781 179.167969 162.128906 180 162.128906 C 180.832031 162.128906 181.625 161.800781 182.214844 161.214844 C 182.800781 160.625 183.128906 159.832031 183.128906 159 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 217.128906 138 C 217.128906 137.167969 216.800781 136.375 216.214844 135.785156 C 215.625 135.199219 214.832031 134.871094 214 134.871094 C 213.167969 134.871094 212.375 135.199219 211.785156 135.785156 C 211.199219 136.375 210.871094 137.167969 210.871094 138 C 210.871094 138.832031 211.199219 139.625 211.785156 140.214844 C 212.375 140.800781 213.167969 141.128906 214 141.128906 C 214.832031 141.128906 215.625 140.800781 216.214844 140.214844 C 216.800781 139.625 217.128906 138.832031 217.128906 138 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 251.128906 115 C 251.128906 114.167969 250.800781 113.375 250.214844 112.785156 C 249.625 112.199219 248.832031 111.871094 248 111.871094 C 247.167969 111.871094 246.375 112.199219 245.785156 112.785156 C 245.199219 113.375 244.871094 114.167969 244.871094 115 C 244.871094 115.832031 245.199219 116.625 245.785156 117.214844 C 246.375 117.800781 247.167969 118.128906 248 118.128906 C 248.832031 118.128906 249.625 117.800781 250.214844 117.214844 C 250.800781 116.625 251.128906 115.832031 251.128906 115 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 284.128906 91 C 284.128906 90.167969 283.800781 89.375 283.214844 88.785156 C 282.625 88.199219 281.832031 87.871094 281 87.871094 C 280.167969 87.871094 279.375 88.199219 278.785156 88.785156 C 278.199219 89.375 277.871094 90.167969 277.871094 91 C 277.871094 91.832031 278.199219 92.625 278.785156 93.214844 C 279.375 93.800781 280.167969 94.128906 281 94.128906 C 281.832031 94.128906 282.625 93.800781 283.214844 93.214844 C 283.800781 92.625 284.128906 91.832031 284.128906 91 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 318.128906 65 C 318.128906 64.167969 317.800781 63.375 317.214844 62.785156 C 316.625 62.199219 315.832031 61.871094 315 61.871094 C 314.167969 61.871094 313.375 62.199219 312.785156 62.785156 C 312.199219 63.375 311.871094 64.167969 311.871094 65 C 311.871094 65.832031 312.199219 66.625 312.785156 67.214844 C 313.375 67.800781 314.167969 68.128906 315 68.128906 C 315.832031 68.128906 316.625 67.800781 317.214844 67.214844 C 317.800781 66.625 318.128906 65.832031 318.128906 65 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 352.128906 38 C 352.128906 37.167969 351.800781 36.375 351.214844 35.785156 C 350.625 35.199219 349.832031 34.871094 349 34.871094 C 348.167969 34.871094 347.375 35.199219 346.785156 35.785156 C 346.199219 36.375 345.871094 37.167969 345.871094 38 C 345.871094 38.832031 346.199219 39.625 346.785156 40.214844 C 347.375 40.800781 348.167969 41.128906 349 41.128906 C 349.832031 41.128906 350.625 40.800781 351.214844 40.214844 C 351.800781 39.625 352.128906 38.832031 352.128906 38 Z "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.5;stroke-linecap:square;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 220.007812 L 33 220.007812 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.5;stroke-linecap:square;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 220.007812 L 33 21 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.5;stroke-linecap:square;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 21 L 355 21 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.5;stroke-linecap:square;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 21 L 355 220.007812 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 90.226562 220.007812 L 90.226562 216.785156 "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-1" x="84.725786" y="232.006944"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-2" x="90.28731" y="232.006944"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 201.996094 220.007812 L 201.996094 216.785156 "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-1" x="193.49443" y="232.006944"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-2" x="199.055953" y="232.006944"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-2" x="204.617477" y="232.006944"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 313.761719 220.007812 L 313.761719 216.785156 "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-1" x="302.763074" y="232.006944"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-2" x="308.324597" y="232.006944"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-2" x="313.88612" y="232.006944"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-2" x="319.447644" y="232.006944"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 45.75 220.007812 L 45.75 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 56.578125 220.007812 L 56.578125 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 65.429688 220.007812 L 65.429688 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 72.914062 220.007812 L 72.914062 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 79.394531 220.007812 L 79.394531 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 85.113281 220.007812 L 85.113281 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 123.871094 220.007812 L 123.871094 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 143.554688 220.007812 L 143.554688 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 157.515625 220.007812 L 157.515625 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 168.347656 220.007812 L 168.347656 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 177.199219 220.007812 L 177.199219 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 184.679688 220.007812 L 184.679688 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 191.164062 220.007812 L 191.164062 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 196.878906 220.007812 L 196.878906 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 235.640625 220.007812 L 235.640625 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 255.320312 220.007812 L 255.320312 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 269.285156 220.007812 L 269.285156 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 280.117188 220.007812 L 280.117188 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 288.96875 220.007812 L 288.96875 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 296.449219 220.007812 L 296.449219 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 302.929688 220.007812 L 302.929688 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 308.648438 220.007812 L 308.648438 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 347.410156 220.007812 L 347.410156 218.398438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 180.734375 L 36.21875 180.734375 "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-3" x="24" y="183.235493"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 146.960938 L 36.21875 146.960938 "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-4" x="24" y="149.45964"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 121.410156 L 36.21875 121.410156 "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-1" x="19" y="123.909193"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-2" x="24.561523" y="123.909193"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 95.859375 L 36.21875 95.859375 "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-3" x="19" y="98.358747"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-2" x="24.561523" y="98.358747"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 62.082031 L 36.21875 62.082031 "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-4" x="19" y="64.582894"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-2" x="24.561523" y="64.582894"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 206.285156 L 34.609375 206.285156 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 165.789062 L 34.609375 165.789062 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 155.183594 L 34.609375 155.183594 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 140.238281 L 34.609375 140.238281 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 134.558594 L 34.609375 134.558594 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 129.632812 L 34.609375 129.632812 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 125.292969 L 34.609375 125.292969 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 80.914062 L 34.609375 80.914062 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 70.308594 L 34.609375 70.308594 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 33 36.53125 L 34.609375 36.53125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 90.226562 21 L 90.226562 24.21875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 201.996094 21 L 201.996094 24.21875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 313.761719 21 L 313.761719 24.21875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 45.75 21 L 45.75 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 56.578125 21 L 56.578125 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 65.429688 21 L 65.429688 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 72.914062 21 L 72.914062 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 79.394531 21 L 79.394531 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 85.113281 21 L 85.113281 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 123.871094 21 L 123.871094 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 143.554688 21 L 143.554688 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 157.515625 21 L 157.515625 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 168.347656 21 L 168.347656 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 177.199219 21 L 177.199219 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 184.679688 21 L 184.679688 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 191.164062 21 L 191.164062 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 196.878906 21 L 196.878906 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 235.640625 21 L 235.640625 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 255.320312 21 L 255.320312 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 269.285156 21 L 269.285156 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 280.117188 21 L 280.117188 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 288.96875 21 L 288.96875 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 296.449219 21 L 296.449219 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 302.929688 21 L 302.929688 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 308.648438 21 L 308.648438 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 347.410156 21 L 347.410156 22.609375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 180.734375 L 351.78125 180.734375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 146.960938 L 351.78125 146.960938 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 121.410156 L 351.78125 121.410156 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 95.859375 L 351.78125 95.859375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 62.082031 L 351.78125 62.082031 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 206.285156 L 353.390625 206.285156 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 165.789062 L 353.390625 165.789062 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 155.183594 L 353.390625 155.183594 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 140.238281 L 353.390625 140.238281 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 134.558594 L 353.390625 134.558594 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 129.632812 L 353.390625 129.632812 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 125.292969 L 353.390625 125.292969 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 80.914062 L 353.390625 80.914062 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 70.308594 L 353.390625 70.308594 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 36.53125 L 353.390625 36.53125 "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-5" x="172.5" y="251.006944"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-6" x="178.608398" y="251.006944"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-7" x="184.169922" y="251.006944"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-8" x="189.731445" y="251.006944"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-9" x="194.731445" y="251.006944"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-10" x="197.509766" y="251.006944"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-11" x="199.731445" y="251.006944"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-7" x="205.292969" y="251.006944"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-12" x="210.854492" y="251.006944"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph1-1" x="9" y="140.003472"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph1-2" x="9" y="133.33355"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph1-3" x="9" y="127.772027"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph1-4" x="9" y="122.772027"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph1-5" x="9" y="117.210503"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph1-6" x="9" y="111.64898"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph1-7" x="9" y="106.087457"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-1" x="122" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-2" x="130.666016" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-3" x="137.339844" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-4" x="147.335938" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-5" x="154.009766" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-6" x="156.675781" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-7" x="159.341797" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-8" x="166.015625" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-5" x="169.349609" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-2" x="172.015625" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-9" x="178.689453" y="12"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-8" x="188" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-5" x="191.333984" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-3" x="194" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-10" x="203.996094" y="12"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-2" x="214" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-11" x="220.673828" y="12"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-3" x="227" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-2" x="236.996094" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-12" x="243.669922" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-13" x="250.34375" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-6" x="257.017578" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-10" x="259.683594" y="12"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 382.148438 116 C 382.148438 115.164062 381.816406 114.363281 381.226562 113.773438 C 380.636719 113.183594 379.835938 112.851562 379 112.851562 C 378.164062 112.851562 377.363281 113.183594 376.773438 113.773438 C 376.183594 114.363281 375.851562 115.164062 375.851562 116 C 375.851562 116.835938 376.183594 117.636719 376.773438 118.226562 C 377.363281 118.816406 378.164062 119.148438 379 119.148438 C 379.835938 119.148438 380.636719 118.816406 381.226562 118.226562 C 381.816406 117.636719 382.148438 116.835938 382.148438 116 Z "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(0%,0%,0%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-1" x="391" y="120.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-2" x="399.670898" y="120.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-2" x="406.901367" y="120.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-3" x="414.131836" y="120.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-4" x="420.631836" y="120.28418"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(0%,0%,0%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-5" x="424" y="120.28418"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(0%,0%,0%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-6" x="428" y="120.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-7" x="436.670898" y="120.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-4" x="443.170898" y="120.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-8" x="446.783203" y="120.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-2" x="454.013672" y="120.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-9" x="461.244141" y="120.28418"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 382.148438 139 C 382.148438 138.164062 381.816406 137.363281 381.226562 136.773438 C 380.636719 136.183594 379.835938 135.851562 379 135.851562 C 378.164062 135.851562 377.363281 136.183594 376.773438 136.773438 C 376.183594 137.363281 375.851562 138.164062 375.851562 139 C 375.851562 139.835938 376.183594 140.636719 376.773438 141.226562 C 377.363281 141.816406 378.164062 142.148438 379 142.148438 C 379.835938 142.148438 380.636719 141.816406 381.226562 141.226562 C 381.816406 140.636719 382.148438 139.835938 382.148438 139 Z "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(0%,0%,0%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-10" x="391" y="143.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-7" x="398.230469" y="143.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-11" x="404.730469" y="143.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-12" x="411.960938" y="143.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-9" x="414.849609" y="143.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-13" x="422.080078" y="143.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-14" x="429.310547" y="143.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-14" x="436.541016" y="143.28418"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
</g> |
|||
</svg> |
|||
|
After 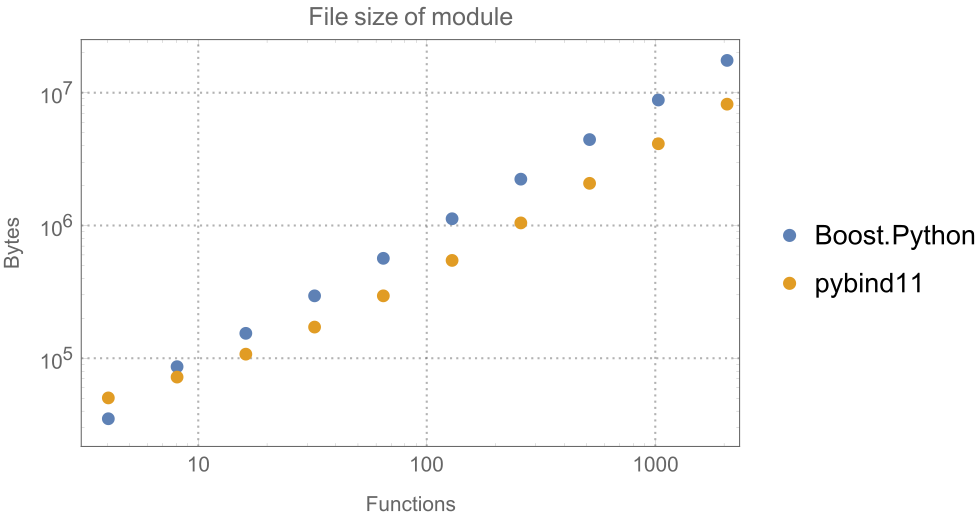
Width: 975 | Height: 513 | Size: 40 KiB |
@ -0,0 +1,427 @@ |
|||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> |
|||
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink" width="468pt" height="246pt" viewBox="0 0 468 246" version="1.1"> |
|||
<defs> |
|||
<g> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-0"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d=""/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-1"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 3.726562 0 L 2.847656 0 L 2.847656 -5.601562 C 2.636719 -5.398438 2.359375 -5.195312 2.015625 -4.996094 C 1.671875 -4.792969 1.363281 -4.640625 1.089844 -4.539062 L 1.089844 -5.390625 C 1.582031 -5.621094 2.011719 -5.902344 2.378906 -6.230469 C 2.746094 -6.558594 3.007812 -6.878906 3.160156 -7.1875 L 3.726562 -7.1875 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-2"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.414062 -3.53125 C 0.414062 -4.375 0.503906 -5.058594 0.675781 -5.574219 C 0.851562 -6.089844 1.109375 -6.488281 1.453125 -6.765625 C 1.796875 -7.046875 2.226562 -7.1875 2.75 -7.1875 C 3.132812 -7.1875 3.46875 -7.109375 3.757812 -6.957031 C 4.046875 -6.800781 4.289062 -6.578125 4.476562 -6.285156 C 4.664062 -5.996094 4.8125 -5.640625 4.921875 -5.222656 C 5.03125 -4.804688 5.082031 -4.238281 5.082031 -3.53125 C 5.082031 -2.691406 4.996094 -2.011719 4.824219 -1.496094 C 4.652344 -0.980469 4.394531 -0.582031 4.050781 -0.300781 C 3.707031 -0.0195312 3.273438 0.121094 2.75 0.121094 C 2.058594 0.121094 1.515625 -0.125 1.125 -0.621094 C 0.652344 -1.214844 0.414062 -2.1875 0.414062 -3.53125 Z M 1.320312 -3.53125 C 1.320312 -2.355469 1.457031 -1.574219 1.730469 -1.183594 C 2.007812 -0.796875 2.34375 -0.601562 2.75 -0.601562 C 3.152344 -0.601562 3.492188 -0.796875 3.765625 -1.1875 C 4.042969 -1.578125 4.179688 -2.359375 4.179688 -3.53125 C 4.179688 -4.710938 4.042969 -5.492188 3.765625 -5.878906 C 3.492188 -6.265625 3.148438 -6.460938 2.738281 -6.460938 C 2.335938 -6.460938 2.011719 -6.289062 1.773438 -5.945312 C 1.46875 -5.511719 1.320312 -4.707031 1.320312 -3.53125 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-3"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.820312 0 L 0.820312 -7.15625 L 5.648438 -7.15625 L 5.648438 -6.3125 L 1.765625 -6.3125 L 1.765625 -4.097656 L 5.125 -4.097656 L 5.125 -3.25 L 1.765625 -3.25 L 1.765625 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-4"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 4.058594 0 L 4.058594 -0.761719 C 3.65625 -0.175781 3.105469 0.117188 2.414062 0.117188 C 2.105469 0.117188 1.820312 0.0585938 1.554688 -0.0585938 C 1.289062 -0.175781 1.09375 -0.324219 0.964844 -0.5 C 0.835938 -0.679688 0.746094 -0.894531 0.695312 -1.152344 C 0.65625 -1.324219 0.640625 -1.597656 0.640625 -1.972656 L 0.640625 -5.1875 L 1.519531 -5.1875 L 1.519531 -2.308594 C 1.519531 -1.851562 1.535156 -1.542969 1.570312 -1.382812 C 1.625 -1.152344 1.746094 -0.96875 1.921875 -0.835938 C 2.101562 -0.703125 2.324219 -0.640625 2.585938 -0.640625 C 2.851562 -0.640625 3.097656 -0.707031 3.328125 -0.84375 C 3.5625 -0.976562 3.726562 -1.160156 3.820312 -1.394531 C 3.917969 -1.625 3.964844 -1.964844 3.964844 -2.40625 L 3.964844 -5.1875 L 4.84375 -5.1875 L 4.84375 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-5"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.660156 0 L 0.660156 -5.1875 L 1.449219 -5.1875 L 1.449219 -4.449219 C 1.832031 -5.019531 2.382812 -5.304688 3.101562 -5.304688 C 3.414062 -5.304688 3.699219 -5.246094 3.960938 -5.132812 C 4.222656 -5.023438 4.421875 -4.875 4.550781 -4.691406 C 4.679688 -4.507812 4.773438 -4.292969 4.824219 -4.042969 C 4.855469 -3.878906 4.875 -3.59375 4.875 -3.1875 L 4.875 0 L 3.992188 0 L 3.992188 -3.15625 C 3.992188 -3.511719 3.960938 -3.78125 3.890625 -3.957031 C 3.824219 -4.132812 3.703125 -4.277344 3.527344 -4.382812 C 3.351562 -4.488281 3.148438 -4.539062 2.914062 -4.539062 C 2.539062 -4.539062 2.21875 -4.421875 1.945312 -4.183594 C 1.671875 -3.945312 1.539062 -3.496094 1.539062 -2.832031 L 1.539062 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-6"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 4.042969 -1.898438 L 4.90625 -1.789062 C 4.8125 -1.191406 4.570312 -0.726562 4.183594 -0.386719 C 3.792969 -0.0507812 3.316406 0.117188 2.75 0.117188 C 2.039062 0.117188 1.46875 -0.113281 1.039062 -0.578125 C 0.605469 -1.042969 0.390625 -1.707031 0.390625 -2.574219 C 0.390625 -3.132812 0.484375 -3.625 0.667969 -4.042969 C 0.855469 -4.460938 1.136719 -4.777344 1.515625 -4.988281 C 1.894531 -5.199219 2.308594 -5.304688 2.753906 -5.304688 C 3.316406 -5.304688 3.777344 -5.160156 4.136719 -4.875 C 4.492188 -4.589844 4.722656 -4.1875 4.824219 -3.664062 L 3.96875 -3.53125 C 3.886719 -3.878906 3.746094 -4.140625 3.539062 -4.316406 C 3.332031 -4.492188 3.082031 -4.578125 2.789062 -4.578125 C 2.34375 -4.578125 1.984375 -4.421875 1.710938 -4.105469 C 1.433594 -3.789062 1.292969 -3.285156 1.292969 -2.597656 C 1.292969 -1.902344 1.425781 -1.394531 1.695312 -1.078125 C 1.960938 -0.761719 2.308594 -0.605469 2.738281 -0.605469 C 3.085938 -0.605469 3.371094 -0.710938 3.601562 -0.921875 C 3.835938 -1.132812 3.980469 -1.460938 4.042969 -1.898438 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-7"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 2.578125 -0.785156 L 2.703125 -0.0078125 C 2.457031 0.0429688 2.234375 0.0703125 2.039062 0.0703125 C 1.722656 0.0703125 1.476562 0.0195312 1.296875 -0.0820312 C 1.121094 -0.183594 1 -0.316406 0.929688 -0.480469 C 0.855469 -0.644531 0.820312 -0.992188 0.820312 -1.519531 L 0.820312 -4.5 L 0.175781 -4.5 L 0.175781 -5.1875 L 0.820312 -5.1875 L 0.820312 -6.46875 L 1.695312 -6.996094 L 1.695312 -5.1875 L 2.578125 -5.1875 L 2.578125 -4.5 L 1.695312 -4.5 L 1.695312 -1.46875 C 1.695312 -1.21875 1.710938 -1.058594 1.742188 -0.984375 C 1.773438 -0.914062 1.820312 -0.859375 1.890625 -0.816406 C 1.960938 -0.773438 2.0625 -0.75 2.191406 -0.75 C 2.289062 -0.75 2.417969 -0.761719 2.578125 -0.785156 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-8"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.664062 -6.148438 L 0.664062 -7.15625 L 1.542969 -7.15625 L 1.542969 -6.148438 Z M 0.664062 0 L 0.664062 -5.1875 L 1.542969 -5.1875 L 1.542969 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-9"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.332031 -2.59375 C 0.332031 -3.554688 0.597656 -4.265625 1.132812 -4.726562 C 1.578125 -5.109375 2.121094 -5.304688 2.765625 -5.304688 C 3.476562 -5.304688 4.058594 -5.070312 4.511719 -4.601562 C 4.964844 -4.132812 5.191406 -3.488281 5.191406 -2.664062 C 5.191406 -2 5.089844 -1.472656 4.890625 -1.089844 C 4.691406 -0.707031 4.398438 -0.410156 4.015625 -0.199219 C 3.632812 0.0117188 3.214844 0.117188 2.765625 0.117188 C 2.039062 0.117188 1.449219 -0.117188 1.003906 -0.582031 C 0.554688 -1.046875 0.332031 -1.71875 0.332031 -2.59375 Z M 1.234375 -2.59375 C 1.234375 -1.929688 1.378906 -1.429688 1.671875 -1.101562 C 1.960938 -0.769531 2.324219 -0.605469 2.765625 -0.605469 C 3.199219 -0.605469 3.5625 -0.773438 3.851562 -1.101562 C 4.140625 -1.433594 4.289062 -1.941406 4.289062 -2.621094 C 4.289062 -3.261719 4.140625 -3.75 3.851562 -4.078125 C 3.558594 -4.410156 3.195312 -4.574219 2.765625 -4.574219 C 2.324219 -4.574219 1.960938 -4.410156 1.671875 -4.082031 C 1.382812 -3.753906 1.234375 -3.257812 1.234375 -2.59375 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph0-10"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.308594 -1.546875 L 1.175781 -1.683594 C 1.226562 -1.335938 1.363281 -1.070312 1.585938 -0.882812 C 1.808594 -0.699219 2.117188 -0.605469 2.519531 -0.605469 C 2.921875 -0.605469 3.222656 -0.6875 3.417969 -0.851562 C 3.613281 -1.015625 3.710938 -1.210938 3.710938 -1.429688 C 3.710938 -1.628906 3.625 -1.785156 3.453125 -1.898438 C 3.332031 -1.976562 3.03125 -2.078125 2.554688 -2.195312 C 1.910156 -2.359375 1.460938 -2.5 1.214844 -2.621094 C 0.964844 -2.738281 0.777344 -2.902344 0.648438 -3.113281 C 0.519531 -3.324219 0.453125 -3.554688 0.453125 -3.808594 C 0.453125 -4.039062 0.507812 -4.253906 0.613281 -4.449219 C 0.71875 -4.648438 0.863281 -4.8125 1.046875 -4.941406 C 1.183594 -5.042969 1.367188 -5.128906 1.605469 -5.199219 C 1.839844 -5.269531 2.09375 -5.304688 2.363281 -5.304688 C 2.769531 -5.304688 3.128906 -5.242188 3.433594 -5.125 C 3.742188 -5.007812 3.96875 -4.851562 4.117188 -4.652344 C 4.261719 -4.453125 4.363281 -4.183594 4.417969 -3.847656 L 3.558594 -3.730469 C 3.519531 -3.996094 3.40625 -4.207031 3.21875 -4.355469 C 3.03125 -4.503906 2.769531 -4.578125 2.425781 -4.578125 C 2.023438 -4.578125 1.734375 -4.511719 1.5625 -4.378906 C 1.390625 -4.246094 1.304688 -4.089844 1.304688 -3.910156 C 1.304688 -3.796875 1.339844 -3.695312 1.410156 -3.601562 C 1.484375 -3.507812 1.59375 -3.429688 1.75 -3.367188 C 1.835938 -3.335938 2.09375 -3.261719 2.523438 -3.144531 C 3.144531 -2.976562 3.578125 -2.84375 3.824219 -2.738281 C 4.070312 -2.632812 4.265625 -2.476562 4.40625 -2.273438 C 4.546875 -2.074219 4.613281 -1.824219 4.613281 -1.523438 C 4.613281 -1.230469 4.527344 -0.953125 4.359375 -0.695312 C 4.1875 -0.4375 3.941406 -0.238281 3.617188 -0.09375 C 3.296875 0.046875 2.929688 0.117188 2.523438 0.117188 C 1.851562 0.117188 1.335938 -0.0234375 0.984375 -0.304688 C 0.632812 -0.582031 0.40625 -0.996094 0.308594 -1.546875 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph1-0"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d=""/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph1-1"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.375 -1.6875 L 1.203125 -1.757812 C 1.265625 -1.351562 1.410156 -1.050781 1.632812 -0.847656 C 1.855469 -0.644531 2.125 -0.539062 2.445312 -0.539062 C 2.824219 -0.539062 3.148438 -0.683594 3.410156 -0.972656 C 3.671875 -1.257812 3.804688 -1.640625 3.804688 -2.113281 C 3.804688 -2.566406 3.679688 -2.921875 3.425781 -3.179688 C 3.171875 -3.441406 2.839844 -3.574219 2.429688 -3.574219 C 2.175781 -3.574219 1.945312 -3.515625 1.742188 -3.398438 C 1.535156 -3.28125 1.375 -3.132812 1.257812 -2.949219 L 0.515625 -3.046875 L 1.136719 -6.355469 L 4.34375 -6.355469 L 4.34375 -5.597656 L 1.769531 -5.597656 L 1.421875 -3.867188 C 1.808594 -4.136719 2.214844 -4.273438 2.640625 -4.273438 C 3.203125 -4.273438 3.679688 -4.078125 4.066406 -3.6875 C 4.453125 -3.296875 4.644531 -2.796875 4.644531 -2.183594 C 4.644531 -1.601562 4.476562 -1.097656 4.136719 -0.671875 C 3.722656 -0.152344 3.15625 0.109375 2.445312 0.109375 C 1.859375 0.109375 1.378906 -0.0546875 1.007812 -0.382812 C 0.636719 -0.710938 0.425781 -1.144531 0.375 -1.6875 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph1-2"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 4.476562 -4.863281 L 3.691406 -4.804688 C 3.621094 -5.113281 3.523438 -5.339844 3.390625 -5.480469 C 3.179688 -5.707031 2.914062 -5.820312 2.601562 -5.820312 C 2.351562 -5.820312 2.128906 -5.75 1.9375 -5.609375 C 1.6875 -5.425781 1.492188 -5.160156 1.347656 -4.8125 C 1.203125 -4.464844 1.132812 -3.96875 1.125 -3.320312 C 1.316406 -3.613281 1.546875 -3.828125 1.824219 -3.96875 C 2.097656 -4.109375 2.386719 -4.179688 2.6875 -4.179688 C 3.214844 -4.179688 3.664062 -3.984375 4.035156 -3.597656 C 4.40625 -3.210938 4.59375 -2.707031 4.59375 -2.09375 C 4.59375 -1.6875 4.503906 -1.3125 4.332031 -0.964844 C 4.15625 -0.617188 3.917969 -0.351562 3.613281 -0.167969 C 3.308594 0.015625 2.960938 0.109375 2.574219 0.109375 C 1.914062 0.109375 1.378906 -0.132812 0.960938 -0.617188 C 0.546875 -1.101562 0.339844 -1.902344 0.339844 -3.015625 C 0.339844 -4.261719 0.570312 -5.164062 1.027344 -5.730469 C 1.429688 -6.222656 1.96875 -6.46875 2.648438 -6.46875 C 3.15625 -6.46875 3.570312 -6.328125 3.894531 -6.042969 C 4.21875 -5.757812 4.414062 -5.367188 4.476562 -4.863281 Z M 1.25 -2.085938 C 1.25 -1.8125 1.304688 -1.554688 1.421875 -1.304688 C 1.539062 -1.054688 1.699219 -0.867188 1.90625 -0.734375 C 2.113281 -0.605469 2.332031 -0.539062 2.5625 -0.539062 C 2.894531 -0.539062 3.183594 -0.675781 3.421875 -0.945312 C 3.664062 -1.214844 3.785156 -1.582031 3.785156 -2.042969 C 3.785156 -2.488281 3.664062 -2.839844 3.429688 -3.097656 C 3.191406 -3.351562 2.890625 -3.480469 2.53125 -3.480469 C 2.171875 -3.480469 1.871094 -3.351562 1.621094 -3.097656 C 1.371094 -2.839844 1.25 -2.503906 1.25 -2.085938 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph1-3"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.425781 -5.597656 L 0.425781 -6.359375 L 4.597656 -6.359375 L 4.597656 -5.742188 C 4.1875 -5.304688 3.78125 -4.726562 3.378906 -4.003906 C 2.976562 -3.28125 2.664062 -2.535156 2.445312 -1.769531 C 2.285156 -1.230469 2.183594 -0.640625 2.140625 0 L 1.328125 0 C 1.335938 -0.507812 1.4375 -1.117188 1.625 -1.835938 C 1.816406 -2.554688 2.089844 -3.246094 2.445312 -3.914062 C 2.800781 -4.578125 3.179688 -5.140625 3.582031 -5.597656 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-0"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d=""/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-1"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0 -0.734375 L -7.15625 -0.734375 L -7.15625 -3.417969 C -7.15625 -3.964844 -7.085938 -4.402344 -6.941406 -4.734375 C -6.796875 -5.0625 -6.574219 -5.324219 -6.273438 -5.511719 C -5.972656 -5.699219 -5.65625 -5.789062 -5.328125 -5.789062 C -5.023438 -5.789062 -4.734375 -5.707031 -4.460938 -5.542969 C -4.191406 -5.375 -3.976562 -5.125 -3.808594 -4.789062 C -3.679688 -5.222656 -3.464844 -5.554688 -3.160156 -5.789062 C -2.851562 -6.023438 -2.492188 -6.136719 -2.074219 -6.136719 C -1.738281 -6.136719 -1.429688 -6.066406 -1.140625 -5.925781 C -0.851562 -5.785156 -0.628906 -5.609375 -0.472656 -5.398438 C -0.316406 -5.191406 -0.199219 -4.929688 -0.121094 -4.617188 C -0.0390625 -4.304688 0 -3.917969 0 -3.460938 Z M -4.148438 -1.679688 L -4.148438 -3.226562 C -4.148438 -3.648438 -4.179688 -3.949219 -4.234375 -4.132812 C -4.304688 -4.371094 -4.421875 -4.554688 -4.589844 -4.675781 C -4.757812 -4.796875 -4.964844 -4.859375 -5.214844 -4.859375 C -5.453125 -4.859375 -5.660156 -4.800781 -5.84375 -4.6875 C -6.023438 -4.574219 -6.148438 -4.410156 -6.214844 -4.199219 C -6.28125 -3.988281 -6.3125 -3.625 -6.3125 -3.109375 L -6.3125 -1.679688 Z M -0.84375 -1.679688 L -0.84375 -3.460938 C -0.84375 -3.765625 -0.855469 -3.984375 -0.878906 -4.105469 C -0.917969 -4.324219 -0.984375 -4.507812 -1.074219 -4.652344 C -1.164062 -4.800781 -1.296875 -4.921875 -1.472656 -5.015625 C -1.648438 -5.109375 -1.847656 -5.15625 -2.074219 -5.15625 C -2.34375 -5.15625 -2.574219 -5.085938 -2.769531 -4.953125 C -2.96875 -4.816406 -3.105469 -4.625 -3.1875 -4.382812 C -3.265625 -4.140625 -3.304688 -3.789062 -3.304688 -3.335938 L -3.304688 -1.679688 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-2"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 1.996094 -0.621094 L 1.171875 -0.523438 C 1.222656 -0.714844 1.25 -0.882812 1.25 -1.023438 C 1.25 -1.21875 1.21875 -1.375 1.152344 -1.492188 C 1.085938 -1.609375 0.996094 -1.707031 0.878906 -1.78125 C 0.789062 -1.835938 0.574219 -1.925781 0.226562 -2.050781 C 0.175781 -2.066406 0.105469 -2.09375 0.0078125 -2.128906 L -5.1875 -0.160156 L -5.1875 -1.109375 L -2.183594 -2.1875 C -1.800781 -2.328125 -1.402344 -2.453125 -0.980469 -2.5625 C -1.382812 -2.664062 -1.777344 -2.785156 -2.164062 -2.925781 L -5.1875 -4.03125 L -5.1875 -4.914062 L 0.0859375 -2.9375 C 0.65625 -2.726562 1.050781 -2.5625 1.265625 -2.445312 C 1.554688 -2.289062 1.765625 -2.109375 1.902344 -1.910156 C 2.039062 -1.707031 2.105469 -1.464844 2.105469 -1.1875 C 2.105469 -1.015625 2.070312 -0.828125 1.996094 -0.621094 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-3"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M -0.785156 -2.578125 L -0.0078125 -2.703125 C 0.0429688 -2.457031 0.0703125 -2.234375 0.0703125 -2.039062 C 0.0703125 -1.722656 0.0195312 -1.476562 -0.0820312 -1.296875 C -0.183594 -1.121094 -0.316406 -1 -0.480469 -0.929688 C -0.644531 -0.855469 -0.992188 -0.820312 -1.519531 -0.820312 L -4.5 -0.820312 L -4.5 -0.175781 L -5.1875 -0.175781 L -5.1875 -0.820312 L -6.46875 -0.820312 L -6.996094 -1.695312 L -5.1875 -1.695312 L -5.1875 -2.578125 L -4.5 -2.578125 L -4.5 -1.695312 L -1.46875 -1.695312 C -1.21875 -1.695312 -1.058594 -1.710938 -0.984375 -1.742188 C -0.914062 -1.773438 -0.859375 -1.820312 -0.816406 -1.890625 C -0.773438 -1.960938 -0.75 -2.0625 -0.75 -2.191406 C -0.75 -2.289062 -0.761719 -2.417969 -0.785156 -2.578125 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-4"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M -1.671875 -4.210938 L -1.558594 -5.117188 C -1.027344 -4.972656 -0.617188 -4.707031 -0.320312 -4.320312 C -0.0273438 -3.933594 0.117188 -3.4375 0.117188 -2.835938 C 0.117188 -2.078125 -0.117188 -1.476562 -0.582031 -1.03125 C -1.050781 -0.585938 -1.707031 -0.367188 -2.546875 -0.367188 C -3.421875 -0.367188 -4.097656 -0.589844 -4.578125 -1.039062 C -5.0625 -1.488281 -5.304688 -2.070312 -5.304688 -2.789062 C -5.304688 -3.480469 -5.066406 -4.046875 -4.59375 -4.488281 C -4.121094 -4.925781 -3.457031 -5.148438 -2.601562 -5.148438 C -2.550781 -5.148438 -2.472656 -5.144531 -2.367188 -5.140625 L -2.367188 -1.273438 C -1.796875 -1.304688 -1.363281 -1.46875 -1.058594 -1.757812 C -0.757812 -2.046875 -0.605469 -2.410156 -0.605469 -2.84375 C -0.605469 -3.164062 -0.691406 -3.4375 -0.859375 -3.667969 C -1.027344 -3.894531 -1.296875 -4.074219 -1.671875 -4.210938 Z M -3.089844 -1.324219 L -3.089844 -4.21875 C -3.527344 -4.179688 -3.855469 -4.070312 -4.070312 -3.886719 C -4.410156 -3.605469 -4.578125 -3.242188 -4.578125 -2.796875 C -4.578125 -2.394531 -4.445312 -2.054688 -4.175781 -1.78125 C -3.90625 -1.503906 -3.542969 -1.351562 -3.089844 -1.324219 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph2-5"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M -1.546875 -0.308594 L -1.683594 -1.175781 C -1.335938 -1.226562 -1.070312 -1.363281 -0.882812 -1.585938 C -0.699219 -1.808594 -0.605469 -2.117188 -0.605469 -2.519531 C -0.605469 -2.921875 -0.6875 -3.222656 -0.851562 -3.417969 C -1.015625 -3.613281 -1.210938 -3.710938 -1.429688 -3.710938 C -1.628906 -3.710938 -1.785156 -3.625 -1.898438 -3.453125 C -1.976562 -3.332031 -2.078125 -3.03125 -2.195312 -2.554688 C -2.359375 -1.910156 -2.5 -1.460938 -2.621094 -1.214844 C -2.738281 -0.964844 -2.902344 -0.777344 -3.113281 -0.648438 C -3.324219 -0.519531 -3.554688 -0.453125 -3.808594 -0.453125 C -4.039062 -0.453125 -4.253906 -0.507812 -4.449219 -0.613281 C -4.648438 -0.71875 -4.8125 -0.863281 -4.941406 -1.046875 C -5.042969 -1.183594 -5.128906 -1.367188 -5.199219 -1.605469 C -5.269531 -1.839844 -5.304688 -2.09375 -5.304688 -2.363281 C -5.304688 -2.769531 -5.242188 -3.128906 -5.125 -3.433594 C -5.007812 -3.742188 -4.851562 -3.96875 -4.652344 -4.117188 C -4.453125 -4.261719 -4.183594 -4.363281 -3.847656 -4.417969 L -3.730469 -3.558594 C -3.996094 -3.519531 -4.207031 -3.40625 -4.355469 -3.21875 C -4.503906 -3.03125 -4.578125 -2.769531 -4.578125 -2.425781 C -4.578125 -2.023438 -4.511719 -1.734375 -4.378906 -1.5625 C -4.246094 -1.390625 -4.089844 -1.304688 -3.910156 -1.304688 C -3.796875 -1.304688 -3.695312 -1.339844 -3.601562 -1.410156 C -3.507812 -1.484375 -3.429688 -1.59375 -3.367188 -1.75 C -3.335938 -1.835938 -3.261719 -2.09375 -3.144531 -2.523438 C -2.976562 -3.144531 -2.84375 -3.578125 -2.738281 -3.824219 C -2.632812 -4.070312 -2.476562 -4.265625 -2.273438 -4.40625 C -2.074219 -4.546875 -1.824219 -4.613281 -1.523438 -4.613281 C -1.230469 -4.613281 -0.953125 -4.527344 -0.695312 -4.359375 C -0.4375 -4.1875 -0.238281 -3.941406 -0.09375 -3.617188 C 0.046875 -3.296875 0.117188 -2.929688 0.117188 -2.523438 C 0.117188 -1.851562 -0.0234375 -1.335938 -0.304688 -0.984375 C -0.582031 -0.632812 -0.996094 -0.40625 -1.546875 -0.308594 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-0"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d=""/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-1"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.984375 0 L 0.984375 -8.589844 L 6.78125 -8.589844 L 6.78125 -7.578125 L 2.121094 -7.578125 L 2.121094 -4.914062 L 6.152344 -4.914062 L 6.152344 -3.902344 L 2.121094 -3.902344 L 2.121094 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-2"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.796875 -7.375 L 0.796875 -8.589844 L 1.851562 -8.589844 L 1.851562 -7.375 Z M 0.796875 0 L 0.796875 -6.222656 L 1.851562 -6.222656 L 1.851562 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-3"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.765625 0 L 0.765625 -8.589844 L 1.820312 -8.589844 L 1.820312 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-4"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 5.050781 -2.003906 L 6.140625 -1.867188 C 5.96875 -1.230469 5.648438 -0.738281 5.1875 -0.386719 C 4.722656 -0.0351562 4.125 0.140625 3.40625 0.140625 C 2.496094 0.140625 1.773438 -0.140625 1.238281 -0.699219 C 0.707031 -1.261719 0.4375 -2.046875 0.4375 -3.058594 C 0.4375 -4.105469 0.710938 -4.917969 1.25 -5.496094 C 1.789062 -6.074219 2.484375 -6.363281 3.34375 -6.363281 C 4.175781 -6.363281 4.859375 -6.078125 5.382812 -5.515625 C 5.910156 -4.949219 6.175781 -4.148438 6.175781 -3.125 C 6.175781 -3.0625 6.171875 -2.96875 6.171875 -2.84375 L 1.53125 -2.84375 C 1.570312 -2.160156 1.761719 -1.632812 2.109375 -1.273438 C 2.457031 -0.910156 2.890625 -0.726562 3.410156 -0.726562 C 3.796875 -0.726562 4.125 -0.828125 4.398438 -1.03125 C 4.671875 -1.234375 4.890625 -1.558594 5.050781 -2.003906 Z M 1.585938 -3.710938 L 5.0625 -3.710938 C 5.015625 -4.234375 4.882812 -4.625 4.664062 -4.886719 C 4.328125 -5.292969 3.890625 -5.496094 3.359375 -5.496094 C 2.875 -5.496094 2.464844 -5.335938 2.136719 -5.007812 C 1.804688 -4.683594 1.625 -4.25 1.585938 -3.710938 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-5"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.367188 -1.859375 L 1.414062 -2.023438 C 1.472656 -1.605469 1.632812 -1.28125 1.902344 -1.0625 C 2.167969 -0.839844 2.542969 -0.726562 3.023438 -0.726562 C 3.507812 -0.726562 3.867188 -0.824219 4.101562 -1.023438 C 4.335938 -1.21875 4.453125 -1.453125 4.453125 -1.71875 C 4.453125 -1.957031 4.351562 -2.140625 4.140625 -2.28125 C 3.996094 -2.375 3.640625 -2.492188 3.0625 -2.636719 C 2.289062 -2.832031 1.753906 -3 1.457031 -3.144531 C 1.15625 -3.285156 0.929688 -3.484375 0.777344 -3.734375 C 0.621094 -3.988281 0.546875 -4.265625 0.546875 -4.570312 C 0.546875 -4.847656 0.609375 -5.105469 0.734375 -5.339844 C 0.863281 -5.578125 1.035156 -5.773438 1.253906 -5.929688 C 1.417969 -6.050781 1.640625 -6.152344 1.925781 -6.238281 C 2.207031 -6.320312 2.511719 -6.363281 2.835938 -6.363281 C 3.324219 -6.363281 3.753906 -6.292969 4.121094 -6.152344 C 4.492188 -6.011719 4.765625 -5.820312 4.9375 -5.582031 C 5.113281 -5.339844 5.234375 -5.019531 5.304688 -4.617188 L 4.273438 -4.476562 C 4.226562 -4.796875 4.089844 -5.046875 3.863281 -5.226562 C 3.640625 -5.40625 3.320312 -5.496094 2.914062 -5.496094 C 2.429688 -5.496094 2.082031 -5.414062 1.875 -5.257812 C 1.667969 -5.097656 1.5625 -4.90625 1.5625 -4.695312 C 1.5625 -4.558594 1.609375 -4.433594 1.695312 -4.324219 C 1.78125 -4.210938 1.914062 -4.117188 2.097656 -4.042969 C 2.203125 -4.003906 2.515625 -3.914062 3.03125 -3.773438 C 3.777344 -3.574219 4.296875 -3.410156 4.589844 -3.285156 C 4.886719 -3.15625 5.117188 -2.972656 5.285156 -2.730469 C 5.453125 -2.488281 5.539062 -2.1875 5.539062 -1.828125 C 5.539062 -1.476562 5.433594 -1.144531 5.230469 -0.835938 C 5.023438 -0.523438 4.726562 -0.285156 4.34375 -0.113281 C 3.957031 0.0546875 3.515625 0.140625 3.03125 0.140625 C 2.222656 0.140625 1.605469 -0.0273438 1.179688 -0.363281 C 0.757812 -0.699219 0.484375 -1.195312 0.367188 -1.859375 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-6"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.234375 0 L 0.234375 -0.855469 L 4.195312 -5.402344 C 3.746094 -5.378906 3.351562 -5.367188 3.007812 -5.367188 L 0.46875 -5.367188 L 0.46875 -6.222656 L 5.554688 -6.222656 L 5.554688 -5.523438 L 2.1875 -1.578125 L 1.535156 -0.855469 C 2.007812 -0.890625 2.453125 -0.90625 2.867188 -0.90625 L 5.742188 -0.90625 L 5.742188 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-7"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.398438 -3.109375 C 0.398438 -4.261719 0.71875 -5.117188 1.359375 -5.671875 C 1.894531 -6.132812 2.546875 -6.363281 3.316406 -6.363281 C 4.171875 -6.363281 4.871094 -6.082031 5.414062 -5.523438 C 5.957031 -4.960938 6.226562 -4.1875 6.226562 -3.199219 C 6.226562 -2.398438 6.109375 -1.769531 5.867188 -1.308594 C 5.628906 -0.851562 5.277344 -0.492188 4.820312 -0.242188 C 4.359375 0.0117188 3.859375 0.140625 3.316406 0.140625 C 2.445312 0.140625 1.742188 -0.140625 1.203125 -0.695312 C 0.667969 -1.253906 0.398438 -2.0625 0.398438 -3.109375 Z M 1.484375 -3.109375 C 1.484375 -2.3125 1.65625 -1.71875 2.003906 -1.320312 C 2.351562 -0.925781 2.789062 -0.726562 3.316406 -0.726562 C 3.839844 -0.726562 4.273438 -0.925781 4.625 -1.324219 C 4.972656 -1.722656 5.144531 -2.328125 5.144531 -3.148438 C 5.144531 -3.917969 4.96875 -4.5 4.621094 -4.894531 C 4.269531 -5.292969 3.835938 -5.492188 3.316406 -5.492188 C 2.789062 -5.492188 2.351562 -5.292969 2.003906 -4.898438 C 1.65625 -4.503906 1.484375 -3.90625 1.484375 -3.109375 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-8"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 1.042969 0 L 1.042969 -5.402344 L 0.109375 -5.402344 L 0.109375 -6.222656 L 1.042969 -6.222656 L 1.042969 -6.882812 C 1.042969 -7.300781 1.078125 -7.613281 1.15625 -7.816406 C 1.257812 -8.089844 1.433594 -8.3125 1.691406 -8.480469 C 1.945312 -8.652344 2.304688 -8.734375 2.765625 -8.734375 C 3.0625 -8.734375 3.390625 -8.703125 3.75 -8.632812 L 3.59375 -7.710938 C 3.375 -7.75 3.164062 -7.769531 2.96875 -7.769531 C 2.648438 -7.769531 2.421875 -7.703125 2.289062 -7.5625 C 2.15625 -7.425781 2.09375 -7.171875 2.09375 -6.796875 L 2.09375 -6.222656 L 3.304688 -6.222656 L 3.304688 -5.402344 L 2.09375 -5.402344 L 2.09375 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-9"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.789062 0 L 0.789062 -6.222656 L 1.734375 -6.222656 L 1.734375 -5.351562 C 1.929688 -5.65625 2.1875 -5.898438 2.515625 -6.085938 C 2.839844 -6.269531 3.207031 -6.363281 3.621094 -6.363281 C 4.082031 -6.363281 4.460938 -6.265625 4.753906 -6.078125 C 5.050781 -5.886719 5.257812 -5.617188 5.378906 -5.273438 C 5.871094 -6 6.511719 -6.363281 7.300781 -6.363281 C 7.917969 -6.363281 8.390625 -6.191406 8.726562 -5.851562 C 9.058594 -5.507812 9.222656 -4.984375 9.222656 -4.273438 L 9.222656 0 L 8.171875 0 L 8.171875 -3.921875 C 8.171875 -4.34375 8.140625 -4.644531 8.070312 -4.832031 C 8.003906 -5.015625 7.878906 -5.164062 7.699219 -5.28125 C 7.519531 -5.394531 7.308594 -5.449219 7.066406 -5.449219 C 6.628906 -5.449219 6.265625 -5.304688 5.976562 -5.011719 C 5.6875 -4.722656 5.542969 -4.257812 5.542969 -3.617188 L 5.542969 0 L 4.488281 0 L 4.488281 -4.042969 C 4.488281 -4.511719 4.402344 -4.863281 4.230469 -5.097656 C 4.058594 -5.332031 3.777344 -5.449219 3.386719 -5.449219 C 3.089844 -5.449219 2.816406 -5.371094 2.5625 -5.214844 C 2.3125 -5.058594 2.128906 -4.828125 2.015625 -4.53125 C 1.902344 -4.230469 1.84375 -3.796875 1.84375 -3.226562 L 1.84375 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-10"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 4.828125 0 L 4.828125 -0.785156 C 4.433594 -0.167969 3.851562 0.140625 3.085938 0.140625 C 2.589844 0.140625 2.136719 0.00390625 1.71875 -0.269531 C 1.304688 -0.542969 0.980469 -0.925781 0.753906 -1.414062 C 0.523438 -1.90625 0.410156 -2.46875 0.410156 -3.105469 C 0.410156 -3.726562 0.515625 -4.289062 0.71875 -4.796875 C 0.925781 -5.300781 1.238281 -5.6875 1.652344 -5.960938 C 2.066406 -6.230469 2.53125 -6.363281 3.039062 -6.363281 C 3.414062 -6.363281 3.75 -6.285156 4.042969 -6.125 C 4.335938 -5.96875 4.574219 -5.761719 4.757812 -5.507812 L 4.757812 -8.589844 L 5.804688 -8.589844 L 5.804688 0 Z M 1.492188 -3.105469 C 1.492188 -2.308594 1.664062 -1.710938 2 -1.320312 C 2.335938 -0.925781 2.730469 -0.726562 3.1875 -0.726562 C 3.648438 -0.726562 4.039062 -0.914062 4.363281 -1.292969 C 4.683594 -1.667969 4.84375 -2.242188 4.84375 -3.015625 C 4.84375 -3.867188 4.679688 -4.492188 4.351562 -4.890625 C 4.023438 -5.289062 3.621094 -5.492188 3.140625 -5.492188 C 2.671875 -5.492188 2.28125 -5.296875 1.964844 -4.914062 C 1.652344 -4.53125 1.492188 -3.929688 1.492188 -3.105469 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph3-11"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 4.867188 0 L 4.867188 -0.914062 C 4.382812 -0.210938 3.726562 0.140625 2.894531 0.140625 C 2.527344 0.140625 2.183594 0.0703125 1.867188 -0.0703125 C 1.546875 -0.210938 1.3125 -0.386719 1.15625 -0.601562 C 1.003906 -0.8125 0.894531 -1.074219 0.832031 -1.382812 C 0.789062 -1.589844 0.765625 -1.917969 0.765625 -2.367188 L 0.765625 -6.222656 L 1.820312 -6.222656 L 1.820312 -2.773438 C 1.820312 -2.222656 1.84375 -1.851562 1.886719 -1.65625 C 1.953125 -1.378906 2.09375 -1.164062 2.308594 -1.003906 C 2.523438 -0.847656 2.789062 -0.765625 3.105469 -0.765625 C 3.421875 -0.765625 3.71875 -0.847656 3.996094 -1.011719 C 4.273438 -1.171875 4.46875 -1.394531 4.585938 -1.671875 C 4.699219 -1.953125 4.757812 -2.359375 4.757812 -2.890625 L 4.757812 -6.222656 L 5.8125 -6.222656 L 5.8125 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph4-0"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d=""/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph4-1"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.953125 0 L 0.953125 -9.304688 L 4.445312 -9.304688 C 5.15625 -9.304688 5.722656 -9.210938 6.152344 -9.023438 C 6.582031 -8.835938 6.921875 -8.546875 7.164062 -8.152344 C 7.40625 -7.761719 7.527344 -7.351562 7.527344 -6.925781 C 7.527344 -6.527344 7.421875 -6.152344 7.203125 -5.800781 C 6.988281 -5.449219 6.664062 -5.167969 6.226562 -4.953125 C 6.789062 -4.785156 7.222656 -4.503906 7.523438 -4.105469 C 7.828125 -3.707031 7.980469 -3.238281 7.980469 -2.699219 C 7.980469 -2.261719 7.886719 -1.855469 7.703125 -1.480469 C 7.519531 -1.105469 7.292969 -0.820312 7.019531 -0.617188 C 6.75 -0.414062 6.410156 -0.257812 6 -0.15625 C 5.59375 -0.0507812 5.09375 0 4.5 0 Z M 2.183594 -5.394531 L 4.195312 -5.394531 C 4.742188 -5.394531 5.132812 -5.429688 5.371094 -5.503906 C 5.683594 -5.597656 5.917969 -5.75 6.078125 -5.96875 C 6.238281 -6.183594 6.316406 -6.453125 6.316406 -6.78125 C 6.316406 -7.089844 6.242188 -7.359375 6.09375 -7.59375 C 5.945312 -7.828125 5.734375 -7.992188 5.460938 -8.078125 C 5.183594 -8.164062 4.710938 -8.207031 4.042969 -8.207031 L 2.183594 -8.207031 Z M 2.183594 -1.097656 L 4.5 -1.097656 C 4.898438 -1.097656 5.175781 -1.113281 5.339844 -1.140625 C 5.621094 -1.191406 5.859375 -1.277344 6.050781 -1.398438 C 6.242188 -1.515625 6.394531 -1.6875 6.519531 -1.914062 C 6.640625 -2.140625 6.703125 -2.402344 6.703125 -2.699219 C 6.703125 -3.046875 6.613281 -3.347656 6.4375 -3.601562 C 6.257812 -3.859375 6.011719 -4.039062 5.695312 -4.140625 C 5.382812 -4.246094 4.929688 -4.296875 4.335938 -4.296875 L 2.183594 -4.296875 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph4-2"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.429688 -3.371094 C 0.429688 -4.617188 0.777344 -5.542969 1.472656 -6.144531 C 2.050781 -6.644531 2.757812 -6.894531 3.59375 -6.894531 C 4.519531 -6.894531 5.277344 -6.589844 5.867188 -5.984375 C 6.453125 -5.375 6.746094 -4.535156 6.746094 -3.464844 C 6.746094 -2.597656 6.617188 -1.914062 6.355469 -1.417969 C 6.097656 -0.921875 5.71875 -0.535156 5.222656 -0.261719 C 4.722656 0.015625 4.179688 0.152344 3.59375 0.152344 C 2.648438 0.152344 1.886719 -0.148438 1.304688 -0.753906 C 0.722656 -1.359375 0.429688 -2.230469 0.429688 -3.371094 Z M 1.605469 -3.371094 C 1.605469 -2.507812 1.792969 -1.859375 2.171875 -1.429688 C 2.546875 -1 3.023438 -0.789062 3.59375 -0.789062 C 4.160156 -0.789062 4.632812 -1.003906 5.007812 -1.433594 C 5.382812 -1.867188 5.574219 -2.523438 5.574219 -3.410156 C 5.574219 -4.242188 5.382812 -4.875 5.003906 -5.304688 C 4.625 -5.734375 4.15625 -5.949219 3.59375 -5.949219 C 3.023438 -5.949219 2.546875 -5.734375 2.171875 -5.304688 C 1.792969 -4.878906 1.605469 -4.234375 1.605469 -3.371094 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph4-3"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.398438 -2.011719 L 1.53125 -2.191406 C 1.59375 -1.738281 1.769531 -1.390625 2.058594 -1.148438 C 2.347656 -0.90625 2.753906 -0.789062 3.273438 -0.789062 C 3.800781 -0.789062 4.1875 -0.894531 4.445312 -1.109375 C 4.699219 -1.320312 4.824219 -1.570312 4.824219 -1.859375 C 4.824219 -2.117188 4.710938 -2.320312 4.488281 -2.46875 C 4.332031 -2.570312 3.941406 -2.699219 3.320312 -2.855469 C 2.480469 -3.066406 1.902344 -3.25 1.578125 -3.40625 C 1.253906 -3.558594 1.007812 -3.773438 0.839844 -4.046875 C 0.671875 -4.320312 0.589844 -4.621094 0.589844 -4.953125 C 0.589844 -5.253906 0.660156 -5.53125 0.796875 -5.785156 C 0.933594 -6.042969 1.121094 -6.253906 1.359375 -6.421875 C 1.535156 -6.554688 1.777344 -6.667969 2.085938 -6.757812 C 2.390625 -6.847656 2.722656 -6.894531 3.070312 -6.894531 C 3.601562 -6.894531 4.066406 -6.816406 4.464844 -6.664062 C 4.867188 -6.511719 5.160156 -6.304688 5.351562 -6.046875 C 5.542969 -5.785156 5.671875 -5.4375 5.746094 -5 L 4.628906 -4.851562 C 4.578125 -5.195312 4.429688 -5.46875 4.1875 -5.664062 C 3.945312 -5.859375 3.597656 -5.953125 3.15625 -5.953125 C 2.628906 -5.953125 2.253906 -5.867188 2.03125 -5.695312 C 1.808594 -5.519531 1.695312 -5.316406 1.695312 -5.085938 C 1.695312 -4.9375 1.742188 -4.804688 1.835938 -4.683594 C 1.929688 -4.5625 2.074219 -4.460938 2.273438 -4.378906 C 2.386719 -4.335938 2.722656 -4.242188 3.28125 -4.085938 C 4.089844 -3.871094 4.652344 -3.695312 4.972656 -3.558594 C 5.292969 -3.421875 5.542969 -3.21875 5.726562 -2.957031 C 5.90625 -2.695312 6 -2.371094 6 -1.980469 C 6 -1.601562 5.886719 -1.242188 5.664062 -0.90625 C 5.441406 -0.570312 5.121094 -0.308594 4.703125 -0.125 C 4.285156 0.0585938 3.8125 0.152344 3.28125 0.152344 C 2.40625 0.152344 1.738281 -0.03125 1.277344 -0.394531 C 0.820312 -0.757812 0.527344 -1.296875 0.398438 -2.011719 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph4-4"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 3.351562 -1.023438 L 3.515625 -0.0117188 C 3.195312 0.0546875 2.90625 0.0898438 2.652344 0.0898438 C 2.238281 0.0898438 1.917969 0.0234375 1.6875 -0.109375 C 1.460938 -0.238281 1.300781 -0.410156 1.207031 -0.625 C 1.113281 -0.839844 1.066406 -1.289062 1.066406 -1.972656 L 1.066406 -5.851562 L 0.226562 -5.851562 L 0.226562 -6.742188 L 1.066406 -6.742188 L 1.066406 -8.410156 L 2.203125 -9.097656 L 2.203125 -6.742188 L 3.351562 -6.742188 L 3.351562 -5.851562 L 2.203125 -5.851562 L 2.203125 -1.910156 C 2.203125 -1.585938 2.222656 -1.375 2.261719 -1.28125 C 2.304688 -1.1875 2.367188 -1.113281 2.460938 -1.058594 C 2.550781 -1.003906 2.679688 -0.976562 2.851562 -0.976562 C 2.976562 -0.976562 3.144531 -0.992188 3.351562 -1.023438 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph4-5"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 1.179688 0 L 1.179688 -1.300781 L 2.480469 -1.300781 L 2.480469 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph4-6"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 1.003906 0 L 1.003906 -9.304688 L 4.511719 -9.304688 C 5.128906 -9.304688 5.601562 -9.277344 5.929688 -9.21875 C 6.386719 -9.140625 6.769531 -8.996094 7.078125 -8.78125 C 7.386719 -8.566406 7.636719 -8.269531 7.824219 -7.882812 C 8.011719 -7.5 8.105469 -7.074219 8.105469 -6.613281 C 8.105469 -5.824219 7.855469 -5.152344 7.351562 -4.605469 C 6.847656 -4.058594 5.9375 -3.78125 4.621094 -3.78125 L 2.234375 -3.78125 L 2.234375 0 Z M 2.234375 -4.882812 L 4.640625 -4.882812 C 5.4375 -4.882812 6 -5.03125 6.335938 -5.324219 C 6.667969 -5.621094 6.835938 -6.039062 6.835938 -6.578125 C 6.835938 -6.964844 6.738281 -7.296875 6.542969 -7.574219 C 6.34375 -7.851562 6.085938 -8.035156 5.765625 -8.125 C 5.558594 -8.179688 5.171875 -8.207031 4.613281 -8.207031 L 2.234375 -8.207031 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph4-7"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.804688 2.597656 L 0.679688 1.523438 C 0.929688 1.589844 1.148438 1.625 1.332031 1.625 C 1.585938 1.625 1.789062 1.582031 1.941406 1.5 C 2.09375 1.414062 2.21875 1.296875 2.316406 1.140625 C 2.390625 1.027344 2.503906 0.746094 2.664062 0.292969 C 2.6875 0.230469 2.722656 0.136719 2.765625 0.0117188 L 0.210938 -6.742188 L 1.441406 -6.742188 L 2.84375 -2.835938 C 3.027344 -2.34375 3.1875 -1.820312 3.332031 -1.277344 C 3.464844 -1.800781 3.621094 -2.3125 3.800781 -2.8125 L 5.242188 -6.742188 L 6.386719 -6.742188 L 3.820312 0.113281 C 3.546875 0.855469 3.332031 1.363281 3.179688 1.644531 C 2.976562 2.019531 2.746094 2.296875 2.480469 2.472656 C 2.21875 2.648438 1.90625 2.734375 1.542969 2.734375 C 1.324219 2.734375 1.078125 2.6875 0.804688 2.597656 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph4-8"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.855469 0 L 0.855469 -9.304688 L 2 -9.304688 L 2 -5.96875 C 2.53125 -6.585938 3.207031 -6.894531 4.019531 -6.894531 C 4.519531 -6.894531 4.953125 -6.796875 5.320312 -6.597656 C 5.6875 -6.402344 5.949219 -6.128906 6.109375 -5.78125 C 6.269531 -5.433594 6.347656 -4.933594 6.347656 -4.273438 L 6.347656 0 L 5.203125 0 L 5.203125 -4.273438 C 5.203125 -4.84375 5.082031 -5.257812 4.832031 -5.519531 C 4.585938 -5.78125 4.234375 -5.910156 3.78125 -5.910156 C 3.445312 -5.910156 3.125 -5.820312 2.828125 -5.644531 C 2.53125 -5.46875 2.316406 -5.234375 2.191406 -4.933594 C 2.0625 -4.632812 2 -4.21875 2 -3.6875 L 2 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph4-9"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.855469 0 L 0.855469 -6.742188 L 1.886719 -6.742188 L 1.886719 -5.78125 C 2.382812 -6.523438 3.09375 -6.894531 4.03125 -6.894531 C 4.4375 -6.894531 4.808594 -6.820312 5.152344 -6.675781 C 5.492188 -6.527344 5.746094 -6.335938 5.914062 -6.101562 C 6.085938 -5.863281 6.203125 -5.582031 6.273438 -5.257812 C 6.3125 -5.046875 6.335938 -4.675781 6.335938 -4.144531 L 6.335938 0 L 5.191406 0 L 5.191406 -4.101562 C 5.191406 -4.566406 5.148438 -4.914062 5.058594 -5.144531 C 4.96875 -5.375 4.8125 -5.558594 4.585938 -5.695312 C 4.359375 -5.835938 4.09375 -5.902344 3.789062 -5.902344 C 3.304688 -5.902344 2.882812 -5.75 2.53125 -5.441406 C 2.175781 -5.132812 2 -4.546875 2 -3.679688 L 2 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph4-10"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.855469 2.582031 L 0.855469 -6.742188 L 1.898438 -6.742188 L 1.898438 -5.867188 C 2.144531 -6.207031 2.421875 -6.464844 2.730469 -6.636719 C 3.039062 -6.808594 3.414062 -6.894531 3.851562 -6.894531 C 4.429688 -6.894531 4.9375 -6.746094 5.375 -6.449219 C 5.816406 -6.152344 6.148438 -5.734375 6.375 -5.195312 C 6.597656 -4.65625 6.710938 -4.066406 6.710938 -3.421875 C 6.710938 -2.730469 6.585938 -2.109375 6.339844 -1.558594 C 6.089844 -1.007812 5.730469 -0.582031 5.257812 -0.289062 C 4.785156 0.00390625 4.289062 0.152344 3.769531 0.152344 C 3.390625 0.152344 3.046875 0.0703125 2.746094 -0.0898438 C 2.441406 -0.25 2.195312 -0.453125 2 -0.699219 L 2 2.582031 Z M 1.890625 -3.332031 C 1.890625 -2.464844 2.066406 -1.824219 2.417969 -1.410156 C 2.769531 -0.996094 3.195312 -0.789062 3.695312 -0.789062 C 4.203125 -0.789062 4.636719 -1 5 -1.429688 C 5.359375 -1.859375 5.542969 -2.527344 5.542969 -3.429688 C 5.542969 -4.289062 5.363281 -4.929688 5.011719 -5.359375 C 4.65625 -5.785156 4.234375 -6 3.746094 -6 C 3.257812 -6 2.828125 -5.769531 2.453125 -5.316406 C 2.078125 -4.859375 1.890625 -4.199219 1.890625 -3.332031 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph4-11"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 1.910156 0 L 0.851562 0 L 0.851562 -9.304688 L 1.992188 -9.304688 L 1.992188 -5.984375 C 2.476562 -6.589844 3.089844 -6.894531 3.839844 -6.894531 C 4.253906 -6.894531 4.648438 -6.808594 5.019531 -6.644531 C 5.390625 -6.476562 5.691406 -6.242188 5.933594 -5.9375 C 6.171875 -5.636719 6.359375 -5.269531 6.492188 -4.84375 C 6.628906 -4.414062 6.695312 -3.957031 6.695312 -3.472656 C 6.695312 -2.316406 6.410156 -1.425781 5.839844 -0.792969 C 5.269531 -0.164062 4.582031 0.152344 3.78125 0.152344 C 2.988281 0.152344 2.363281 -0.179688 1.910156 -0.84375 Z M 1.898438 -3.421875 C 1.898438 -2.613281 2.007812 -2.027344 2.226562 -1.667969 C 2.585938 -1.082031 3.074219 -0.789062 3.6875 -0.789062 C 4.1875 -0.789062 4.617188 -1.003906 4.984375 -1.4375 C 5.347656 -1.871094 5.527344 -2.519531 5.527344 -3.375 C 5.527344 -4.257812 5.355469 -4.90625 5.003906 -5.324219 C 4.65625 -5.742188 4.234375 -5.953125 3.738281 -5.953125 C 3.238281 -5.953125 2.808594 -5.738281 2.445312 -5.304688 C 2.082031 -4.871094 1.898438 -4.242188 1.898438 -3.421875 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph4-12"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 0.863281 -7.992188 L 0.863281 -9.304688 L 2.007812 -9.304688 L 2.007812 -7.992188 Z M 0.863281 0 L 0.863281 -6.742188 L 2.007812 -6.742188 L 2.007812 0 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph4-13"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 5.230469 0 L 5.230469 -0.851562 C 4.804688 -0.183594 4.175781 0.152344 3.34375 0.152344 C 2.808594 0.152344 2.3125 0.00390625 1.863281 -0.292969 C 1.414062 -0.589844 1.0625 -1 0.816406 -1.53125 C 0.570312 -2.0625 0.445312 -2.675781 0.445312 -3.363281 C 0.445312 -4.035156 0.554688 -4.648438 0.78125 -5.195312 C 1.003906 -5.742188 1.339844 -6.164062 1.789062 -6.457031 C 2.238281 -6.75 2.738281 -6.894531 3.292969 -6.894531 C 3.699219 -6.894531 4.0625 -6.808594 4.378906 -6.636719 C 4.695312 -6.464844 4.957031 -6.242188 5.15625 -5.96875 L 5.15625 -9.304688 L 6.289062 -9.304688 L 6.289062 0 Z M 1.617188 -3.363281 C 1.617188 -2.5 1.800781 -1.855469 2.164062 -1.429688 C 2.527344 -1 2.957031 -0.789062 3.453125 -0.789062 C 3.953125 -0.789062 4.375 -0.992188 4.726562 -1.398438 C 5.074219 -1.808594 5.25 -2.429688 5.25 -3.269531 C 5.25 -4.191406 5.070312 -4.867188 4.714844 -5.300781 C 4.359375 -5.730469 3.921875 -5.949219 3.402344 -5.949219 C 2.894531 -5.949219 2.46875 -5.742188 2.128906 -5.324219 C 1.789062 -4.910156 1.617188 -4.257812 1.617188 -3.363281 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
<symbol overflow="visible" id="glyph4-14"> |
|||
<path style="stroke:none;" d="M 4.84375 0 L 3.699219 0 L 3.699219 -7.28125 C 3.425781 -7.019531 3.066406 -6.757812 2.617188 -6.492188 C 2.171875 -6.230469 1.769531 -6.035156 1.414062 -5.902344 L 1.414062 -7.007812 C 2.054688 -7.308594 2.613281 -7.671875 3.089844 -8.101562 C 3.570312 -8.527344 3.90625 -8.941406 4.105469 -9.34375 L 4.84375 -9.34375 Z "/> |
|||
</symbol> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<clipPath id="clip1"> |
|||
<path d="M 94 19 L 96 19 L 96 215 L 94 215 Z "/> |
|||
</clipPath> |
|||
<clipPath id="clip2"> |
|||
<path d="M 204 19 L 206 19 L 206 215 L 204 215 Z "/> |
|||
</clipPath> |
|||
<clipPath id="clip3"> |
|||
<path d="M 314 19 L 316 19 L 316 215 L 314 215 Z "/> |
|||
</clipPath> |
|||
<clipPath id="clip4"> |
|||
<path d="M 39 171 L 355 171 L 355 173 L 39 173 Z "/> |
|||
</clipPath> |
|||
<clipPath id="clip5"> |
|||
<path d="M 39 107 L 355 107 L 355 109 L 39 109 Z "/> |
|||
</clipPath> |
|||
<clipPath id="clip6"> |
|||
<path d="M 39 44 L 355 44 L 355 46 L 39 46 Z "/> |
|||
</clipPath> |
|||
</defs> |
|||
<g id="surface18"> |
|||
<g clip-path="url(#clip1)" clip-rule="nonzero"> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:0.5;stroke-dasharray:1,2;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 95.160156 214.296875 L 95.160156 19 "/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g clip-path="url(#clip2)" clip-rule="nonzero"> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:0.5;stroke-dasharray:1,2;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 204.84375 214.296875 L 204.84375 19 "/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g clip-path="url(#clip3)" clip-rule="nonzero"> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:0.5;stroke-dasharray:1,2;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 314.53125 214.296875 L 314.53125 19 "/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g clip-path="url(#clip4)" clip-rule="nonzero"> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:0.5;stroke-dasharray:1,2;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 171.960938 L 355 171.960938 "/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g clip-path="url(#clip5)" clip-rule="nonzero"> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:0.5;stroke-dasharray:1,2;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 108.234375 L 355 108.234375 "/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g clip-path="url(#clip6)" clip-rule="nonzero"> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:0.5;stroke-dasharray:1,2;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 44.511719 L 355 44.511719 "/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 55.070312 201 C 55.070312 200.183594 54.75 199.402344 54.171875 198.828125 C 53.597656 198.25 52.816406 197.929688 52 197.929688 C 51.183594 197.929688 50.402344 198.25 49.828125 198.828125 C 49.25 199.402344 48.929688 200.183594 48.929688 201 C 48.929688 201.816406 49.25 202.597656 49.828125 203.171875 C 50.402344 203.75 51.183594 204.070312 52 204.070312 C 52.816406 204.070312 53.597656 203.75 54.171875 203.171875 C 54.75 202.597656 55.070312 201.816406 55.070312 201 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 88.070312 176 C 88.070312 175.183594 87.75 174.402344 87.171875 173.828125 C 86.597656 173.25 85.816406 172.929688 85 172.929688 C 84.183594 172.929688 83.402344 173.25 82.828125 173.828125 C 82.25 174.402344 81.929688 175.183594 81.929688 176 C 81.929688 176.816406 82.25 177.597656 82.828125 178.171875 C 83.402344 178.75 84.183594 179.070312 85 179.070312 C 85.816406 179.070312 86.597656 178.75 87.171875 178.171875 C 87.75 177.597656 88.070312 176.816406 88.070312 176 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 121.070312 160 C 121.070312 159.183594 120.75 158.402344 120.171875 157.828125 C 119.597656 157.25 118.816406 156.929688 118 156.929688 C 117.183594 156.929688 116.402344 157.25 115.828125 157.828125 C 115.25 158.402344 114.929688 159.183594 114.929688 160 C 114.929688 160.816406 115.25 161.597656 115.828125 162.171875 C 116.402344 162.75 117.183594 163.070312 118 163.070312 C 118.816406 163.070312 119.597656 162.75 120.171875 162.171875 C 120.75 161.597656 121.070312 160.816406 121.070312 160 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 154.070312 142 C 154.070312 141.183594 153.75 140.402344 153.171875 139.828125 C 152.597656 139.25 151.816406 138.929688 151 138.929688 C 150.183594 138.929688 149.402344 139.25 148.828125 139.828125 C 148.25 140.402344 147.929688 141.183594 147.929688 142 C 147.929688 142.816406 148.25 143.597656 148.828125 144.171875 C 149.402344 144.75 150.183594 145.070312 151 145.070312 C 151.816406 145.070312 152.597656 144.75 153.171875 144.171875 C 153.75 143.597656 154.070312 142.816406 154.070312 142 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 187.070312 124 C 187.070312 123.183594 186.75 122.402344 186.171875 121.828125 C 185.597656 121.25 184.816406 120.929688 184 120.929688 C 183.183594 120.929688 182.402344 121.25 181.828125 121.828125 C 181.25 122.402344 180.929688 123.183594 180.929688 124 C 180.929688 124.816406 181.25 125.597656 181.828125 126.171875 C 182.402344 126.75 183.183594 127.070312 184 127.070312 C 184.816406 127.070312 185.597656 126.75 186.171875 126.171875 C 186.75 125.597656 187.070312 124.816406 187.070312 124 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 220.070312 105 C 220.070312 104.183594 219.75 103.402344 219.171875 102.828125 C 218.597656 102.25 217.816406 101.929688 217 101.929688 C 216.183594 101.929688 215.402344 102.25 214.828125 102.828125 C 214.25 103.402344 213.929688 104.183594 213.929688 105 C 213.929688 105.816406 214.25 106.597656 214.828125 107.171875 C 215.402344 107.75 216.183594 108.070312 217 108.070312 C 217.816406 108.070312 218.597656 107.75 219.171875 107.171875 C 219.75 106.597656 220.070312 105.816406 220.070312 105 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 253.070312 86 C 253.070312 85.183594 252.75 84.402344 252.171875 83.828125 C 251.597656 83.25 250.816406 82.929688 250 82.929688 C 249.183594 82.929688 248.402344 83.25 247.828125 83.828125 C 247.25 84.402344 246.929688 85.183594 246.929688 86 C 246.929688 86.816406 247.25 87.597656 247.828125 88.171875 C 248.402344 88.75 249.183594 89.070312 250 89.070312 C 250.816406 89.070312 251.597656 88.75 252.171875 88.171875 C 252.75 87.597656 253.070312 86.816406 253.070312 86 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 286.070312 67 C 286.070312 66.183594 285.75 65.402344 285.171875 64.828125 C 284.597656 64.25 283.816406 63.929688 283 63.929688 C 282.183594 63.929688 281.402344 64.25 280.828125 64.828125 C 280.25 65.402344 279.929688 66.183594 279.929688 67 C 279.929688 67.816406 280.25 68.597656 280.828125 69.171875 C 281.402344 69.75 282.183594 70.070312 283 70.070312 C 283.816406 70.070312 284.597656 69.75 285.171875 69.171875 C 285.75 68.597656 286.070312 67.816406 286.070312 67 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 319.070312 48 C 319.070312 47.183594 318.75 46.402344 318.171875 45.828125 C 317.597656 45.25 316.816406 44.929688 316 44.929688 C 315.183594 44.929688 314.402344 45.25 313.828125 45.828125 C 313.25 46.402344 312.929688 47.183594 312.929688 48 C 312.929688 48.816406 313.25 49.597656 313.828125 50.171875 C 314.402344 50.75 315.183594 51.070312 316 51.070312 C 316.816406 51.070312 317.597656 50.75 318.171875 50.171875 C 318.75 49.597656 319.070312 48.816406 319.070312 48 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 352.070312 29 C 352.070312 28.183594 351.75 27.402344 351.171875 26.828125 C 350.597656 26.25 349.816406 25.929688 349 25.929688 C 348.183594 25.929688 347.402344 26.25 346.828125 26.828125 C 346.25 27.402344 345.929688 28.183594 345.929688 29 C 345.929688 29.816406 346.25 30.597656 346.828125 31.171875 C 347.402344 31.75 348.183594 32.070312 349 32.070312 C 349.816406 32.070312 350.597656 31.75 351.171875 31.171875 C 351.75 30.597656 352.070312 29.816406 352.070312 29 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 55.070312 191 C 55.070312 190.183594 54.75 189.402344 54.171875 188.828125 C 53.597656 188.25 52.816406 187.929688 52 187.929688 C 51.183594 187.929688 50.402344 188.25 49.828125 188.828125 C 49.25 189.402344 48.929688 190.183594 48.929688 191 C 48.929688 191.816406 49.25 192.597656 49.828125 193.171875 C 50.402344 193.75 51.183594 194.070312 52 194.070312 C 52.816406 194.070312 53.597656 193.75 54.171875 193.171875 C 54.75 192.597656 55.070312 191.816406 55.070312 191 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 88.070312 181 C 88.070312 180.183594 87.75 179.402344 87.171875 178.828125 C 86.597656 178.25 85.816406 177.929688 85 177.929688 C 84.183594 177.929688 83.402344 178.25 82.828125 178.828125 C 82.25 179.402344 81.929688 180.183594 81.929688 181 C 81.929688 181.816406 82.25 182.597656 82.828125 183.171875 C 83.402344 183.75 84.183594 184.070312 85 184.070312 C 85.816406 184.070312 86.597656 183.75 87.171875 183.171875 C 87.75 182.597656 88.070312 181.816406 88.070312 181 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 121.070312 170 C 121.070312 169.183594 120.75 168.402344 120.171875 167.828125 C 119.597656 167.25 118.816406 166.929688 118 166.929688 C 117.183594 166.929688 116.402344 167.25 115.828125 167.828125 C 115.25 168.402344 114.929688 169.183594 114.929688 170 C 114.929688 170.816406 115.25 171.597656 115.828125 172.171875 C 116.402344 172.75 117.183594 173.070312 118 173.070312 C 118.816406 173.070312 119.597656 172.75 120.171875 172.171875 C 120.75 171.597656 121.070312 170.816406 121.070312 170 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 154.070312 157 C 154.070312 156.183594 153.75 155.402344 153.171875 154.828125 C 152.597656 154.25 151.816406 153.929688 151 153.929688 C 150.183594 153.929688 149.402344 154.25 148.828125 154.828125 C 148.25 155.402344 147.929688 156.183594 147.929688 157 C 147.929688 157.816406 148.25 158.597656 148.828125 159.171875 C 149.402344 159.75 150.183594 160.070312 151 160.070312 C 151.816406 160.070312 152.597656 159.75 153.171875 159.171875 C 153.75 158.597656 154.070312 157.816406 154.070312 157 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 187.070312 142 C 187.070312 141.183594 186.75 140.402344 186.171875 139.828125 C 185.597656 139.25 184.816406 138.929688 184 138.929688 C 183.183594 138.929688 182.402344 139.25 181.828125 139.828125 C 181.25 140.402344 180.929688 141.183594 180.929688 142 C 180.929688 142.816406 181.25 143.597656 181.828125 144.171875 C 182.402344 144.75 183.183594 145.070312 184 145.070312 C 184.816406 145.070312 185.597656 144.75 186.171875 144.171875 C 186.75 143.597656 187.070312 142.816406 187.070312 142 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 220.070312 125 C 220.070312 124.183594 219.75 123.402344 219.171875 122.828125 C 218.597656 122.25 217.816406 121.929688 217 121.929688 C 216.183594 121.929688 215.402344 122.25 214.828125 122.828125 C 214.25 123.402344 213.929688 124.183594 213.929688 125 C 213.929688 125.816406 214.25 126.597656 214.828125 127.171875 C 215.402344 127.75 216.183594 128.070312 217 128.070312 C 217.816406 128.070312 218.597656 127.75 219.171875 127.171875 C 219.75 126.597656 220.070312 125.816406 220.070312 125 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 253.070312 107 C 253.070312 106.183594 252.75 105.402344 252.171875 104.828125 C 251.597656 104.25 250.816406 103.929688 250 103.929688 C 249.183594 103.929688 248.402344 104.25 247.828125 104.828125 C 247.25 105.402344 246.929688 106.183594 246.929688 107 C 246.929688 107.816406 247.25 108.597656 247.828125 109.171875 C 248.402344 109.75 249.183594 110.070312 250 110.070312 C 250.816406 110.070312 251.597656 109.75 252.171875 109.171875 C 252.75 108.597656 253.070312 107.816406 253.070312 107 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 286.070312 88 C 286.070312 87.183594 285.75 86.402344 285.171875 85.828125 C 284.597656 85.25 283.816406 84.929688 283 84.929688 C 282.183594 84.929688 281.402344 85.25 280.828125 85.828125 C 280.25 86.402344 279.929688 87.183594 279.929688 88 C 279.929688 88.816406 280.25 89.597656 280.828125 90.171875 C 281.402344 90.75 282.183594 91.070312 283 91.070312 C 283.816406 91.070312 284.597656 90.75 285.171875 90.171875 C 285.75 89.597656 286.070312 88.816406 286.070312 88 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 319.070312 69 C 319.070312 68.183594 318.75 67.402344 318.171875 66.828125 C 317.597656 66.25 316.816406 65.929688 316 65.929688 C 315.183594 65.929688 314.402344 66.25 313.828125 66.828125 C 313.25 67.402344 312.929688 68.183594 312.929688 69 C 312.929688 69.816406 313.25 70.597656 313.828125 71.171875 C 314.402344 71.75 315.183594 72.070312 316 72.070312 C 316.816406 72.070312 317.597656 71.75 318.171875 71.171875 C 318.75 70.597656 319.070312 69.816406 319.070312 69 Z "/> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 352.070312 50 C 352.070312 49.183594 351.75 48.402344 351.171875 47.828125 C 350.597656 47.25 349.816406 46.929688 349 46.929688 C 348.183594 46.929688 347.402344 47.25 346.828125 47.828125 C 346.25 48.402344 345.929688 49.183594 345.929688 50 C 345.929688 50.816406 346.25 51.597656 346.828125 52.171875 C 347.402344 52.75 348.183594 53.070312 349 53.070312 C 349.816406 53.070312 350.597656 52.75 351.171875 52.171875 C 351.75 51.597656 352.070312 50.816406 352.070312 50 Z "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.5;stroke-linecap:square;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 214.296875 L 39 214.296875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.5;stroke-linecap:square;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 214.296875 L 39 19 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.5;stroke-linecap:square;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 19 L 355 19 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.5;stroke-linecap:square;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 19 L 355 214.296875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 95.160156 214.296875 L 95.160156 211.140625 "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-1" x="89.659467" y="226.29874"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-2" x="95.220991" y="226.29874"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 204.84375 214.296875 L 204.84375 211.140625 "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-1" x="196.345465" y="226.29874"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-2" x="201.906989" y="226.29874"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-2" x="207.468512" y="226.29874"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 314.53125 214.296875 L 314.53125 211.140625 "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-1" x="303.531463" y="226.29874"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-2" x="309.092987" y="226.29874"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-2" x="314.65451" y="226.29874"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-2" x="320.216034" y="226.29874"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 51.511719 214.296875 L 51.511719 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 62.140625 214.296875 L 62.140625 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 70.824219 214.296875 L 70.824219 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 78.167969 214.296875 L 78.167969 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 84.53125 214.296875 L 84.53125 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 90.140625 214.296875 L 90.140625 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 128.179688 214.296875 L 128.179688 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 147.492188 214.296875 L 147.492188 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 161.195312 214.296875 L 161.195312 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 171.828125 214.296875 L 171.828125 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 180.511719 214.296875 L 180.511719 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 187.855469 214.296875 L 187.855469 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 194.214844 214.296875 L 194.214844 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 199.828125 214.296875 L 199.828125 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 237.863281 214.296875 L 237.863281 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 257.179688 214.296875 L 257.179688 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 270.882812 214.296875 L 270.882812 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 281.511719 214.296875 L 281.511719 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 290.199219 214.296875 L 290.199219 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 297.539062 214.296875 L 297.539062 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 303.902344 214.296875 L 303.902344 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 309.511719 214.296875 L 309.511719 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 347.550781 214.296875 L 347.550781 212.71875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 171.960938 L 42.160156 171.960938 "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-1" x="19" y="176.961688"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-2" x="24.561523" y="176.961688"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph1-1" x="30" y="172.81325"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 108.234375 L 42.160156 108.234375 "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-1" x="19" y="113.23603"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-2" x="24.561523" y="113.23603"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph1-2" x="30" y="109.087593"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 44.511719 L 42.160156 44.511719 "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-1" x="19" y="49.510373"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-2" x="24.561523" y="49.510373"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph1-3" x="30" y="45.361936"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 205.28125 L 40.578125 205.28125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 197.320312 L 40.578125 197.320312 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 191.144531 L 40.578125 191.144531 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 186.097656 L 40.578125 186.097656 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 181.832031 L 40.578125 181.832031 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 178.136719 L 40.578125 178.136719 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 174.878906 L 40.578125 174.878906 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 152.777344 L 40.578125 152.777344 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 141.558594 L 40.578125 141.558594 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 133.59375 L 40.578125 133.59375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 127.417969 L 40.578125 127.417969 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 122.375 L 40.578125 122.375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 118.105469 L 40.578125 118.105469 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 114.410156 L 40.578125 114.410156 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 111.152344 L 40.578125 111.152344 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 89.050781 L 40.578125 89.050781 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 77.832031 L 40.578125 77.832031 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 69.871094 L 40.578125 69.871094 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 63.695312 L 40.578125 63.695312 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 58.648438 L 40.578125 58.648438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 54.382812 L 40.578125 54.382812 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 50.6875 L 40.578125 50.6875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 47.425781 L 40.578125 47.425781 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 39 25.328125 L 40.578125 25.328125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 95.160156 19 L 95.160156 22.160156 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 204.84375 19 L 204.84375 22.160156 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 314.53125 19 L 314.53125 22.160156 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 51.511719 19 L 51.511719 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 62.140625 19 L 62.140625 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 70.824219 19 L 70.824219 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 78.167969 19 L 78.167969 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 84.53125 19 L 84.53125 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 90.140625 19 L 90.140625 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 128.179688 19 L 128.179688 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 147.492188 19 L 147.492188 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 161.195312 19 L 161.195312 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 171.828125 19 L 171.828125 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 180.511719 19 L 180.511719 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 187.855469 19 L 187.855469 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 194.214844 19 L 194.214844 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 199.828125 19 L 199.828125 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 237.863281 19 L 237.863281 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 257.179688 19 L 257.179688 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 270.882812 19 L 270.882812 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 281.511719 19 L 281.511719 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 290.199219 19 L 290.199219 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 297.539062 19 L 297.539062 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 303.902344 19 L 303.902344 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 309.511719 19 L 309.511719 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 347.550781 19 L 347.550781 20.578125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 171.960938 L 351.839844 171.960938 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 108.234375 L 351.839844 108.234375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 44.511719 L 351.839844 44.511719 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 205.28125 L 353.421875 205.28125 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 197.320312 L 353.421875 197.320312 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 191.144531 L 353.421875 191.144531 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 186.097656 L 353.421875 186.097656 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 181.832031 L 353.421875 181.832031 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 178.136719 L 353.421875 178.136719 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 174.878906 L 353.421875 174.878906 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 152.777344 L 353.421875 152.777344 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 141.558594 L 353.421875 141.558594 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 133.59375 L 353.421875 133.59375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 127.417969 L 353.421875 127.417969 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 122.375 L 353.421875 122.375 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 118.105469 L 353.421875 118.105469 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 114.410156 L 353.421875 114.410156 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 111.152344 L 353.421875 111.152344 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 89.050781 L 353.421875 89.050781 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 77.832031 L 353.421875 77.832031 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 69.871094 L 353.421875 69.871094 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 63.695312 L 353.421875 63.695312 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 58.648438 L 353.421875 58.648438 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 54.382812 L 353.421875 54.382812 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 50.6875 L 353.421875 50.6875 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 47.425781 L 353.421875 47.425781 "/> |
|||
<path style="fill:none;stroke-width:0.1;stroke-linecap:butt;stroke-linejoin:miter;stroke:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);stroke-opacity:1;stroke-miterlimit:3.25;" d="M 355 25.328125 L 353.421875 25.328125 "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-3" x="175.5" y="245.29874"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-4" x="181.608398" y="245.29874"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-5" x="187.169922" y="245.29874"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-6" x="192.731445" y="245.29874"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-7" x="197.731445" y="245.29874"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-8" x="200.509766" y="245.29874"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-9" x="202.731445" y="245.29874"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-5" x="208.292969" y="245.29874"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph0-10" x="213.854492" y="245.29874"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-1" x="9" y="129.14937"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-2" x="9" y="122.479448"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-3" x="9" y="117.479448"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-4" x="9" y="114.701128"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph2-5" x="9" y="109.139605"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-1" x="148" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-2" x="155.330078" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-3" x="157.996094" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-4" x="160.662109" y="12"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-5" x="170" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-2" x="176" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-6" x="178.666016" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-4" x="184.666016" y="12"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-7" x="194" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-8" x="200.673828" y="12"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(39.99939%,39.99939%,39.99939%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-9" x="207" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-7" x="216.996094" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-10" x="223.669922" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-11" x="230.34375" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-3" x="237.017578" y="12"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph3-4" x="239.683594" y="12"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(36.84082%,50.67749%,70.979309%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 382.148438 113 C 382.148438 112.164062 381.816406 111.363281 381.226562 110.773438 C 380.636719 110.183594 379.835938 109.851562 379 109.851562 C 378.164062 109.851562 377.363281 110.183594 376.773438 110.773438 C 376.183594 111.363281 375.851562 112.164062 375.851562 113 C 375.851562 113.835938 376.183594 114.636719 376.773438 115.226562 C 377.363281 115.816406 378.164062 116.148438 379 116.148438 C 379.835938 116.148438 380.636719 115.816406 381.226562 115.226562 C 381.816406 114.636719 382.148438 113.835938 382.148438 113 Z "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(0%,0%,0%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-1" x="391" y="117.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-2" x="399.670898" y="117.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-2" x="406.901367" y="117.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-3" x="414.131836" y="117.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-4" x="420.631836" y="117.28418"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(0%,0%,0%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-5" x="424" y="117.28418"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(0%,0%,0%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-6" x="428" y="117.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-7" x="436.670898" y="117.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-4" x="443.170898" y="117.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-8" x="446.783203" y="117.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-2" x="454.013672" y="117.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-9" x="461.244141" y="117.28418"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
<path style=" stroke:none;fill-rule:evenodd;fill:rgb(88.070679%,61.103821%,14.204407%);fill-opacity:1;" d="M 382.148438 136 C 382.148438 135.164062 381.816406 134.363281 381.226562 133.773438 C 380.636719 133.183594 379.835938 132.851562 379 132.851562 C 378.164062 132.851562 377.363281 133.183594 376.773438 133.773438 C 376.183594 134.363281 375.851562 135.164062 375.851562 136 C 375.851562 136.835938 376.183594 137.636719 376.773438 138.226562 C 377.363281 138.816406 378.164062 139.148438 379 139.148438 C 379.835938 139.148438 380.636719 138.816406 381.226562 138.226562 C 381.816406 137.636719 382.148438 136.835938 382.148438 136 Z "/> |
|||
<g style="fill:rgb(0%,0%,0%);fill-opacity:1;"> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-10" x="391" y="140.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-7" x="398.230469" y="140.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-11" x="404.730469" y="140.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-12" x="411.960938" y="140.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-9" x="414.849609" y="140.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-13" x="422.080078" y="140.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-14" x="429.310547" y="140.28418"/> |
|||
<use xlink:href="#glyph4-14" x="436.541016" y="140.28418"/> |
|||
</g> |
|||
</g> |
|||
</svg> |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,247 @@ |
|||
.. _reference: |
|||
|
|||
.. warning:: |
|||
|
|||
Please be advised that the reference documentation discussing pybind11 |
|||
internals is currently incomplete. Please refer to the previous sections |
|||
and the pybind11 header files for the nitty gritty details. |
|||
|
|||
Reference |
|||
######### |
|||
|
|||
Macros |
|||
====== |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: PYBIND11_PLUGIN(const char *name) |
|||
|
|||
This macro creates the entry point that will be invoked when the Python |
|||
interpreter imports a plugin library. Please create a |
|||
:class:`module` in the function body and return the pointer to its |
|||
underlying Python object at the end. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_PLUGIN(example) { |
|||
pybind11::module m("example", "pybind11 example plugin"); |
|||
/// Set up bindings here |
|||
return m.ptr(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
.. _core_types: |
|||
|
|||
Convenience classes for arbitrary Python types |
|||
============================================== |
|||
|
|||
Without reference counting |
|||
-------------------------- |
|||
|
|||
.. class:: handle |
|||
|
|||
The :class:`handle` class is a thin wrapper around an arbitrary Python |
|||
object (i.e. a ``PyObject *`` in Python's C API). It does not perform any |
|||
automatic reference counting and merely provides a basic C++ interface to |
|||
various Python API functions. |
|||
|
|||
.. seealso:: |
|||
|
|||
The :class:`object` class inherits from :class:`handle` and adds automatic |
|||
reference counting features. |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: handle::handle() |
|||
|
|||
The default constructor creates a handle with a ``nullptr``-valued pointer. |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: handle::handle(const handle&) |
|||
|
|||
Copy constructor |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: handle::handle(PyObject *) |
|||
|
|||
Creates a :class:`handle` from the given raw Python object pointer. |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: PyObject * handle::ptr() const |
|||
|
|||
Return the ``PyObject *`` underlying a :class:`handle`. |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: const handle& handle::inc_ref() const |
|||
|
|||
Manually increase the reference count of the Python object. Usually, it is |
|||
preferable to use the :class:`object` class which derives from |
|||
:class:`handle` and calls this function automatically. Returns a reference |
|||
to itself. |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: const handle& handle::dec_ref() const |
|||
|
|||
Manually decrease the reference count of the Python object. Usually, it is |
|||
preferable to use the :class:`object` class which derives from |
|||
:class:`handle` and calls this function automatically. Returns a reference |
|||
to itself. |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: void handle::ref_count() const |
|||
|
|||
Return the object's current reference count |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: handle handle::get_type() const |
|||
|
|||
Return a handle to the Python type object underlying the instance |
|||
|
|||
.. function detail::accessor handle::operator[](handle key) const |
|||
|
|||
Return an internal functor to invoke the object's sequence protocol. |
|||
Casting the returned ``detail::accessor`` instance to a :class:`handle` or |
|||
:class:`object` subclass causes a corresponding call to ``__getitem__``. |
|||
Assigning a :class:`handle` or :class:`object` subclass causes a call to |
|||
``__setitem__``. |
|||
|
|||
.. function detail::accessor handle::operator[](const char *key) const |
|||
|
|||
See the above function (the only difference is that they key is provided as |
|||
a string literal). |
|||
|
|||
.. function detail::accessor handle::attr(handle key) const |
|||
|
|||
Return an internal functor to access the object's attributes. |
|||
Casting the returned ``detail::accessor`` instance to a :class:`handle` or |
|||
:class:`object` subclass causes a corresponding call to ``__getattr``. |
|||
Assigning a :class:`handle` or :class:`object` subclass causes a call to |
|||
``__setattr``. |
|||
|
|||
.. function detail::accessor handle::attr(const char *key) const |
|||
|
|||
See the above function (the only difference is that they key is provided as |
|||
a string literal). |
|||
|
|||
.. function operator handle::bool() const |
|||
|
|||
Return ``true`` when the :class:`handle` wraps a valid Python object. |
|||
|
|||
.. function str handle::str() const |
|||
|
|||
Return a string representation of the object. This is analogous to |
|||
the ``str()`` function in Python. |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: template <typename T> T handle::cast() const |
|||
|
|||
Attempt to cast the Python object into the given C++ type. A |
|||
:class:`cast_error` will be throw upon failure. |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: template <typename ... Args> object handle::call(Args&&... args) const |
|||
|
|||
Assuming the Python object is a function or implements the ``__call__`` |
|||
protocol, ``call()`` invokes the underlying function, passing an arbitrary |
|||
set of parameters. The result is returned as a :class:`object` and may need |
|||
to be converted back into a Python object using :func:`handle::cast`. |
|||
|
|||
When some of the arguments cannot be converted to Python objects, the |
|||
function will throw a :class:`cast_error` exception. When the Python |
|||
function call fails, a :class:`error_already_set` exception is thrown. |
|||
|
|||
With reference counting |
|||
----------------------- |
|||
|
|||
.. class:: object : public handle |
|||
|
|||
Like :class:`handle`, the object class is a thin wrapper around an |
|||
arbitrary Python object (i.e. a ``PyObject *`` in Python's C API). In |
|||
contrast to :class:`handle`, it optionally increases the object's reference |
|||
count upon construction, and it *always* decreases the reference count when |
|||
the :class:`object` instance goes out of scope and is destructed. When |
|||
using :class:`object` instances consistently, it is much easier to get |
|||
reference counting right at the first attempt. |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: object::object(const object &o) |
|||
|
|||
Copy constructor; always increases the reference count |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: object::object(const handle &h, bool borrowed) |
|||
|
|||
Creates a :class:`object` from the given :class:`handle`. The reference |
|||
count is only increased if the ``borrowed`` parameter is set to ``true``. |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: object::object(PyObject *ptr, bool borrowed) |
|||
|
|||
Creates a :class:`object` from the given raw Python object pointer. The |
|||
reference count is only increased if the ``borrowed`` parameter is set to |
|||
``true``. |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: object::object(object &&other) |
|||
|
|||
Move constructor; steals the object from ``other`` and preserves its |
|||
reference count. |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: handle object::release() |
|||
|
|||
Resets the internal pointer to ``nullptr`` without without decreasing the |
|||
object's reference count. The function returns a raw handle to the original |
|||
Python object. |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: object::~object() |
|||
|
|||
Destructor, which automatically calls :func:`handle::dec_ref()`. |
|||
|
|||
Convenience classes for specific Python types |
|||
============================================= |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
.. class:: module : public object |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: module::module(const char *name, const char *doc = nullptr) |
|||
|
|||
Create a new top-level Python module with the given name and docstring |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: module module::def_submodule(const char *name, const char *doc = nullptr) |
|||
|
|||
Create and return a new Python submodule with the given name and docstring. |
|||
This also works recursively, i.e. |
|||
|
|||
.. code-block:: cpp |
|||
|
|||
pybind11::module m("example", "pybind11 example plugin"); |
|||
pybind11::module m2 = m.def_submodule("sub", "A submodule of 'example'"); |
|||
pybind11::module m3 = m2.def_submodule("subsub", "A submodule of 'example.sub'"); |
|||
|
|||
.. cpp:function:: template <typename Func, typename ... Extra> module& module::def(const char *name, Func && f, Extra && ... extra) |
|||
|
|||
Create Python binding for a new function within the module scope. ``Func`` |
|||
can be a plain C++ function, a function pointer, or a lambda function. For |
|||
details on the ``Extra&& ... extra`` argument, see section :ref:`extras`. |
|||
|
|||
.. _extras: |
|||
|
|||
Passing extra arguments to the def function |
|||
=========================================== |
|||
|
|||
.. class:: arg |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: arg::arg(const char *name) |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: template <typename T> arg_v arg::operator=(T &&value) |
|||
|
|||
.. class:: arg_v : public arg |
|||
|
|||
Represents a named argument with a default value |
|||
|
|||
.. class:: sibling |
|||
|
|||
Used to specify a handle to an existing sibling function; used internally |
|||
to implement function overloading in :func:`module::def` and |
|||
:func:`class_::def`. |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: sibling::sibling(handle handle) |
|||
|
|||
.. class doc |
|||
|
|||
This is class is internally used by pybind11. |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: doc::doc(const char *value) |
|||
|
|||
Create a new docstring with the specified value |
|||
|
|||
.. class name |
|||
|
|||
This is class is internally used by pybind11. |
|||
|
|||
.. function:: name::name(const char *value) |
|||
|
|||
Used to specify the function name |
|||
|
|||
@ -0,0 +1,22 @@ |
|||
To release a new version of pybind11: |
|||
|
|||
- Update the version number and push to pypi |
|||
- Update ``pybind11/_version.py`` (set release version, remove 'dev') |
|||
- Update version in ``docs/conf.py`` |
|||
- Tag release date in ``docs/changelog.rst``. |
|||
- ``git add`` and ``git commit``. |
|||
- if new minor version: ``git checkout -b vX.Y``, ``git push -u origin vX.Y`` |
|||
- ``git tag -a vX.Y.Z -m 'vX.Y.Z release'``. |
|||
- ``git push`` |
|||
- ``git push --tags``. |
|||
- ``python setup.py sdist upload``. |
|||
- ``python setup.py bdist_wheel upload``. |
|||
- Update conda-forge (https://github.com/conda-forge/pybind11-feedstock) via PR |
|||
- change version number in ``recipe/meta.yml`` |
|||
- update checksum to match the one computed by pypi |
|||
- Get back to work |
|||
- Update ``_version.py`` (add 'dev' and increment minor). |
|||
- Update version in ``docs/conf.py`` |
|||
- Update version macros in ``include/pybind11/common.h`` |
|||
- ``git add`` and ``git commit``. |
|||
``git push`` |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,362 @@ |
|||
/* |
|||
pybind11/pybind11.h: Infrastructure for processing custom |
|||
type and function attributes |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#pragma once |
|||
|
|||
#include "cast.h" |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(pybind11) |
|||
|
|||
/// Annotation for methods |
|||
struct is_method { handle class_; is_method(const handle &c) : class_(c) { } }; |
|||
|
|||
/// Annotation for operators |
|||
struct is_operator { }; |
|||
|
|||
/// Annotation for parent scope |
|||
struct scope { handle value; scope(const handle &s) : value(s) { } }; |
|||
|
|||
/// Annotation for documentation |
|||
struct doc { const char *value; doc(const char *value) : value(value) { } }; |
|||
|
|||
/// Annotation for function names |
|||
struct name { const char *value; name(const char *value) : value(value) { } }; |
|||
|
|||
/// Annotation indicating that a function is an overload associated with a given "sibling" |
|||
struct sibling { handle value; sibling(const handle &value) : value(value.ptr()) { } }; |
|||
|
|||
/// Annotation indicating that a class derives from another given type |
|||
template <typename T> struct base { |
|||
PYBIND11_DEPRECATED("base<T>() was deprecated in favor of specifying 'T' as a template argument to class_") |
|||
base() { } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Keep patient alive while nurse lives |
|||
template <int Nurse, int Patient> struct keep_alive { }; |
|||
|
|||
/// Annotation indicating that a class is involved in a multiple inheritance relationship |
|||
struct multiple_inheritance { }; |
|||
|
|||
/// Annotation which enables dynamic attributes, i.e. adds `__dict__` to a class |
|||
struct dynamic_attr { }; |
|||
|
|||
/// Annotation to mark enums as an arithmetic type |
|||
struct arithmetic { }; |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(detail) |
|||
/* Forward declarations */ |
|||
enum op_id : int; |
|||
enum op_type : int; |
|||
struct undefined_t; |
|||
template <op_id id, op_type ot, typename L = undefined_t, typename R = undefined_t> struct op_; |
|||
template <typename... Args> struct init; |
|||
template <typename... Args> struct init_alias; |
|||
inline void keep_alive_impl(int Nurse, int Patient, handle args, handle ret); |
|||
|
|||
/// Internal data structure which holds metadata about a keyword argument |
|||
struct argument_record { |
|||
const char *name; ///< Argument name |
|||
const char *descr; ///< Human-readable version of the argument value |
|||
handle value; ///< Associated Python object |
|||
|
|||
argument_record(const char *name, const char *descr, handle value) |
|||
: name(name), descr(descr), value(value) { } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Internal data structure which holds metadata about a bound function (signature, overloads, etc.) |
|||
struct function_record { |
|||
function_record() |
|||
: is_constructor(false), is_stateless(false), is_operator(false), |
|||
has_args(false), has_kwargs(false), is_method(false) { } |
|||
|
|||
/// Function name |
|||
char *name = nullptr; /* why no C++ strings? They generate heavier code.. */ |
|||
|
|||
// User-specified documentation string |
|||
char *doc = nullptr; |
|||
|
|||
/// Human-readable version of the function signature |
|||
char *signature = nullptr; |
|||
|
|||
/// List of registered keyword arguments |
|||
std::vector<argument_record> args; |
|||
|
|||
/// Pointer to lambda function which converts arguments and performs the actual call |
|||
handle (*impl) (function_record *, handle, handle, handle) = nullptr; |
|||
|
|||
/// Storage for the wrapped function pointer and captured data, if any |
|||
void *data[3] = { }; |
|||
|
|||
/// Pointer to custom destructor for 'data' (if needed) |
|||
void (*free_data) (function_record *ptr) = nullptr; |
|||
|
|||
/// Return value policy associated with this function |
|||
return_value_policy policy = return_value_policy::automatic; |
|||
|
|||
/// True if name == '__init__' |
|||
bool is_constructor : 1; |
|||
|
|||
/// True if this is a stateless function pointer |
|||
bool is_stateless : 1; |
|||
|
|||
/// True if this is an operator (__add__), etc. |
|||
bool is_operator : 1; |
|||
|
|||
/// True if the function has a '*args' argument |
|||
bool has_args : 1; |
|||
|
|||
/// True if the function has a '**kwargs' argument |
|||
bool has_kwargs : 1; |
|||
|
|||
/// True if this is a method |
|||
bool is_method : 1; |
|||
|
|||
/// Number of arguments |
|||
uint16_t nargs; |
|||
|
|||
/// Python method object |
|||
PyMethodDef *def = nullptr; |
|||
|
|||
/// Python handle to the parent scope (a class or a module) |
|||
handle scope; |
|||
|
|||
/// Python handle to the sibling function representing an overload chain |
|||
handle sibling; |
|||
|
|||
/// Pointer to next overload |
|||
function_record *next = nullptr; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Special data structure which (temporarily) holds metadata about a bound class |
|||
struct type_record { |
|||
PYBIND11_NOINLINE type_record() { } |
|||
|
|||
/// Handle to the parent scope |
|||
handle scope; |
|||
|
|||
/// Name of the class |
|||
const char *name = nullptr; |
|||
|
|||
// Pointer to RTTI type_info data structure |
|||
const std::type_info *type = nullptr; |
|||
|
|||
/// How large is the underlying C++ type? |
|||
size_t type_size = 0; |
|||
|
|||
/// How large is pybind11::instance<type>? |
|||
size_t instance_size = 0; |
|||
|
|||
/// Function pointer to class_<..>::init_holder |
|||
void (*init_holder)(PyObject *, const void *) = nullptr; |
|||
|
|||
/// Function pointer to class_<..>::dealloc |
|||
void (*dealloc)(PyObject *) = nullptr; |
|||
|
|||
/// List of base classes of the newly created type |
|||
list bases; |
|||
|
|||
/// Optional docstring |
|||
const char *doc = nullptr; |
|||
|
|||
/// Multiple inheritance marker |
|||
bool multiple_inheritance = false; |
|||
|
|||
/// Does the class manage a __dict__? |
|||
bool dynamic_attr = false; |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_NOINLINE void add_base(const std::type_info *base, void *(*caster)(void *)) { |
|||
auto base_info = detail::get_type_info(*base, false); |
|||
if (!base_info) { |
|||
std::string tname(base->name()); |
|||
detail::clean_type_id(tname); |
|||
pybind11_fail("generic_type: type \"" + std::string(name) + |
|||
"\" referenced unknown base type \"" + tname + "\""); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
bases.append((PyObject *) base_info->type); |
|||
|
|||
if (base_info->type->tp_dictoffset != 0) |
|||
dynamic_attr = true; |
|||
|
|||
if (caster) |
|||
base_info->implicit_casts.push_back(std::make_pair(type, caster)); |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/** |
|||
* Partial template specializations to process custom attributes provided to |
|||
* cpp_function_ and class_. These are either used to initialize the respective |
|||
* fields in the type_record and function_record data structures or executed at |
|||
* runtime to deal with custom call policies (e.g. keep_alive). |
|||
*/ |
|||
template <typename T, typename SFINAE = void> struct process_attribute; |
|||
|
|||
template <typename T> struct process_attribute_default { |
|||
/// Default implementation: do nothing |
|||
static void init(const T &, function_record *) { } |
|||
static void init(const T &, type_record *) { } |
|||
static void precall(handle) { } |
|||
static void postcall(handle, handle) { } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Process an attribute specifying the function's name |
|||
template <> struct process_attribute<name> : process_attribute_default<name> { |
|||
static void init(const name &n, function_record *r) { r->name = const_cast<char *>(n.value); } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Process an attribute specifying the function's docstring |
|||
template <> struct process_attribute<doc> : process_attribute_default<doc> { |
|||
static void init(const doc &n, function_record *r) { r->doc = const_cast<char *>(n.value); } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Process an attribute specifying the function's docstring (provided as a C-style string) |
|||
template <> struct process_attribute<const char *> : process_attribute_default<const char *> { |
|||
static void init(const char *d, function_record *r) { r->doc = const_cast<char *>(d); } |
|||
static void init(const char *d, type_record *r) { r->doc = const_cast<char *>(d); } |
|||
}; |
|||
template <> struct process_attribute<char *> : process_attribute<const char *> { }; |
|||
|
|||
/// Process an attribute indicating the function's return value policy |
|||
template <> struct process_attribute<return_value_policy> : process_attribute_default<return_value_policy> { |
|||
static void init(const return_value_policy &p, function_record *r) { r->policy = p; } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Process an attribute which indicates that this is an overloaded function associated with a given sibling |
|||
template <> struct process_attribute<sibling> : process_attribute_default<sibling> { |
|||
static void init(const sibling &s, function_record *r) { r->sibling = s.value; } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Process an attribute which indicates that this function is a method |
|||
template <> struct process_attribute<is_method> : process_attribute_default<is_method> { |
|||
static void init(const is_method &s, function_record *r) { r->is_method = true; r->scope = s.class_; } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Process an attribute which indicates the parent scope of a method |
|||
template <> struct process_attribute<scope> : process_attribute_default<scope> { |
|||
static void init(const scope &s, function_record *r) { r->scope = s.value; } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Process an attribute which indicates that this function is an operator |
|||
template <> struct process_attribute<is_operator> : process_attribute_default<is_operator> { |
|||
static void init(const is_operator &, function_record *r) { r->is_operator = true; } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Process a keyword argument attribute (*without* a default value) |
|||
template <> struct process_attribute<arg> : process_attribute_default<arg> { |
|||
static void init(const arg &a, function_record *r) { |
|||
if (r->is_method && r->args.empty()) |
|||
r->args.emplace_back("self", nullptr, handle()); |
|||
r->args.emplace_back(a.name, nullptr, handle()); |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Process a keyword argument attribute (*with* a default value) |
|||
template <> struct process_attribute<arg_v> : process_attribute_default<arg_v> { |
|||
static void init(const arg_v &a, function_record *r) { |
|||
if (r->is_method && r->args.empty()) |
|||
r->args.emplace_back("self", nullptr, handle()); |
|||
|
|||
if (!a.value) { |
|||
#if !defined(NDEBUG) |
|||
auto descr = "'" + std::string(a.name) + ": " + a.type + "'"; |
|||
if (r->is_method) { |
|||
if (r->name) |
|||
descr += " in method '" + (std::string) str(r->scope) + "." + (std::string) r->name + "'"; |
|||
else |
|||
descr += " in method of '" + (std::string) str(r->scope) + "'"; |
|||
} else if (r->name) { |
|||
descr += " in function named '" + (std::string) r->name + "'"; |
|||
} |
|||
pybind11_fail("arg(): could not convert default keyword argument " |
|||
+ descr + " into a Python object (type not registered yet?)"); |
|||
#else |
|||
pybind11_fail("arg(): could not convert default keyword argument " |
|||
"into a Python object (type not registered yet?). " |
|||
"Compile in debug mode for more information."); |
|||
#endif |
|||
} |
|||
r->args.emplace_back(a.name, a.descr, a.value.inc_ref()); |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Process a parent class attribute |
|||
template <typename T> |
|||
struct process_attribute<T, enable_if_t<is_pyobject<T>::value>> : process_attribute_default<handle> { |
|||
static void init(const handle &h, type_record *r) { r->bases.append(h); } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Process a parent class attribute (deprecated, does not support multiple inheritance) |
|||
template <typename T> |
|||
struct process_attribute<base<T>> : process_attribute_default<base<T>> { |
|||
static void init(const base<T> &, type_record *r) { r->add_base(&typeid(T), nullptr); } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Process a multiple inheritance attribute |
|||
template <> |
|||
struct process_attribute<multiple_inheritance> : process_attribute_default<multiple_inheritance> { |
|||
static void init(const multiple_inheritance &, type_record *r) { r->multiple_inheritance = true; } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
template <> |
|||
struct process_attribute<dynamic_attr> : process_attribute_default<dynamic_attr> { |
|||
static void init(const dynamic_attr &, type_record *r) { r->dynamic_attr = true; } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
/// Process an 'arithmetic' attribute for enums (does nothing here) |
|||
template <> |
|||
struct process_attribute<arithmetic> : process_attribute_default<arithmetic> {}; |
|||
|
|||
/*** |
|||
* Process a keep_alive call policy -- invokes keep_alive_impl during the |
|||
* pre-call handler if both Nurse, Patient != 0 and use the post-call handler |
|||
* otherwise |
|||
*/ |
|||
template <int Nurse, int Patient> struct process_attribute<keep_alive<Nurse, Patient>> : public process_attribute_default<keep_alive<Nurse, Patient>> { |
|||
template <int N = Nurse, int P = Patient, enable_if_t<N != 0 && P != 0, int> = 0> |
|||
static void precall(handle args) { keep_alive_impl(Nurse, Patient, args, handle()); } |
|||
template <int N = Nurse, int P = Patient, enable_if_t<N != 0 && P != 0, int> = 0> |
|||
static void postcall(handle, handle) { } |
|||
template <int N = Nurse, int P = Patient, enable_if_t<N == 0 || P == 0, int> = 0> |
|||
static void precall(handle) { } |
|||
template <int N = Nurse, int P = Patient, enable_if_t<N == 0 || P == 0, int> = 0> |
|||
static void postcall(handle args, handle ret) { keep_alive_impl(Nurse, Patient, args, ret); } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Recursively iterate over variadic template arguments |
|||
template <typename... Args> struct process_attributes { |
|||
static void init(const Args&... args, function_record *r) { |
|||
int unused[] = { 0, (process_attribute<typename std::decay<Args>::type>::init(args, r), 0) ... }; |
|||
ignore_unused(unused); |
|||
} |
|||
static void init(const Args&... args, type_record *r) { |
|||
int unused[] = { 0, (process_attribute<typename std::decay<Args>::type>::init(args, r), 0) ... }; |
|||
ignore_unused(unused); |
|||
} |
|||
static void precall(handle fn_args) { |
|||
int unused[] = { 0, (process_attribute<typename std::decay<Args>::type>::precall(fn_args), 0) ... }; |
|||
ignore_unused(unused); |
|||
} |
|||
static void postcall(handle fn_args, handle fn_ret) { |
|||
int unused[] = { 0, (process_attribute<typename std::decay<Args>::type>::postcall(fn_args, fn_ret), 0) ... }; |
|||
ignore_unused(unused); |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Check the number of named arguments at compile time |
|||
template <typename... Extra, |
|||
size_t named = constexpr_sum(std::is_base_of<arg, Extra>::value...), |
|||
size_t self = constexpr_sum(std::is_same<is_method, Extra>::value...)> |
|||
constexpr bool expected_num_args(size_t nargs) { |
|||
return named == 0 || (self + named) == nargs; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_END(detail) |
|||
NAMESPACE_END(pybind11) |
|||
1464
resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/cast.h
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
@ -0,0 +1,160 @@ |
|||
/* |
|||
pybind11/chrono.h: Transparent conversion between std::chrono and python's datetime |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Trent Houliston <trent@houliston.me> and |
|||
Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#pragma once |
|||
|
|||
#include "pybind11.h" |
|||
#include <cmath> |
|||
#include <ctime> |
|||
#include <chrono> |
|||
#include <datetime.h> |
|||
|
|||
// Backport the PyDateTime_DELTA functions from Python3.3 if required |
|||
#ifndef PyDateTime_DELTA_GET_DAYS |
|||
#define PyDateTime_DELTA_GET_DAYS(o) (((PyDateTime_Delta*)o)->days) |
|||
#endif |
|||
#ifndef PyDateTime_DELTA_GET_SECONDS |
|||
#define PyDateTime_DELTA_GET_SECONDS(o) (((PyDateTime_Delta*)o)->seconds) |
|||
#endif |
|||
#ifndef PyDateTime_DELTA_GET_MICROSECONDS |
|||
#define PyDateTime_DELTA_GET_MICROSECONDS(o) (((PyDateTime_Delta*)o)->microseconds) |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(pybind11) |
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(detail) |
|||
|
|||
template <typename type> class duration_caster { |
|||
public: |
|||
typedef typename type::rep rep; |
|||
typedef typename type::period period; |
|||
|
|||
typedef std::chrono::duration<uint_fast32_t, std::ratio<86400>> days; |
|||
|
|||
bool load(handle src, bool) { |
|||
using namespace std::chrono; |
|||
|
|||
// Lazy initialise the PyDateTime import |
|||
if (!PyDateTimeAPI) { PyDateTime_IMPORT; } |
|||
|
|||
if (!src) return false; |
|||
// If invoked with datetime.delta object |
|||
if (PyDelta_Check(src.ptr())) { |
|||
value = type(duration_cast<duration<rep, period>>( |
|||
days(PyDateTime_DELTA_GET_DAYS(src.ptr())) |
|||
+ seconds(PyDateTime_DELTA_GET_SECONDS(src.ptr())) |
|||
+ microseconds(PyDateTime_DELTA_GET_MICROSECONDS(src.ptr())))); |
|||
return true; |
|||
} |
|||
// If invoked with a float we assume it is seconds and convert |
|||
else if (PyFloat_Check(src.ptr())) { |
|||
value = type(duration_cast<duration<rep, period>>(duration<double>(PyFloat_AsDouble(src.ptr())))); |
|||
return true; |
|||
} |
|||
else return false; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// If this is a duration just return it back |
|||
static const std::chrono::duration<rep, period>& get_duration(const std::chrono::duration<rep, period> &src) { |
|||
return src; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// If this is a time_point get the time_since_epoch |
|||
template <typename Clock> static std::chrono::duration<rep, period> get_duration(const std::chrono::time_point<Clock, std::chrono::duration<rep, period>> &src) { |
|||
return src.time_since_epoch(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
static handle cast(const type &src, return_value_policy /* policy */, handle /* parent */) { |
|||
using namespace std::chrono; |
|||
|
|||
// Use overloaded function to get our duration from our source |
|||
// Works out if it is a duration or time_point and get the duration |
|||
auto d = get_duration(src); |
|||
|
|||
// Lazy initialise the PyDateTime import |
|||
if (!PyDateTimeAPI) { PyDateTime_IMPORT; } |
|||
|
|||
// Declare these special duration types so the conversions happen with the correct primitive types (int) |
|||
using dd_t = duration<int, std::ratio<86400>>; |
|||
using ss_t = duration<int, std::ratio<1>>; |
|||
using us_t = duration<int, std::micro>; |
|||
|
|||
return PyDelta_FromDSU(duration_cast<dd_t>(d).count(), |
|||
duration_cast<ss_t>(d % days(1)).count(), |
|||
duration_cast<us_t>(d % seconds(1)).count()); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_TYPE_CASTER(type, _("datetime.timedelta")); |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
// This is for casting times on the system clock into datetime.datetime instances |
|||
template <typename Duration> class type_caster<std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, Duration>> { |
|||
public: |
|||
typedef std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, Duration> type; |
|||
bool load(handle src, bool) { |
|||
using namespace std::chrono; |
|||
|
|||
// Lazy initialise the PyDateTime import |
|||
if (!PyDateTimeAPI) { PyDateTime_IMPORT; } |
|||
|
|||
if (!src) return false; |
|||
if (PyDateTime_Check(src.ptr())) { |
|||
std::tm cal; |
|||
cal.tm_sec = PyDateTime_DATE_GET_SECOND(src.ptr()); |
|||
cal.tm_min = PyDateTime_DATE_GET_MINUTE(src.ptr()); |
|||
cal.tm_hour = PyDateTime_DATE_GET_HOUR(src.ptr()); |
|||
cal.tm_mday = PyDateTime_GET_DAY(src.ptr()); |
|||
cal.tm_mon = PyDateTime_GET_MONTH(src.ptr()) - 1; |
|||
cal.tm_year = PyDateTime_GET_YEAR(src.ptr()) - 1900; |
|||
cal.tm_isdst = -1; |
|||
|
|||
value = system_clock::from_time_t(std::mktime(&cal)) + microseconds(PyDateTime_DATE_GET_MICROSECOND(src.ptr())); |
|||
return true; |
|||
} |
|||
else return false; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
static handle cast(const std::chrono::time_point<std::chrono::system_clock, Duration> &src, return_value_policy /* policy */, handle /* parent */) { |
|||
using namespace std::chrono; |
|||
|
|||
// Lazy initialise the PyDateTime import |
|||
if (!PyDateTimeAPI) { PyDateTime_IMPORT; } |
|||
|
|||
std::time_t tt = system_clock::to_time_t(src); |
|||
// this function uses static memory so it's best to copy it out asap just in case |
|||
// otherwise other code that is using localtime may break this (not just python code) |
|||
std::tm localtime = *std::localtime(&tt); |
|||
|
|||
// Declare these special duration types so the conversions happen with the correct primitive types (int) |
|||
using us_t = duration<int, std::micro>; |
|||
|
|||
return PyDateTime_FromDateAndTime(localtime.tm_year + 1900, |
|||
localtime.tm_mon + 1, |
|||
localtime.tm_mday, |
|||
localtime.tm_hour, |
|||
localtime.tm_min, |
|||
localtime.tm_sec, |
|||
(duration_cast<us_t>(src.time_since_epoch() % seconds(1))).count()); |
|||
} |
|||
PYBIND11_TYPE_CASTER(type, _("datetime.datetime")); |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
// Other clocks that are not the system clock are not measured as datetime.datetime objects |
|||
// since they are not measured on calendar time. So instead we just make them timedeltas |
|||
// Or if they have passed us a time as a float we convert that |
|||
template <typename Clock, typename Duration> class type_caster<std::chrono::time_point<Clock, Duration>> |
|||
: public duration_caster<std::chrono::time_point<Clock, Duration>> { |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
template <typename Rep, typename Period> class type_caster<std::chrono::duration<Rep, Period>> |
|||
: public duration_caster<std::chrono::duration<Rep, Period>> { |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_END(detail) |
|||
NAMESPACE_END(pybind11) |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,560 @@ |
|||
/* |
|||
pybind11/common.h -- Basic macros |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#pragma once |
|||
|
|||
#if !defined(NAMESPACE_BEGIN) |
|||
# define NAMESPACE_BEGIN(name) namespace name { |
|||
#endif |
|||
#if !defined(NAMESPACE_END) |
|||
# define NAMESPACE_END(name) } |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
// Neither MSVC nor Intel support enough of C++14 yet (in particular, as of MSVC 2015 and ICC 17 |
|||
// beta, neither support extended constexpr, which we rely on in descr.h), so don't enable pybind |
|||
// CPP14 features for them. |
|||
#if !defined(_MSC_VER) && !defined(__INTEL_COMPILER) |
|||
# if __cplusplus >= 201402L |
|||
# define PYBIND11_CPP14 |
|||
# if __cplusplus > 201402L /* Temporary: should be updated to >= the final C++17 value once known */ |
|||
# define PYBIND11_CPP17 |
|||
# endif |
|||
# endif |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
#if !defined(PYBIND11_EXPORT) |
|||
# if defined(WIN32) || defined(_WIN32) |
|||
# define PYBIND11_EXPORT __declspec(dllexport) |
|||
# else |
|||
# define PYBIND11_EXPORT __attribute__ ((visibility("default"))) |
|||
# endif |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
#if defined(_MSC_VER) |
|||
# define PYBIND11_NOINLINE __declspec(noinline) |
|||
#else |
|||
# define PYBIND11_NOINLINE __attribute__ ((noinline)) |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
#if defined(PYBIND11_CPP14) |
|||
# define PYBIND11_DEPRECATED(reason) [[deprecated(reason)]] |
|||
#elif defined(__clang__) |
|||
# define PYBIND11_DEPRECATED(reason) __attribute__((deprecated(reason))) |
|||
#elif defined(__GNUG__) |
|||
# define PYBIND11_DEPRECATED(reason) __attribute__((deprecated)) |
|||
#elif defined(_MSC_VER) |
|||
# define PYBIND11_DEPRECATED(reason) __declspec(deprecated) |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
#define PYBIND11_VERSION_MAJOR 1 |
|||
#define PYBIND11_VERSION_MINOR 9 |
|||
#define PYBIND11_VERSION_PATCH dev0 |
|||
|
|||
/// Include Python header, disable linking to pythonX_d.lib on Windows in debug mode |
|||
#if defined(_MSC_VER) |
|||
# define HAVE_ROUND |
|||
# pragma warning(push) |
|||
# pragma warning(disable: 4510 4610 4512 4005) |
|||
# if _DEBUG |
|||
# define PYBIND11_DEBUG_MARKER |
|||
# undef _DEBUG |
|||
# endif |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
#include <Python.h> |
|||
#include <frameobject.h> |
|||
#include <pythread.h> |
|||
|
|||
#if defined(_WIN32) && (defined(min) || defined(max)) |
|||
# error Macro clash with min and max -- define NOMINMAX when compiling your program on Windows |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
#if defined(isalnum) |
|||
# undef isalnum |
|||
# undef isalpha |
|||
# undef islower |
|||
# undef isspace |
|||
# undef isupper |
|||
# undef tolower |
|||
# undef toupper |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
#if defined(_MSC_VER) |
|||
# if defined(PYBIND11_DEBUG_MARKER) |
|||
# define _DEBUG |
|||
# undef PYBIND11_DEBUG_MARKER |
|||
# endif |
|||
# pragma warning(pop) |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
#include <cstddef> |
|||
#include <forward_list> |
|||
#include <vector> |
|||
#include <string> |
|||
#include <stdexcept> |
|||
#include <unordered_set> |
|||
#include <unordered_map> |
|||
#include <memory> |
|||
#include <typeindex> |
|||
#include <type_traits> |
|||
|
|||
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3 /// Compatibility macros for various Python versions |
|||
#define PYBIND11_INSTANCE_METHOD_NEW(ptr, class_) PyInstanceMethod_New(ptr) |
|||
#define PYBIND11_BYTES_CHECK PyBytes_Check |
|||
#define PYBIND11_BYTES_FROM_STRING PyBytes_FromString |
|||
#define PYBIND11_BYTES_FROM_STRING_AND_SIZE PyBytes_FromStringAndSize |
|||
#define PYBIND11_BYTES_AS_STRING_AND_SIZE PyBytes_AsStringAndSize |
|||
#define PYBIND11_BYTES_AS_STRING PyBytes_AsString |
|||
#define PYBIND11_LONG_CHECK(o) PyLong_Check(o) |
|||
#define PYBIND11_LONG_AS_LONGLONG(o) PyLong_AsLongLong(o) |
|||
#define PYBIND11_LONG_AS_UNSIGNED_LONGLONG(o) PyLong_AsUnsignedLongLong(o) |
|||
#define PYBIND11_BYTES_NAME "bytes" |
|||
#define PYBIND11_STRING_NAME "str" |
|||
#define PYBIND11_SLICE_OBJECT PyObject |
|||
#define PYBIND11_FROM_STRING PyUnicode_FromString |
|||
#define PYBIND11_STR_TYPE ::pybind11::str |
|||
#define PYBIND11_OB_TYPE(ht_type) (ht_type).ob_base.ob_base.ob_type |
|||
#define PYBIND11_PLUGIN_IMPL(name) \ |
|||
extern "C" PYBIND11_EXPORT PyObject *PyInit_##name() |
|||
#else |
|||
#define PYBIND11_INSTANCE_METHOD_NEW(ptr, class_) PyMethod_New(ptr, nullptr, class_) |
|||
#define PYBIND11_BYTES_CHECK PyString_Check |
|||
#define PYBIND11_BYTES_FROM_STRING PyString_FromString |
|||
#define PYBIND11_BYTES_FROM_STRING_AND_SIZE PyString_FromStringAndSize |
|||
#define PYBIND11_BYTES_AS_STRING_AND_SIZE PyString_AsStringAndSize |
|||
#define PYBIND11_BYTES_AS_STRING PyString_AsString |
|||
#define PYBIND11_LONG_CHECK(o) (PyInt_Check(o) || PyLong_Check(o)) |
|||
#define PYBIND11_LONG_AS_LONGLONG(o) (PyInt_Check(o) ? (long long) PyLong_AsLong(o) : PyLong_AsLongLong(o)) |
|||
#define PYBIND11_LONG_AS_UNSIGNED_LONGLONG(o) (PyInt_Check(o) ? (unsigned long long) PyLong_AsUnsignedLong(o) : PyLong_AsUnsignedLongLong(o)) |
|||
#define PYBIND11_BYTES_NAME "str" |
|||
#define PYBIND11_STRING_NAME "unicode" |
|||
#define PYBIND11_SLICE_OBJECT PySliceObject |
|||
#define PYBIND11_FROM_STRING PyString_FromString |
|||
#define PYBIND11_STR_TYPE ::pybind11::bytes |
|||
#define PYBIND11_OB_TYPE(ht_type) (ht_type).ob_type |
|||
#define PYBIND11_PLUGIN_IMPL(name) \ |
|||
extern "C" PYBIND11_EXPORT PyObject *init##name() |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x03050000 && PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x03050200 |
|||
extern "C" { |
|||
struct _Py_atomic_address { void *value; }; |
|||
PyAPI_DATA(_Py_atomic_address) _PyThreadState_Current; |
|||
} |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
#define PYBIND11_TRY_NEXT_OVERLOAD ((PyObject *) 1) // special failure return code |
|||
#define PYBIND11_STRINGIFY(x) #x |
|||
#define PYBIND11_TOSTRING(x) PYBIND11_STRINGIFY(x) |
|||
#define PYBIND11_INTERNALS_ID "__pybind11_" \ |
|||
PYBIND11_TOSTRING(PYBIND11_VERSION_MAJOR) "_" PYBIND11_TOSTRING(PYBIND11_VERSION_MINOR) "__" |
|||
|
|||
#define PYBIND11_PLUGIN(name) \ |
|||
static PyObject *pybind11_init(); \ |
|||
PYBIND11_PLUGIN_IMPL(name) { \ |
|||
int major, minor; \ |
|||
if (sscanf(Py_GetVersion(), "%i.%i", &major, &minor) != 2) { \ |
|||
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_ImportError, "Can't parse Python version."); \ |
|||
return nullptr; \ |
|||
} else if (major != PY_MAJOR_VERSION || minor != PY_MINOR_VERSION) { \ |
|||
PyErr_Format(PyExc_ImportError, \ |
|||
"Python version mismatch: module was compiled for " \ |
|||
"version %i.%i, while the interpreter is running " \ |
|||
"version %i.%i.", PY_MAJOR_VERSION, PY_MINOR_VERSION, \ |
|||
major, minor); \ |
|||
return nullptr; \ |
|||
} \ |
|||
try { \ |
|||
return pybind11_init(); \ |
|||
} catch (const std::exception &e) { \ |
|||
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_ImportError, e.what()); \ |
|||
return nullptr; \ |
|||
} \ |
|||
} \ |
|||
PyObject *pybind11_init() |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(pybind11) |
|||
|
|||
using ssize_t = Py_ssize_t; |
|||
using size_t = std::size_t; |
|||
|
|||
/// Approach used to cast a previously unknown C++ instance into a Python object |
|||
enum class return_value_policy : uint8_t { |
|||
/** This is the default return value policy, which falls back to the policy |
|||
return_value_policy::take_ownership when the return value is a pointer. |
|||
Otherwise, it uses return_value::move or return_value::copy for rvalue |
|||
and lvalue references, respectively. See below for a description of what |
|||
all of these different policies do. */ |
|||
automatic = 0, |
|||
|
|||
/** As above, but use policy return_value_policy::reference when the return |
|||
value is a pointer. This is the default conversion policy for function |
|||
arguments when calling Python functions manually from C++ code (i.e. via |
|||
handle::operator()). You probably won't need to use this. */ |
|||
automatic_reference, |
|||
|
|||
/** Reference an existing object (i.e. do not create a new copy) and take |
|||
ownership. Python will call the destructor and delete operator when the |
|||
object’s reference count reaches zero. Undefined behavior ensues when |
|||
the C++ side does the same.. */ |
|||
take_ownership, |
|||
|
|||
/** Create a new copy of the returned object, which will be owned by |
|||
Python. This policy is comparably safe because the lifetimes of the two |
|||
instances are decoupled. */ |
|||
copy, |
|||
|
|||
/** Use std::move to move the return value contents into a new instance |
|||
that will be owned by Python. This policy is comparably safe because the |
|||
lifetimes of the two instances (move source and destination) are |
|||
decoupled. */ |
|||
move, |
|||
|
|||
/** Reference an existing object, but do not take ownership. The C++ side |
|||
is responsible for managing the object’s lifetime and deallocating it |
|||
when it is no longer used. Warning: undefined behavior will ensue when |
|||
the C++ side deletes an object that is still referenced and used by |
|||
Python. */ |
|||
reference, |
|||
|
|||
/** This policy only applies to methods and properties. It references the |
|||
object without taking ownership similar to the above |
|||
return_value_policy::reference policy. In contrast to that policy, the |
|||
function or property’s implicit this argument (called the parent) is |
|||
considered to be the the owner of the return value (the child). |
|||
pybind11 then couples the lifetime of the parent to the child via a |
|||
reference relationship that ensures that the parent cannot be garbage |
|||
collected while Python is still using the child. More advanced |
|||
variations of this scheme are also possible using combinations of |
|||
return_value_policy::reference and the keep_alive call policy */ |
|||
reference_internal |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Information record describing a Python buffer object |
|||
struct buffer_info { |
|||
void *ptr = nullptr; // Pointer to the underlying storage |
|||
size_t itemsize = 0; // Size of individual items in bytes |
|||
size_t size = 0; // Total number of entries |
|||
std::string format; // For homogeneous buffers, this should be set to format_descriptor<T>::format() |
|||
size_t ndim = 0; // Number of dimensions |
|||
std::vector<size_t> shape; // Shape of the tensor (1 entry per dimension) |
|||
std::vector<size_t> strides; // Number of entries between adjacent entries (for each per dimension) |
|||
|
|||
buffer_info() { } |
|||
|
|||
buffer_info(void *ptr, size_t itemsize, const std::string &format, size_t ndim, |
|||
const std::vector<size_t> &shape, const std::vector<size_t> &strides) |
|||
: ptr(ptr), itemsize(itemsize), size(1), format(format), |
|||
ndim(ndim), shape(shape), strides(strides) { |
|||
for (size_t i = 0; i < ndim; ++i) |
|||
size *= shape[i]; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
buffer_info(void *ptr, size_t itemsize, const std::string &format, size_t size) |
|||
: buffer_info(ptr, itemsize, format, 1, std::vector<size_t> { size }, |
|||
std::vector<size_t> { itemsize }) { } |
|||
|
|||
explicit buffer_info(Py_buffer *view, bool ownview = true) |
|||
: ptr(view->buf), itemsize((size_t) view->itemsize), size(1), format(view->format), |
|||
ndim((size_t) view->ndim), shape((size_t) view->ndim), strides((size_t) view->ndim), view(view), ownview(ownview) { |
|||
for (size_t i = 0; i < (size_t) view->ndim; ++i) { |
|||
shape[i] = (size_t) view->shape[i]; |
|||
strides[i] = (size_t) view->strides[i]; |
|||
size *= shape[i]; |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
buffer_info(const buffer_info &) = delete; |
|||
buffer_info& operator=(const buffer_info &) = delete; |
|||
|
|||
buffer_info(buffer_info &&other) { |
|||
(*this) = std::move(other); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
buffer_info& operator=(buffer_info &&rhs) { |
|||
ptr = rhs.ptr; |
|||
itemsize = rhs.itemsize; |
|||
size = rhs.size; |
|||
format = std::move(rhs.format); |
|||
ndim = rhs.ndim; |
|||
shape = std::move(rhs.shape); |
|||
strides = std::move(rhs.strides); |
|||
std::swap(view, rhs.view); |
|||
std::swap(ownview, rhs.ownview); |
|||
return *this; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
~buffer_info() { |
|||
if (view && ownview) { PyBuffer_Release(view); delete view; } |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
private: |
|||
Py_buffer *view = nullptr; |
|||
bool ownview = false; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(detail) |
|||
|
|||
inline static constexpr int log2(size_t n, int k = 0) { return (n <= 1) ? k : log2(n >> 1, k + 1); } |
|||
|
|||
inline std::string error_string(); |
|||
|
|||
/// Core part of the 'instance' type which POD (needed to be able to use 'offsetof') |
|||
template <typename type> struct instance_essentials { |
|||
PyObject_HEAD |
|||
type *value; |
|||
PyObject *weakrefs; |
|||
bool owned : 1; |
|||
bool holder_constructed : 1; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// PyObject wrapper around generic types, includes a special holder type that is responsible for lifetime management |
|||
template <typename type, typename holder_type = std::unique_ptr<type>> struct instance : instance_essentials<type> { |
|||
holder_type holder; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
struct overload_hash { |
|||
inline size_t operator()(const std::pair<const PyObject *, const char *>& v) const { |
|||
size_t value = std::hash<const void *>()(v.first); |
|||
value ^= std::hash<const void *>()(v.second) + 0x9e3779b9 + (value<<6) + (value>>2); |
|||
return value; |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Internal data struture used to track registered instances and types |
|||
struct internals { |
|||
std::unordered_map<std::type_index, void*> registered_types_cpp; // std::type_index -> type_info |
|||
std::unordered_map<const void *, void*> registered_types_py; // PyTypeObject* -> type_info |
|||
std::unordered_multimap<const void *, void*> registered_instances; // void * -> PyObject* |
|||
std::unordered_set<std::pair<const PyObject *, const char *>, overload_hash> inactive_overload_cache; |
|||
std::unordered_map<std::type_index, std::vector<bool (*)(PyObject *, void *&)>> direct_conversions; |
|||
std::forward_list<void (*) (std::exception_ptr)> registered_exception_translators; |
|||
std::unordered_map<std::string, void *> shared_data; // Custom data to be shared across extensions |
|||
#if defined(WITH_THREAD) |
|||
decltype(PyThread_create_key()) tstate = 0; // Usually an int but a long on Cygwin64 with Python 3.x |
|||
PyInterpreterState *istate = nullptr; |
|||
#endif |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Return a reference to the current 'internals' information |
|||
inline internals &get_internals(); |
|||
|
|||
/// Index sequence for convenient template metaprogramming involving tuples |
|||
#ifdef PYBIND11_CPP14 |
|||
using std::index_sequence; |
|||
using std::make_index_sequence; |
|||
#else |
|||
template<size_t ...> struct index_sequence { }; |
|||
template<size_t N, size_t ...S> struct make_index_sequence_impl : make_index_sequence_impl <N - 1, N - 1, S...> { }; |
|||
template<size_t ...S> struct make_index_sequence_impl <0, S...> { typedef index_sequence<S...> type; }; |
|||
template<size_t N> using make_index_sequence = typename make_index_sequence_impl<N>::type; |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
/// Strip the class from a method type |
|||
template <typename T> struct remove_class { }; |
|||
template <typename C, typename R, typename... A> struct remove_class<R (C::*)(A...)> { typedef R type(A...); }; |
|||
template <typename C, typename R, typename... A> struct remove_class<R (C::*)(A...) const> { typedef R type(A...); }; |
|||
|
|||
/// Helper template to strip away type modifiers |
|||
template <typename T> struct intrinsic_type { typedef T type; }; |
|||
template <typename T> struct intrinsic_type<const T> { typedef typename intrinsic_type<T>::type type; }; |
|||
template <typename T> struct intrinsic_type<T*> { typedef typename intrinsic_type<T>::type type; }; |
|||
template <typename T> struct intrinsic_type<T&> { typedef typename intrinsic_type<T>::type type; }; |
|||
template <typename T> struct intrinsic_type<T&&> { typedef typename intrinsic_type<T>::type type; }; |
|||
template <typename T, size_t N> struct intrinsic_type<const T[N]> { typedef typename intrinsic_type<T>::type type; }; |
|||
template <typename T, size_t N> struct intrinsic_type<T[N]> { typedef typename intrinsic_type<T>::type type; }; |
|||
template <typename T> using intrinsic_t = typename intrinsic_type<T>::type; |
|||
|
|||
/// Helper type to replace 'void' in some expressions |
|||
struct void_type { }; |
|||
|
|||
/// Helper template which holds a list of types |
|||
template <typename...> struct type_list { }; |
|||
|
|||
/// from __cpp_future__ import (convenient aliases from C++14/17) |
|||
template <bool B> using bool_constant = std::integral_constant<bool, B>; |
|||
template <class T> using negation = bool_constant<!T::value>; |
|||
template <bool B, typename T = void> using enable_if_t = typename std::enable_if<B, T>::type; |
|||
template <bool B, typename T, typename F> using conditional_t = typename std::conditional<B, T, F>::type; |
|||
|
|||
/// Compile-time integer sum |
|||
constexpr size_t constexpr_sum() { return 0; } |
|||
template <typename T, typename... Ts> |
|||
constexpr size_t constexpr_sum(T n, Ts... ns) { return size_t{n} + constexpr_sum(ns...); } |
|||
|
|||
// Counts the number of types in the template parameter pack matching the predicate |
|||
#if !defined(_MSC_VER) |
|||
template <template<typename> class Predicate, typename... Ts> |
|||
using count_t = std::integral_constant<size_t, constexpr_sum(Predicate<Ts>::value...)>; |
|||
#else |
|||
// MSVC workaround (2015 Update 3 has issues with some member type aliases and constexpr) |
|||
template <template<typename> class Predicate, typename... Ts> struct count_t; |
|||
template <template<typename> class Predicate> struct count_t<Predicate> : std::integral_constant<size_t, 0> {}; |
|||
template <template<typename> class Predicate, class T, class... Ts> |
|||
struct count_t<Predicate, T, Ts...> : std::integral_constant<size_t, Predicate<T>::value + count_t<Predicate, Ts...>::value> {}; |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
/// Return true if all/any Ts satify Predicate<T> |
|||
template <template<typename> class Predicate, typename... Ts> |
|||
using all_of_t = bool_constant<(count_t<Predicate, Ts...>::value == sizeof...(Ts))>; |
|||
template <template<typename> class Predicate, typename... Ts> |
|||
using any_of_t = bool_constant<(count_t<Predicate, Ts...>::value > 0)>; |
|||
|
|||
// Extracts the first type from the template parameter pack matching the predicate, or Default if none match. |
|||
template <template<class> class Predicate, class Default, class... Ts> struct first_of; |
|||
template <template<class> class Predicate, class Default> struct first_of<Predicate, Default> { |
|||
using type = Default; |
|||
}; |
|||
template <template<class> class Predicate, class Default, class T, class... Ts> |
|||
struct first_of<Predicate, Default, T, Ts...> { |
|||
using type = typename std::conditional< |
|||
Predicate<T>::value, |
|||
T, |
|||
typename first_of<Predicate, Default, Ts...>::type |
|||
>::type; |
|||
}; |
|||
template <template<class> class Predicate, class Default, class... T> using first_of_t = typename first_of<Predicate, Default, T...>::type; |
|||
|
|||
/// Defer the evaluation of type T until types Us are instantiated |
|||
template <typename T, typename... /*Us*/> struct deferred_type { using type = T; }; |
|||
template <typename T, typename... Us> using deferred_t = typename deferred_type<T, Us...>::type; |
|||
|
|||
template <template<typename...> class Base> |
|||
struct is_template_base_of_impl { |
|||
template <typename... Us> static std::true_type check(Base<Us...> *); |
|||
static std::false_type check(...); |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Check if a template is the base of a type. For example: |
|||
/// `is_template_base_of<Base, T>` is true if `struct T : Base<U> {}` where U can be anything |
|||
template <template<typename...> class Base, typename T> |
|||
#if !defined(_MSC_VER) |
|||
using is_template_base_of = decltype(is_template_base_of_impl<Base>::check((T*)nullptr)); |
|||
#else // MSVC2015 has trouble with decltype in template aliases |
|||
struct is_template_base_of : decltype(is_template_base_of_impl<Base>::check((T*)nullptr)) { }; |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
/// Check if T is std::shared_ptr<U> where U can be anything |
|||
template <typename T> struct is_shared_ptr : std::false_type { }; |
|||
template <typename U> struct is_shared_ptr<std::shared_ptr<U>> : std::true_type { }; |
|||
|
|||
/// Ignore that a variable is unused in compiler warnings |
|||
inline void ignore_unused(const int *) { } |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_END(detail) |
|||
|
|||
/// Returns a named pointer that is shared among all extension modules (using the same |
|||
/// pybind11 version) running in the current interpreter. Names starting with underscores |
|||
/// are reserved for internal usage. Returns `nullptr` if no matching entry was found. |
|||
inline PYBIND11_NOINLINE void* get_shared_data(const std::string& name) { |
|||
auto& internals = detail::get_internals(); |
|||
auto it = internals.shared_data.find(name); |
|||
return it != internals.shared_data.end() ? it->second : nullptr; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
/// Set the shared data that can be later recovered by `get_shared_data()`. |
|||
inline PYBIND11_NOINLINE void *set_shared_data(const std::string& name, void *data) { |
|||
detail::get_internals().shared_data[name] = data; |
|||
return data; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
/// Returns a typed reference to a shared data entry (by using `get_shared_data()`) if |
|||
/// such entry exists. Otherwise, a new object of default-constructible type `T` is |
|||
/// added to the shared data under the given name and a reference to it is returned. |
|||
template<typename T> T& get_or_create_shared_data(const std::string& name) { |
|||
auto& internals = detail::get_internals(); |
|||
auto it = internals.shared_data.find(name); |
|||
T* ptr = (T*) (it != internals.shared_data.end() ? it->second : nullptr); |
|||
if (!ptr) { |
|||
ptr = new T(); |
|||
internals.shared_data[name] = ptr; |
|||
} |
|||
return *ptr; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
/// Fetch and hold an error which was already set in Python |
|||
class error_already_set : public std::runtime_error { |
|||
public: |
|||
error_already_set() : std::runtime_error(detail::error_string()) { |
|||
PyErr_Fetch(&type, &value, &trace); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
error_already_set(const error_already_set &) = delete; |
|||
|
|||
error_already_set(error_already_set &&e) |
|||
: std::runtime_error(e.what()), type(e.type), value(e.value), |
|||
trace(e.trace) { e.type = e.value = e.trace = nullptr; } |
|||
|
|||
inline ~error_already_set(); // implementation in pybind11.h |
|||
|
|||
error_already_set& operator=(const error_already_set &) = delete; |
|||
|
|||
/// Give the error back to Python |
|||
void restore() { PyErr_Restore(type, value, trace); type = value = trace = nullptr; } |
|||
|
|||
private: |
|||
PyObject *type, *value, *trace; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// C++ bindings of builtin Python exceptions |
|||
class builtin_exception : public std::runtime_error { |
|||
public: |
|||
using std::runtime_error::runtime_error; |
|||
virtual void set_error() const = 0; /// Set the error using the Python C API |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
#define PYBIND11_RUNTIME_EXCEPTION(name, type) \ |
|||
class name : public builtin_exception { public: \ |
|||
using builtin_exception::builtin_exception; \ |
|||
name() : name("") { } \ |
|||
void set_error() const override { PyErr_SetString(type, what()); } \ |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_RUNTIME_EXCEPTION(stop_iteration, PyExc_StopIteration) |
|||
PYBIND11_RUNTIME_EXCEPTION(index_error, PyExc_IndexError) |
|||
PYBIND11_RUNTIME_EXCEPTION(key_error, PyExc_KeyError) |
|||
PYBIND11_RUNTIME_EXCEPTION(value_error, PyExc_ValueError) |
|||
PYBIND11_RUNTIME_EXCEPTION(type_error, PyExc_TypeError) |
|||
PYBIND11_RUNTIME_EXCEPTION(cast_error, PyExc_RuntimeError) /// Thrown when pybind11::cast or handle::call fail due to a type casting error |
|||
PYBIND11_RUNTIME_EXCEPTION(reference_cast_error, PyExc_RuntimeError) /// Used internally |
|||
|
|||
[[noreturn]] PYBIND11_NOINLINE inline void pybind11_fail(const char *reason) { throw std::runtime_error(reason); } |
|||
[[noreturn]] PYBIND11_NOINLINE inline void pybind11_fail(const std::string &reason) { throw std::runtime_error(reason); } |
|||
|
|||
/// Format strings for basic number types |
|||
#define PYBIND11_DECL_FMT(t, v) template<> struct format_descriptor<t> \ |
|||
{ static constexpr const char* value = v; /* for backwards compatibility */ \ |
|||
static std::string format() { return value; } } |
|||
|
|||
template <typename T, typename SFINAE = void> struct format_descriptor { }; |
|||
|
|||
template <typename T> struct format_descriptor<T, detail::enable_if_t<std::is_integral<T>::value>> { |
|||
static constexpr const char c = "bBhHiIqQ"[detail::log2(sizeof(T))*2 + std::is_unsigned<T>::value]; |
|||
static constexpr const char value[2] = { c, '\0' }; |
|||
static std::string format() { return std::string(1, c); } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
template <typename T> constexpr const char format_descriptor< |
|||
T, detail::enable_if_t<std::is_integral<T>::value>>::value[2]; |
|||
|
|||
/// RAII wrapper that temporarily clears any Python error state |
|||
struct error_scope { |
|||
PyObject *type, *value, *trace; |
|||
error_scope() { PyErr_Fetch(&type, &value, &trace); } |
|||
~error_scope() { PyErr_Restore(type, value, trace); } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_DECL_FMT(float, "f"); |
|||
PYBIND11_DECL_FMT(double, "d"); |
|||
PYBIND11_DECL_FMT(bool, "?"); |
|||
|
|||
/// Dummy destructor wrapper that can be used to expose classes with a private destructor |
|||
struct nodelete { template <typename T> void operator()(T*) { } }; |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_END(pybind11) |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,47 @@ |
|||
/* |
|||
pybind11/complex.h: Complex number support |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#pragma once |
|||
|
|||
#include "pybind11.h" |
|||
#include <complex> |
|||
|
|||
/// glibc defines I as a macro which breaks things, e.g., boost template names |
|||
#ifdef I |
|||
# undef I |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(pybind11) |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_DECL_FMT(std::complex<float>, "Zf"); |
|||
PYBIND11_DECL_FMT(std::complex<double>, "Zd"); |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(detail) |
|||
template <typename T> class type_caster<std::complex<T>> { |
|||
public: |
|||
bool load(handle src, bool) { |
|||
if (!src) |
|||
return false; |
|||
Py_complex result = PyComplex_AsCComplex(src.ptr()); |
|||
if (result.real == -1.0 && PyErr_Occurred()) { |
|||
PyErr_Clear(); |
|||
return false; |
|||
} |
|||
value = std::complex<T>((T) result.real, (T) result.imag); |
|||
return true; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
static handle cast(const std::complex<T> &src, return_value_policy /* policy */, handle /* parent */) { |
|||
return PyComplex_FromDoubles((double) src.real(), (double) src.imag()); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_TYPE_CASTER(std::complex<T>, _("complex")); |
|||
}; |
|||
NAMESPACE_END(detail) |
|||
NAMESPACE_END(pybind11) |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,177 @@ |
|||
/* |
|||
pybind11/descr.h: Helper type for concatenating type signatures |
|||
either at runtime (C++11) or compile time (C++14) |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#pragma once |
|||
|
|||
#include "common.h" |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(pybind11) |
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(detail) |
|||
|
|||
#if defined(PYBIND11_CPP14) /* Concatenate type signatures at compile time using C++14 */ |
|||
|
|||
template <size_t Size1, size_t Size2> class descr { |
|||
template <size_t Size1_, size_t Size2_> friend class descr; |
|||
public: |
|||
constexpr descr(char const (&text) [Size1+1], const std::type_info * const (&types)[Size2+1]) |
|||
: descr(text, types, |
|||
make_index_sequence<Size1>(), |
|||
make_index_sequence<Size2>()) { } |
|||
|
|||
constexpr const char *text() const { return m_text; } |
|||
constexpr const std::type_info * const * types() const { return m_types; } |
|||
|
|||
template <size_t OtherSize1, size_t OtherSize2> |
|||
constexpr descr<Size1 + OtherSize1, Size2 + OtherSize2> operator+(const descr<OtherSize1, OtherSize2> &other) const { |
|||
return concat(other, |
|||
make_index_sequence<Size1>(), |
|||
make_index_sequence<Size2>(), |
|||
make_index_sequence<OtherSize1>(), |
|||
make_index_sequence<OtherSize2>()); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
protected: |
|||
template <size_t... Indices1, size_t... Indices2> |
|||
constexpr descr( |
|||
char const (&text) [Size1+1], |
|||
const std::type_info * const (&types) [Size2+1], |
|||
index_sequence<Indices1...>, index_sequence<Indices2...>) |
|||
: m_text{text[Indices1]..., '\0'}, |
|||
m_types{types[Indices2]..., nullptr } {} |
|||
|
|||
template <size_t OtherSize1, size_t OtherSize2, size_t... Indices1, |
|||
size_t... Indices2, size_t... OtherIndices1, size_t... OtherIndices2> |
|||
constexpr descr<Size1 + OtherSize1, Size2 + OtherSize2> |
|||
concat(const descr<OtherSize1, OtherSize2> &other, |
|||
index_sequence<Indices1...>, index_sequence<Indices2...>, |
|||
index_sequence<OtherIndices1...>, index_sequence<OtherIndices2...>) const { |
|||
return descr<Size1 + OtherSize1, Size2 + OtherSize2>( |
|||
{ m_text[Indices1]..., other.m_text[OtherIndices1]..., '\0' }, |
|||
{ m_types[Indices2]..., other.m_types[OtherIndices2]..., nullptr } |
|||
); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
protected: |
|||
char m_text[Size1 + 1]; |
|||
const std::type_info * m_types[Size2 + 1]; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
template <size_t Size> constexpr descr<Size - 1, 0> _(char const(&text)[Size]) { |
|||
return descr<Size - 1, 0>(text, { nullptr }); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
template <size_t Rem, size_t... Digits> struct int_to_str : int_to_str<Rem/10, Rem%10, Digits...> { }; |
|||
template <size_t...Digits> struct int_to_str<0, Digits...> { |
|||
static constexpr auto digits = descr<sizeof...(Digits), 0>({ ('0' + Digits)..., '\0' }, { nullptr }); |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
// Ternary description (like std::conditional) |
|||
template <bool B, size_t Size1, size_t Size2> |
|||
constexpr enable_if_t<B, descr<Size1 - 1, 0>> _(char const(&text1)[Size1], char const(&)[Size2]) { |
|||
return _(text1); |
|||
} |
|||
template <bool B, size_t Size1, size_t Size2> |
|||
constexpr enable_if_t<!B, descr<Size2 - 1, 0>> _(char const(&)[Size1], char const(&text2)[Size2]) { |
|||
return _(text2); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
template <size_t Size> auto constexpr _() -> decltype(int_to_str<Size / 10, Size % 10>::digits) { |
|||
return int_to_str<Size / 10, Size % 10>::digits; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
template <typename Type> constexpr descr<1, 1> _() { |
|||
return descr<1, 1>({ '%', '\0' }, { &typeid(Type), nullptr }); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
inline constexpr descr<0, 0> concat() { return _(""); } |
|||
template <size_t Size1, size_t Size2, typename... Args> auto constexpr concat(descr<Size1, Size2> descr) { return descr; } |
|||
template <size_t Size1, size_t Size2, typename... Args> auto constexpr concat(descr<Size1, Size2> descr, Args&&... args) { return descr + _(", ") + concat(args...); } |
|||
template <size_t Size1, size_t Size2> auto constexpr type_descr(descr<Size1, Size2> descr) { return _("{") + descr + _("}"); } |
|||
|
|||
#define PYBIND11_DESCR constexpr auto |
|||
|
|||
#else /* Simpler C++11 implementation based on run-time memory allocation and copying */ |
|||
|
|||
class descr { |
|||
public: |
|||
PYBIND11_NOINLINE descr(const char *text, const std::type_info * const * types) { |
|||
size_t nChars = len(text), nTypes = len(types); |
|||
m_text = new char[nChars]; |
|||
m_types = new const std::type_info *[nTypes]; |
|||
memcpy(m_text, text, nChars * sizeof(char)); |
|||
memcpy(m_types, types, nTypes * sizeof(const std::type_info *)); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_NOINLINE descr friend operator+(descr &&d1, descr &&d2) { |
|||
descr r; |
|||
|
|||
size_t nChars1 = len(d1.m_text), nTypes1 = len(d1.m_types); |
|||
size_t nChars2 = len(d2.m_text), nTypes2 = len(d2.m_types); |
|||
|
|||
r.m_text = new char[nChars1 + nChars2 - 1]; |
|||
r.m_types = new const std::type_info *[nTypes1 + nTypes2 - 1]; |
|||
memcpy(r.m_text, d1.m_text, (nChars1-1) * sizeof(char)); |
|||
memcpy(r.m_text + nChars1 - 1, d2.m_text, nChars2 * sizeof(char)); |
|||
memcpy(r.m_types, d1.m_types, (nTypes1-1) * sizeof(std::type_info *)); |
|||
memcpy(r.m_types + nTypes1 - 1, d2.m_types, nTypes2 * sizeof(std::type_info *)); |
|||
|
|||
delete[] d1.m_text; delete[] d1.m_types; |
|||
delete[] d2.m_text; delete[] d2.m_types; |
|||
|
|||
return r; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
char *text() { return m_text; } |
|||
const std::type_info * * types() { return m_types; } |
|||
|
|||
protected: |
|||
PYBIND11_NOINLINE descr() { } |
|||
|
|||
template <typename T> static size_t len(const T *ptr) { // return length including null termination |
|||
const T *it = ptr; |
|||
while (*it++ != (T) 0) |
|||
; |
|||
return static_cast<size_t>(it - ptr); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
const std::type_info **m_types = nullptr; |
|||
char *m_text = nullptr; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/* The 'PYBIND11_NOINLINE inline' combinations below are intentional to get the desired linkage while producing as little object code as possible */ |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_NOINLINE inline descr _(const char *text) { |
|||
const std::type_info *types[1] = { nullptr }; |
|||
return descr(text, types); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
template <bool B> PYBIND11_NOINLINE enable_if_t<B, descr> _(const char *text1, const char *) { return _(text1); } |
|||
template <bool B> PYBIND11_NOINLINE enable_if_t<!B, descr> _(char const *, const char *text2) { return _(text2); } |
|||
|
|||
template <typename Type> PYBIND11_NOINLINE descr _() { |
|||
const std::type_info *types[2] = { &typeid(Type), nullptr }; |
|||
return descr("%", types); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
template <size_t Size> PYBIND11_NOINLINE descr _() { |
|||
const std::type_info *types[1] = { nullptr }; |
|||
return descr(std::to_string(Size).c_str(), types); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_NOINLINE inline descr concat() { return _(""); } |
|||
PYBIND11_NOINLINE inline descr concat(descr &&d) { return d; } |
|||
template <typename... Args> PYBIND11_NOINLINE descr concat(descr &&d, Args&&... args) { return std::move(d) + _(", ") + concat(std::forward<Args>(args)...); } |
|||
PYBIND11_NOINLINE inline descr type_descr(descr&& d) { return _("{") + std::move(d) + _("}"); } |
|||
|
|||
#define PYBIND11_DESCR ::pybind11::detail::descr |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_END(detail) |
|||
NAMESPACE_END(pybind11) |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,239 @@ |
|||
/* |
|||
pybind11/eigen.h: Transparent conversion for dense and sparse Eigen matrices |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#pragma once |
|||
|
|||
#include "numpy.h" |
|||
|
|||
#if defined(__INTEL_COMPILER) |
|||
# pragma warning(disable: 1682) // implicit conversion of a 64-bit integral type to a smaller integral type (potential portability problem) |
|||
#elif defined(__GNUG__) || defined(__clang__) |
|||
# pragma GCC diagnostic push |
|||
# pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wconversion" |
|||
# pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wdeprecated-declarations" |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
#include <Eigen/Core> |
|||
#include <Eigen/SparseCore> |
|||
|
|||
#if defined(__GNUG__) || defined(__clang__) |
|||
# pragma GCC diagnostic pop |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
#if defined(_MSC_VER) |
|||
#pragma warning(push) |
|||
#pragma warning(disable: 4127) // warning C4127: Conditional expression is constant |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(pybind11) |
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(detail) |
|||
|
|||
template <typename T> using is_eigen_dense = is_template_base_of<Eigen::DenseBase, T>; |
|||
template <typename T> using is_eigen_sparse = is_template_base_of<Eigen::SparseMatrixBase, T>; |
|||
template <typename T> using is_eigen_ref = is_template_base_of<Eigen::RefBase, T>; |
|||
|
|||
// Test for objects inheriting from EigenBase<Derived> that aren't captured by the above. This |
|||
// basically covers anything that can be assigned to a dense matrix but that don't have a typical |
|||
// matrix data layout that can be copied from their .data(). For example, DiagonalMatrix and |
|||
// SelfAdjointView fall into this category. |
|||
template <typename T> using is_eigen_base = bool_constant< |
|||
is_template_base_of<Eigen::EigenBase, T>::value |
|||
&& !is_eigen_dense<T>::value && !is_eigen_sparse<T>::value |
|||
>; |
|||
|
|||
template<typename Type> |
|||
struct type_caster<Type, enable_if_t<is_eigen_dense<Type>::value && !is_eigen_ref<Type>::value>> { |
|||
typedef typename Type::Scalar Scalar; |
|||
static constexpr bool rowMajor = Type::Flags & Eigen::RowMajorBit; |
|||
static constexpr bool isVector = Type::IsVectorAtCompileTime; |
|||
|
|||
bool load(handle src, bool) { |
|||
auto buf = array_t<Scalar>::ensure(src); |
|||
if (!buf) |
|||
return false; |
|||
|
|||
if (buf.ndim() == 1) { |
|||
typedef Eigen::InnerStride<> Strides; |
|||
if (!isVector && |
|||
!(Type::RowsAtCompileTime == Eigen::Dynamic && |
|||
Type::ColsAtCompileTime == Eigen::Dynamic)) |
|||
return false; |
|||
|
|||
if (Type::SizeAtCompileTime != Eigen::Dynamic && |
|||
buf.shape(0) != (size_t) Type::SizeAtCompileTime) |
|||
return false; |
|||
|
|||
Strides::Index n_elts = (Strides::Index) buf.shape(0); |
|||
Strides::Index unity = 1; |
|||
|
|||
value = Eigen::Map<Type, 0, Strides>( |
|||
buf.mutable_data(), |
|||
rowMajor ? unity : n_elts, |
|||
rowMajor ? n_elts : unity, |
|||
Strides(buf.strides(0) / sizeof(Scalar)) |
|||
); |
|||
} else if (buf.ndim() == 2) { |
|||
typedef Eigen::Stride<Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic> Strides; |
|||
|
|||
if ((Type::RowsAtCompileTime != Eigen::Dynamic && buf.shape(0) != (size_t) Type::RowsAtCompileTime) || |
|||
(Type::ColsAtCompileTime != Eigen::Dynamic && buf.shape(1) != (size_t) Type::ColsAtCompileTime)) |
|||
return false; |
|||
|
|||
value = Eigen::Map<Type, 0, Strides>( |
|||
buf.mutable_data(), |
|||
typename Strides::Index(buf.shape(0)), |
|||
typename Strides::Index(buf.shape(1)), |
|||
Strides(buf.strides(rowMajor ? 0 : 1) / sizeof(Scalar), |
|||
buf.strides(rowMajor ? 1 : 0) / sizeof(Scalar)) |
|||
); |
|||
} else { |
|||
return false; |
|||
} |
|||
return true; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
static handle cast(const Type &src, return_value_policy /* policy */, handle /* parent */) { |
|||
if (isVector) { |
|||
return array( |
|||
{ (size_t) src.size() }, // shape |
|||
{ sizeof(Scalar) * static_cast<size_t>(src.innerStride()) }, // strides |
|||
src.data() // data |
|||
).release(); |
|||
} else { |
|||
return array( |
|||
{ (size_t) src.rows(), // shape |
|||
(size_t) src.cols() }, |
|||
{ sizeof(Scalar) * static_cast<size_t>(src.rowStride()), // strides |
|||
sizeof(Scalar) * static_cast<size_t>(src.colStride()) }, |
|||
src.data() // data |
|||
).release(); |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_TYPE_CASTER(Type, _("numpy.ndarray[") + npy_format_descriptor<Scalar>::name() + |
|||
_("[") + rows() + _(", ") + cols() + _("]]")); |
|||
|
|||
protected: |
|||
template <typename T = Type, enable_if_t<T::RowsAtCompileTime == Eigen::Dynamic, int> = 0> |
|||
static PYBIND11_DESCR rows() { return _("m"); } |
|||
template <typename T = Type, enable_if_t<T::RowsAtCompileTime != Eigen::Dynamic, int> = 0> |
|||
static PYBIND11_DESCR rows() { return _<T::RowsAtCompileTime>(); } |
|||
template <typename T = Type, enable_if_t<T::ColsAtCompileTime == Eigen::Dynamic, int> = 0> |
|||
static PYBIND11_DESCR cols() { return _("n"); } |
|||
template <typename T = Type, enable_if_t<T::ColsAtCompileTime != Eigen::Dynamic, int> = 0> |
|||
static PYBIND11_DESCR cols() { return _<T::ColsAtCompileTime>(); } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
// Eigen::Ref<Derived> satisfies is_eigen_dense, but isn't constructable, so it needs a special |
|||
// type_caster to handle argument copying/forwarding. |
|||
template <typename CVDerived, int Options, typename StrideType> |
|||
struct type_caster<Eigen::Ref<CVDerived, Options, StrideType>> { |
|||
protected: |
|||
using Type = Eigen::Ref<CVDerived, Options, StrideType>; |
|||
using Derived = typename std::remove_const<CVDerived>::type; |
|||
using DerivedCaster = type_caster<Derived>; |
|||
DerivedCaster derived_caster; |
|||
std::unique_ptr<Type> value; |
|||
public: |
|||
bool load(handle src, bool convert) { if (derived_caster.load(src, convert)) { value.reset(new Type(derived_caster.operator Derived&())); return true; } return false; } |
|||
static handle cast(const Type &src, return_value_policy policy, handle parent) { return DerivedCaster::cast(src, policy, parent); } |
|||
static handle cast(const Type *src, return_value_policy policy, handle parent) { return DerivedCaster::cast(*src, policy, parent); } |
|||
|
|||
static PYBIND11_DESCR name() { return DerivedCaster::name(); } |
|||
|
|||
operator Type*() { return value.get(); } |
|||
operator Type&() { if (!value) pybind11_fail("Eigen::Ref<...> value not loaded"); return *value; } |
|||
template <typename _T> using cast_op_type = pybind11::detail::cast_op_type<_T>; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
// type_caster for special matrix types (e.g. DiagonalMatrix): load() is not supported, but we can |
|||
// cast them into the python domain by first copying to a regular Eigen::Matrix, then casting that. |
|||
template <typename Type> |
|||
struct type_caster<Type, enable_if_t<is_eigen_base<Type>::value && !is_eigen_ref<Type>::value>> { |
|||
protected: |
|||
using Matrix = Eigen::Matrix<typename Type::Scalar, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic>; |
|||
using MatrixCaster = type_caster<Matrix>; |
|||
public: |
|||
[[noreturn]] bool load(handle, bool) { pybind11_fail("Unable to load() into specialized EigenBase object"); } |
|||
static handle cast(const Type &src, return_value_policy policy, handle parent) { return MatrixCaster::cast(Matrix(src), policy, parent); } |
|||
static handle cast(const Type *src, return_value_policy policy, handle parent) { return MatrixCaster::cast(Matrix(*src), policy, parent); } |
|||
|
|||
static PYBIND11_DESCR name() { return MatrixCaster::name(); } |
|||
|
|||
[[noreturn]] operator Type*() { pybind11_fail("Loading not supported for specialized EigenBase object"); } |
|||
[[noreturn]] operator Type&() { pybind11_fail("Loading not supported for specialized EigenBase object"); } |
|||
template <typename _T> using cast_op_type = pybind11::detail::cast_op_type<_T>; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
template<typename Type> |
|||
struct type_caster<Type, enable_if_t<is_eigen_sparse<Type>::value>> { |
|||
typedef typename Type::Scalar Scalar; |
|||
typedef typename std::remove_reference<decltype(*std::declval<Type>().outerIndexPtr())>::type StorageIndex; |
|||
typedef typename Type::Index Index; |
|||
static constexpr bool rowMajor = Type::Flags & Eigen::RowMajorBit; |
|||
|
|||
bool load(handle src, bool) { |
|||
if (!src) |
|||
return false; |
|||
|
|||
auto obj = reinterpret_borrow<object>(src); |
|||
object sparse_module = module::import("scipy.sparse"); |
|||
object matrix_type = sparse_module.attr( |
|||
rowMajor ? "csr_matrix" : "csc_matrix"); |
|||
|
|||
if (obj.get_type() != matrix_type.ptr()) { |
|||
try { |
|||
obj = matrix_type(obj); |
|||
} catch (const error_already_set &) { |
|||
return false; |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
auto values = array_t<Scalar>((object) obj.attr("data")); |
|||
auto innerIndices = array_t<StorageIndex>((object) obj.attr("indices")); |
|||
auto outerIndices = array_t<StorageIndex>((object) obj.attr("indptr")); |
|||
auto shape = pybind11::tuple((pybind11::object) obj.attr("shape")); |
|||
auto nnz = obj.attr("nnz").cast<Index>(); |
|||
|
|||
if (!values || !innerIndices || !outerIndices) |
|||
return false; |
|||
|
|||
value = Eigen::MappedSparseMatrix<Scalar, Type::Flags, StorageIndex>( |
|||
shape[0].cast<Index>(), shape[1].cast<Index>(), nnz, |
|||
outerIndices.mutable_data(), innerIndices.mutable_data(), values.mutable_data()); |
|||
|
|||
return true; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
static handle cast(const Type &src, return_value_policy /* policy */, handle /* parent */) { |
|||
const_cast<Type&>(src).makeCompressed(); |
|||
|
|||
object matrix_type = module::import("scipy.sparse").attr( |
|||
rowMajor ? "csr_matrix" : "csc_matrix"); |
|||
|
|||
array data((size_t) src.nonZeros(), src.valuePtr()); |
|||
array outerIndices((size_t) (rowMajor ? src.rows() : src.cols()) + 1, src.outerIndexPtr()); |
|||
array innerIndices((size_t) src.nonZeros(), src.innerIndexPtr()); |
|||
|
|||
return matrix_type( |
|||
std::make_tuple(data, innerIndices, outerIndices), |
|||
std::make_pair(src.rows(), src.cols()) |
|||
).release(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_TYPE_CASTER(Type, _<(Type::Flags & Eigen::RowMajorBit) != 0>("scipy.sparse.csr_matrix[", "scipy.sparse.csc_matrix[") |
|||
+ npy_format_descriptor<Scalar>::name() + _("]")); |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_END(detail) |
|||
NAMESPACE_END(pybind11) |
|||
|
|||
#if defined(_MSC_VER) |
|||
#pragma warning(pop) |
|||
#endif |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,105 @@ |
|||
/* |
|||
pybind11/exec.h: Support for evaluating Python expressions and statements |
|||
from strings and files |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Klemens Morgenstern <klemens.morgenstern@ed-chemnitz.de> and |
|||
Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#pragma once |
|||
|
|||
#pragma once |
|||
|
|||
#include "pybind11.h" |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(pybind11) |
|||
|
|||
enum eval_mode { |
|||
/// Evaluate a string containing an isolated expression |
|||
eval_expr, |
|||
|
|||
/// Evaluate a string containing a single statement. Returns \c none |
|||
eval_single_statement, |
|||
|
|||
/// Evaluate a string containing a sequence of statement. Returns \c none |
|||
eval_statements |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
template <eval_mode mode = eval_expr> |
|||
object eval(str expr, object global = object(), object local = object()) { |
|||
if (!global) { |
|||
global = reinterpret_borrow<object>(PyEval_GetGlobals()); |
|||
if (!global) |
|||
global = dict(); |
|||
} |
|||
if (!local) |
|||
local = global; |
|||
|
|||
/* PyRun_String does not accept a PyObject / encoding specifier, |
|||
this seems to be the only alternative */ |
|||
std::string buffer = "# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-\n" + (std::string) expr; |
|||
|
|||
int start; |
|||
switch (mode) { |
|||
case eval_expr: start = Py_eval_input; break; |
|||
case eval_single_statement: start = Py_single_input; break; |
|||
case eval_statements: start = Py_file_input; break; |
|||
default: pybind11_fail("invalid evaluation mode"); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
PyObject *result = PyRun_String(buffer.c_str(), start, global.ptr(), local.ptr()); |
|||
if (!result) |
|||
throw error_already_set(); |
|||
return reinterpret_steal<object>(result); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
template <eval_mode mode = eval_statements> |
|||
object eval_file(str fname, object global = object(), object local = object()) { |
|||
if (!global) { |
|||
global = reinterpret_borrow<object>(PyEval_GetGlobals()); |
|||
if (!global) |
|||
global = dict(); |
|||
} |
|||
if (!local) |
|||
local = global; |
|||
|
|||
int start; |
|||
switch (mode) { |
|||
case eval_expr: start = Py_eval_input; break; |
|||
case eval_single_statement: start = Py_single_input; break; |
|||
case eval_statements: start = Py_file_input; break; |
|||
default: pybind11_fail("invalid evaluation mode"); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
int closeFile = 1; |
|||
std::string fname_str = (std::string) fname; |
|||
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x03040000 |
|||
FILE *f = _Py_fopen_obj(fname.ptr(), "r"); |
|||
#elif PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x03000000 |
|||
FILE *f = _Py_fopen(fname.ptr(), "r"); |
|||
#else |
|||
/* No unicode support in open() :( */ |
|||
auto fobj = reinterpret_steal<object>(PyFile_FromString( |
|||
const_cast<char *>(fname_str.c_str()), |
|||
const_cast<char*>("r"))); |
|||
FILE *f = nullptr; |
|||
if (fobj) |
|||
f = PyFile_AsFile(fobj.ptr()); |
|||
closeFile = 0; |
|||
#endif |
|||
if (!f) { |
|||
PyErr_Clear(); |
|||
pybind11_fail("File \"" + fname_str + "\" could not be opened!"); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
PyObject *result = PyRun_FileEx(f, fname_str.c_str(), start, global.ptr(), |
|||
local.ptr(), closeFile); |
|||
if (!result) |
|||
throw error_already_set(); |
|||
return reinterpret_steal<object>(result); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_END(pybind11) |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,79 @@ |
|||
/* |
|||
pybind11/functional.h: std::function<> support |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#pragma once |
|||
|
|||
#include "pybind11.h" |
|||
#include <functional> |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(pybind11) |
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(detail) |
|||
|
|||
template <typename Return, typename... Args> struct type_caster<std::function<Return(Args...)>> { |
|||
typedef std::function<Return(Args...)> type; |
|||
typedef typename std::conditional<std::is_same<Return, void>::value, void_type, Return>::type retval_type; |
|||
public: |
|||
bool load(handle src_, bool) { |
|||
if (src_.is_none()) |
|||
return true; |
|||
|
|||
src_ = detail::get_function(src_); |
|||
if (!src_ || !PyCallable_Check(src_.ptr())) |
|||
return false; |
|||
|
|||
/* |
|||
When passing a C++ function as an argument to another C++ |
|||
function via Python, every function call would normally involve |
|||
a full C++ -> Python -> C++ roundtrip, which can be prohibitive. |
|||
Here, we try to at least detect the case where the function is |
|||
stateless (i.e. function pointer or lambda function without |
|||
captured variables), in which case the roundtrip can be avoided. |
|||
*/ |
|||
if (PyCFunction_Check(src_.ptr())) { |
|||
auto c = reinterpret_borrow<capsule>(PyCFunction_GetSelf(src_.ptr())); |
|||
auto rec = (function_record *) c; |
|||
using FunctionType = Return (*) (Args...); |
|||
|
|||
if (rec && rec->is_stateless && rec->data[1] == &typeid(FunctionType)) { |
|||
struct capture { FunctionType f; }; |
|||
value = ((capture *) &rec->data)->f; |
|||
return true; |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
auto src = reinterpret_borrow<object>(src_); |
|||
value = [src](Args... args) -> Return { |
|||
gil_scoped_acquire acq; |
|||
object retval(src(std::move(args)...)); |
|||
/* Visual studio 2015 parser issue: need parentheses around this expression */ |
|||
return (retval.template cast<Return>()); |
|||
}; |
|||
return true; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
template <typename Func> |
|||
static handle cast(Func &&f_, return_value_policy policy, handle /* parent */) { |
|||
if (!f_) |
|||
return none().inc_ref(); |
|||
|
|||
auto result = f_.template target<Return (*)(Args...)>(); |
|||
if (result) |
|||
return cpp_function(*result, policy).release(); |
|||
else |
|||
return cpp_function(std::forward<Func>(f_), policy).release(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_TYPE_CASTER(type, _("Callable[[") + |
|||
argument_loader<Args...>::arg_names() + _("], ") + |
|||
type_caster<retval_type>::name() + |
|||
_("]")); |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_END(detail) |
|||
NAMESPACE_END(pybind11) |
|||
1169
resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/numpy.h
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
@ -0,0 +1,154 @@ |
|||
/* |
|||
pybind11/operator.h: Metatemplates for operator overloading |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#pragma once |
|||
|
|||
#include "pybind11.h" |
|||
|
|||
#if defined(__clang__) && !defined(__INTEL_COMPILER) |
|||
# pragma clang diagnostic ignored "-Wunsequenced" // multiple unsequenced modifications to 'self' (when using def(py::self OP Type())) |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(pybind11) |
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(detail) |
|||
|
|||
/// Enumeration with all supported operator types |
|||
enum op_id : int { |
|||
op_add, op_sub, op_mul, op_div, op_mod, op_divmod, op_pow, op_lshift, |
|||
op_rshift, op_and, op_xor, op_or, op_neg, op_pos, op_abs, op_invert, |
|||
op_int, op_long, op_float, op_str, op_cmp, op_gt, op_ge, op_lt, op_le, |
|||
op_eq, op_ne, op_iadd, op_isub, op_imul, op_idiv, op_imod, op_ilshift, |
|||
op_irshift, op_iand, op_ixor, op_ior, op_complex, op_bool, op_nonzero, |
|||
op_repr, op_truediv |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
enum op_type : int { |
|||
op_l, /* base type on left */ |
|||
op_r, /* base type on right */ |
|||
op_u /* unary operator */ |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
struct self_t { }; |
|||
static const self_t self = self_t(); |
|||
|
|||
/// Type for an unused type slot |
|||
struct undefined_t { }; |
|||
|
|||
/// Don't warn about an unused variable |
|||
inline self_t __self() { return self; } |
|||
|
|||
/// base template of operator implementations |
|||
template <op_id, op_type, typename B, typename L, typename R> struct op_impl { }; |
|||
|
|||
/// Operator implementation generator |
|||
template <op_id id, op_type ot, typename L, typename R> struct op_ { |
|||
template <typename Class, typename... Extra> void execute(Class &cl, const Extra&... extra) const { |
|||
typedef typename Class::type Base; |
|||
typedef typename std::conditional<std::is_same<L, self_t>::value, Base, L>::type L_type; |
|||
typedef typename std::conditional<std::is_same<R, self_t>::value, Base, R>::type R_type; |
|||
typedef op_impl<id, ot, Base, L_type, R_type> op; |
|||
cl.def(op::name(), &op::execute, is_operator(), extra...); |
|||
} |
|||
template <typename Class, typename... Extra> void execute_cast(Class &cl, const Extra&... extra) const { |
|||
typedef typename Class::type Base; |
|||
typedef typename std::conditional<std::is_same<L, self_t>::value, Base, L>::type L_type; |
|||
typedef typename std::conditional<std::is_same<R, self_t>::value, Base, R>::type R_type; |
|||
typedef op_impl<id, ot, Base, L_type, R_type> op; |
|||
cl.def(op::name(), &op::execute_cast, is_operator(), extra...); |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
#define PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR(id, rid, op, expr) \ |
|||
template <typename B, typename L, typename R> struct op_impl<op_##id, op_l, B, L, R> { \ |
|||
static char const* name() { return "__" #id "__"; } \ |
|||
static auto execute(const L &l, const R &r) -> decltype(expr) { return (expr); } \ |
|||
static B execute_cast(const L &l, const R &r) { return B(expr); } \ |
|||
}; \ |
|||
template <typename B, typename L, typename R> struct op_impl<op_##id, op_r, B, L, R> { \ |
|||
static char const* name() { return "__" #rid "__"; } \ |
|||
static auto execute(const R &r, const L &l) -> decltype(expr) { return (expr); } \ |
|||
static B execute_cast(const R &r, const L &l) { return B(expr); } \ |
|||
}; \ |
|||
inline op_<op_##id, op_l, self_t, self_t> op(const self_t &, const self_t &) { \ |
|||
return op_<op_##id, op_l, self_t, self_t>(); \ |
|||
} \ |
|||
template <typename T> op_<op_##id, op_l, self_t, T> op(const self_t &, const T &) { \ |
|||
return op_<op_##id, op_l, self_t, T>(); \ |
|||
} \ |
|||
template <typename T> op_<op_##id, op_r, T, self_t> op(const T &, const self_t &) { \ |
|||
return op_<op_##id, op_r, T, self_t>(); \ |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
#define PYBIND11_INPLACE_OPERATOR(id, op, expr) \ |
|||
template <typename B, typename L, typename R> struct op_impl<op_##id, op_l, B, L, R> { \ |
|||
static char const* name() { return "__" #id "__"; } \ |
|||
static auto execute(L &l, const R &r) -> decltype(expr) { return expr; } \ |
|||
static B execute_cast(L &l, const R &r) { return B(expr); } \ |
|||
}; \ |
|||
template <typename T> op_<op_##id, op_l, self_t, T> op(const self_t &, const T &) { \ |
|||
return op_<op_##id, op_l, self_t, T>(); \ |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
#define PYBIND11_UNARY_OPERATOR(id, op, expr) \ |
|||
template <typename B, typename L> struct op_impl<op_##id, op_u, B, L, undefined_t> { \ |
|||
static char const* name() { return "__" #id "__"; } \ |
|||
static auto execute(const L &l) -> decltype(expr) { return expr; } \ |
|||
static B execute_cast(const L &l) { return B(expr); } \ |
|||
}; \ |
|||
inline op_<op_##id, op_u, self_t, undefined_t> op(const self_t &) { \ |
|||
return op_<op_##id, op_u, self_t, undefined_t>(); \ |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR(sub, rsub, operator-, l - r) |
|||
PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR(add, radd, operator+, l + r) |
|||
PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR(mul, rmul, operator*, l * r) |
|||
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3 |
|||
PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR(truediv, rtruediv, operator/, l / r) |
|||
#else |
|||
PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR(div, rdiv, operator/, l / r) |
|||
#endif |
|||
PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR(mod, rmod, operator%, l % r) |
|||
PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR(lshift, rlshift, operator<<, l << r) |
|||
PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR(rshift, rrshift, operator>>, l >> r) |
|||
PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR(and, rand, operator&, l & r) |
|||
PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR(xor, rxor, operator^, l ^ r) |
|||
PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR(eq, eq, operator==, l == r) |
|||
PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR(ne, ne, operator!=, l != r) |
|||
PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR(or, ror, operator|, l | r) |
|||
PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR(gt, lt, operator>, l > r) |
|||
PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR(ge, le, operator>=, l >= r) |
|||
PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR(lt, gt, operator<, l < r) |
|||
PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR(le, ge, operator<=, l <= r) |
|||
//PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR(pow, rpow, pow, std::pow(l, r)) |
|||
PYBIND11_INPLACE_OPERATOR(iadd, operator+=, l += r) |
|||
PYBIND11_INPLACE_OPERATOR(isub, operator-=, l -= r) |
|||
PYBIND11_INPLACE_OPERATOR(imul, operator*=, l *= r) |
|||
PYBIND11_INPLACE_OPERATOR(idiv, operator/=, l /= r) |
|||
PYBIND11_INPLACE_OPERATOR(imod, operator%=, l %= r) |
|||
PYBIND11_INPLACE_OPERATOR(ilshift, operator<<=, l <<= r) |
|||
PYBIND11_INPLACE_OPERATOR(irshift, operator>>=, l >>= r) |
|||
PYBIND11_INPLACE_OPERATOR(iand, operator&=, l &= r) |
|||
PYBIND11_INPLACE_OPERATOR(ixor, operator^=, l ^= r) |
|||
PYBIND11_INPLACE_OPERATOR(ior, operator|=, l |= r) |
|||
PYBIND11_UNARY_OPERATOR(neg, operator-, -l) |
|||
PYBIND11_UNARY_OPERATOR(pos, operator+, +l) |
|||
PYBIND11_UNARY_OPERATOR(abs, abs, std::abs(l)) |
|||
PYBIND11_UNARY_OPERATOR(invert, operator~, (~l)) |
|||
PYBIND11_UNARY_OPERATOR(bool, operator!, !!l) |
|||
PYBIND11_UNARY_OPERATOR(int, int_, (int) l) |
|||
PYBIND11_UNARY_OPERATOR(float, float_, (double) l) |
|||
|
|||
#undef PYBIND11_BINARY_OPERATOR |
|||
#undef PYBIND11_INPLACE_OPERATOR |
|||
#undef PYBIND11_UNARY_OPERATOR |
|||
NAMESPACE_END(detail) |
|||
|
|||
using detail::self; |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_END(pybind11) |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,65 @@ |
|||
/* |
|||
pybind11/options.h: global settings that are configurable at runtime. |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#pragma once |
|||
|
|||
#include "common.h" |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(pybind11) |
|||
|
|||
class options { |
|||
public: |
|||
|
|||
// Default RAII constructor, which leaves settings as they currently are. |
|||
options() : previous_state(global_state()) {} |
|||
|
|||
// Class is non-copyable. |
|||
options(const options&) = delete; |
|||
options& operator=(const options&) = delete; |
|||
|
|||
// Destructor, which restores settings that were in effect before. |
|||
~options() { |
|||
global_state() = previous_state; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Setter methods (affect the global state): |
|||
|
|||
options& disable_user_defined_docstrings() & { global_state().show_user_defined_docstrings = false; return *this; } |
|||
|
|||
options& enable_user_defined_docstrings() & { global_state().show_user_defined_docstrings = true; return *this; } |
|||
|
|||
options& disable_function_signatures() & { global_state().show_function_signatures = false; return *this; } |
|||
|
|||
options& enable_function_signatures() & { global_state().show_function_signatures = true; return *this; } |
|||
|
|||
// Getter methods (return the global state): |
|||
|
|||
static bool show_user_defined_docstrings() { return global_state().show_user_defined_docstrings; } |
|||
|
|||
static bool show_function_signatures() { return global_state().show_function_signatures; } |
|||
|
|||
// This type is not meant to be allocated on the heap. |
|||
void* operator new(size_t) = delete; |
|||
|
|||
private: |
|||
|
|||
struct state { |
|||
bool show_user_defined_docstrings = true; //< Include user-supplied texts in docstrings. |
|||
bool show_function_signatures = true; //< Include auto-generated function signatures in docstrings. |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
static state &global_state() { |
|||
static state instance; |
|||
return instance; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
state previous_state; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_END(pybind11) |
|||
1735
resources/pybind11/include/pybind11/pybind11.h
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
File diff suppressed because it is too large
View File
@ -0,0 +1,899 @@ |
|||
/* |
|||
pybind11/typeid.h: Convenience wrapper classes for basic Python types |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#pragma once |
|||
|
|||
#include "common.h" |
|||
#include <utility> |
|||
#include <type_traits> |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(pybind11) |
|||
|
|||
/* A few forward declarations */ |
|||
class handle; class object; |
|||
class str; class iterator; |
|||
struct arg; struct arg_v; |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(detail) |
|||
class args_proxy; |
|||
inline bool isinstance_generic(handle obj, const std::type_info &tp); |
|||
|
|||
// Accessor forward declarations |
|||
template <typename Policy> class accessor; |
|||
namespace accessor_policies { |
|||
struct obj_attr; |
|||
struct str_attr; |
|||
struct generic_item; |
|||
struct sequence_item; |
|||
struct list_item; |
|||
struct tuple_item; |
|||
} |
|||
using obj_attr_accessor = accessor<accessor_policies::obj_attr>; |
|||
using str_attr_accessor = accessor<accessor_policies::str_attr>; |
|||
using item_accessor = accessor<accessor_policies::generic_item>; |
|||
using sequence_accessor = accessor<accessor_policies::sequence_item>; |
|||
using list_accessor = accessor<accessor_policies::list_item>; |
|||
using tuple_accessor = accessor<accessor_policies::tuple_item>; |
|||
|
|||
/// Tag and check to identify a class which implements the Python object API |
|||
class pyobject_tag { }; |
|||
template <typename T> using is_pyobject = std::is_base_of<pyobject_tag, T>; |
|||
|
|||
/// Mixin which adds common functions to handle, object and various accessors. |
|||
/// The only requirement for `Derived` is to implement `PyObject *Derived::ptr() const`. |
|||
template <typename Derived> |
|||
class object_api : public pyobject_tag { |
|||
const Derived &derived() const { return static_cast<const Derived &>(*this); } |
|||
|
|||
public: |
|||
iterator begin() const; |
|||
iterator end() const; |
|||
item_accessor operator[](handle key) const; |
|||
item_accessor operator[](const char *key) const; |
|||
obj_attr_accessor attr(handle key) const; |
|||
str_attr_accessor attr(const char *key) const; |
|||
args_proxy operator*() const; |
|||
template <typename T> bool contains(T &&key) const; |
|||
|
|||
template <return_value_policy policy = return_value_policy::automatic_reference, typename... Args> |
|||
object operator()(Args &&...args) const; |
|||
template <return_value_policy policy = return_value_policy::automatic_reference, typename... Args> |
|||
PYBIND11_DEPRECATED("call(...) was deprecated in favor of operator()(...)") |
|||
object call(Args&&... args) const; |
|||
|
|||
bool is_none() const { return derived().ptr() == Py_None; } |
|||
PYBIND11_DEPRECATED("Instead of obj.str(), use py::str(obj)") |
|||
pybind11::str str() const; |
|||
|
|||
int ref_count() const { return static_cast<int>(Py_REFCNT(derived().ptr())); } |
|||
handle get_type() const; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_END(detail) |
|||
|
|||
/// Holds a reference to a Python object (no reference counting) |
|||
class handle : public detail::object_api<handle> { |
|||
public: |
|||
handle() = default; |
|||
handle(PyObject *ptr) : m_ptr(ptr) { } |
|||
|
|||
PyObject *ptr() const { return m_ptr; } |
|||
PyObject *&ptr() { return m_ptr; } |
|||
const handle& inc_ref() const { Py_XINCREF(m_ptr); return *this; } |
|||
const handle& dec_ref() const { Py_XDECREF(m_ptr); return *this; } |
|||
|
|||
template <typename T> T cast() const; |
|||
explicit operator bool() const { return m_ptr != nullptr; } |
|||
bool operator==(const handle &h) const { return m_ptr == h.m_ptr; } |
|||
bool operator!=(const handle &h) const { return m_ptr != h.m_ptr; } |
|||
PYBIND11_DEPRECATED("Use handle::operator bool() instead") |
|||
bool check() const { return m_ptr != nullptr; } |
|||
protected: |
|||
PyObject *m_ptr = nullptr; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Holds a reference to a Python object (with reference counting) |
|||
class object : public handle { |
|||
public: |
|||
object() = default; |
|||
PYBIND11_DEPRECATED("Use reinterpret_borrow<object>() or reinterpret_steal<object>()") |
|||
object(handle h, bool is_borrowed) : handle(h) { if (is_borrowed) inc_ref(); } |
|||
object(const object &o) : handle(o) { inc_ref(); } |
|||
object(object &&other) noexcept { m_ptr = other.m_ptr; other.m_ptr = nullptr; } |
|||
~object() { dec_ref(); } |
|||
|
|||
handle release() { |
|||
PyObject *tmp = m_ptr; |
|||
m_ptr = nullptr; |
|||
return handle(tmp); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
object& operator=(const object &other) { |
|||
other.inc_ref(); |
|||
dec_ref(); |
|||
m_ptr = other.m_ptr; |
|||
return *this; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
object& operator=(object &&other) noexcept { |
|||
if (this != &other) { |
|||
handle temp(m_ptr); |
|||
m_ptr = other.m_ptr; |
|||
other.m_ptr = nullptr; |
|||
temp.dec_ref(); |
|||
} |
|||
return *this; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Calling cast() on an object lvalue just copies (via handle::cast) |
|||
template <typename T> T cast() const &; |
|||
// Calling on an object rvalue does a move, if needed and/or possible |
|||
template <typename T> T cast() &&; |
|||
|
|||
protected: |
|||
// Tags for choosing constructors from raw PyObject * |
|||
struct borrowed_t { }; static constexpr borrowed_t borrowed{}; |
|||
struct stolen_t { }; static constexpr stolen_t stolen{}; |
|||
|
|||
template <typename T> friend T reinterpret_borrow(handle); |
|||
template <typename T> friend T reinterpret_steal(handle); |
|||
|
|||
public: |
|||
// Only accessible from derived classes and the reinterpret_* functions |
|||
object(handle h, borrowed_t) : handle(h) { inc_ref(); } |
|||
object(handle h, stolen_t) : handle(h) { } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/** The following functions don't do any kind of conversion, they simply declare |
|||
that a PyObject is a certain type and borrow or steal the reference. */ |
|||
template <typename T> T reinterpret_borrow(handle h) { return {h, object::borrowed}; } |
|||
template <typename T> T reinterpret_steal(handle h) { return {h, object::stolen}; } |
|||
|
|||
/// Check if `obj` is an instance of type `T` |
|||
template <typename T, detail::enable_if_t<std::is_base_of<object, T>::value, int> = 0> |
|||
bool isinstance(handle obj) { return T::_check(obj); } |
|||
|
|||
template <typename T, detail::enable_if_t<!std::is_base_of<object, T>::value, int> = 0> |
|||
bool isinstance(handle obj) { return detail::isinstance_generic(obj, typeid(T)); } |
|||
|
|||
template <> inline bool isinstance<handle>(handle obj) = delete; |
|||
template <> inline bool isinstance<object>(handle obj) { return obj.ptr() != nullptr; } |
|||
|
|||
inline bool hasattr(handle obj, handle name) { |
|||
return PyObject_HasAttr(obj.ptr(), name.ptr()) == 1; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
inline bool hasattr(handle obj, const char *name) { |
|||
return PyObject_HasAttrString(obj.ptr(), name) == 1; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
inline object getattr(handle obj, handle name) { |
|||
PyObject *result = PyObject_GetAttr(obj.ptr(), name.ptr()); |
|||
if (!result) { throw error_already_set(); } |
|||
return reinterpret_steal<object>(result); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
inline object getattr(handle obj, const char *name) { |
|||
PyObject *result = PyObject_GetAttrString(obj.ptr(), name); |
|||
if (!result) { throw error_already_set(); } |
|||
return reinterpret_steal<object>(result); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
inline object getattr(handle obj, handle name, handle default_) { |
|||
if (PyObject *result = PyObject_GetAttr(obj.ptr(), name.ptr())) { |
|||
return reinterpret_steal<object>(result); |
|||
} else { |
|||
PyErr_Clear(); |
|||
return reinterpret_borrow<object>(default_); |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
inline object getattr(handle obj, const char *name, handle default_) { |
|||
if (PyObject *result = PyObject_GetAttrString(obj.ptr(), name)) { |
|||
return reinterpret_steal<object>(result); |
|||
} else { |
|||
PyErr_Clear(); |
|||
return reinterpret_borrow<object>(default_); |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
inline void setattr(handle obj, handle name, handle value) { |
|||
if (PyObject_SetAttr(obj.ptr(), name.ptr(), value.ptr()) != 0) { throw error_already_set(); } |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
inline void setattr(handle obj, const char *name, handle value) { |
|||
if (PyObject_SetAttrString(obj.ptr(), name, value.ptr()) != 0) { throw error_already_set(); } |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(detail) |
|||
inline handle get_function(handle value) { |
|||
if (value) { |
|||
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3 |
|||
if (PyInstanceMethod_Check(value.ptr())) |
|||
value = PyInstanceMethod_GET_FUNCTION(value.ptr()); |
|||
#endif |
|||
if (PyMethod_Check(value.ptr())) |
|||
value = PyMethod_GET_FUNCTION(value.ptr()); |
|||
} |
|||
return value; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
template <typename Policy> |
|||
class accessor : public object_api<accessor<Policy>> { |
|||
using key_type = typename Policy::key_type; |
|||
|
|||
public: |
|||
accessor(handle obj, key_type key) : obj(obj), key(std::move(key)) { } |
|||
|
|||
void operator=(const accessor &a) && { std::move(*this).operator=(handle(a)); } |
|||
void operator=(const accessor &a) & { operator=(handle(a)); } |
|||
void operator=(const object &o) && { std::move(*this).operator=(handle(o)); } |
|||
void operator=(const object &o) & { operator=(handle(o)); } |
|||
void operator=(handle value) && { Policy::set(obj, key, value); } |
|||
void operator=(handle value) & { get_cache() = reinterpret_borrow<object>(value); } |
|||
|
|||
template <typename T = Policy> |
|||
PYBIND11_DEPRECATED("Use of obj.attr(...) as bool is deprecated in favor of pybind11::hasattr(obj, ...)") |
|||
explicit operator enable_if_t<std::is_same<T, accessor_policies::str_attr>::value || |
|||
std::is_same<T, accessor_policies::obj_attr>::value, bool>() const { |
|||
return hasattr(obj, key); |
|||
} |
|||
template <typename T = Policy> |
|||
PYBIND11_DEPRECATED("Use of obj[key] as bool is deprecated in favor of obj.contains(key)") |
|||
explicit operator enable_if_t<std::is_same<T, accessor_policies::generic_item>::value, bool>() const { |
|||
return obj.contains(key); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
operator object() const { return get_cache(); } |
|||
PyObject *ptr() const { return get_cache().ptr(); } |
|||
template <typename T> T cast() const { return get_cache().template cast<T>(); } |
|||
|
|||
private: |
|||
object &get_cache() const { |
|||
if (!cache) { cache = Policy::get(obj, key); } |
|||
return cache; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
private: |
|||
handle obj; |
|||
key_type key; |
|||
mutable object cache; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(accessor_policies) |
|||
struct obj_attr { |
|||
using key_type = object; |
|||
static object get(handle obj, handle key) { return getattr(obj, key); } |
|||
static void set(handle obj, handle key, handle val) { setattr(obj, key, val); } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
struct str_attr { |
|||
using key_type = const char *; |
|||
static object get(handle obj, const char *key) { return getattr(obj, key); } |
|||
static void set(handle obj, const char *key, handle val) { setattr(obj, key, val); } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
struct generic_item { |
|||
using key_type = object; |
|||
|
|||
static object get(handle obj, handle key) { |
|||
PyObject *result = PyObject_GetItem(obj.ptr(), key.ptr()); |
|||
if (!result) { throw error_already_set(); } |
|||
return reinterpret_steal<object>(result); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
static void set(handle obj, handle key, handle val) { |
|||
if (PyObject_SetItem(obj.ptr(), key.ptr(), val.ptr()) != 0) { throw error_already_set(); } |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
struct sequence_item { |
|||
using key_type = size_t; |
|||
|
|||
static object get(handle obj, size_t index) { |
|||
PyObject *result = PySequence_GetItem(obj.ptr(), static_cast<ssize_t>(index)); |
|||
if (!result) { throw error_already_set(); } |
|||
return reinterpret_borrow<object>(result); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
static void set(handle obj, size_t index, handle val) { |
|||
// PySequence_SetItem does not steal a reference to 'val' |
|||
if (PySequence_SetItem(obj.ptr(), static_cast<ssize_t>(index), val.ptr()) != 0) { |
|||
throw error_already_set(); |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
struct list_item { |
|||
using key_type = size_t; |
|||
|
|||
static object get(handle obj, size_t index) { |
|||
PyObject *result = PyList_GetItem(obj.ptr(), static_cast<ssize_t>(index)); |
|||
if (!result) { throw error_already_set(); } |
|||
return reinterpret_borrow<object>(result); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
static void set(handle obj, size_t index, handle val) { |
|||
// PyList_SetItem steals a reference to 'val' |
|||
if (PyList_SetItem(obj.ptr(), static_cast<ssize_t>(index), val.inc_ref().ptr()) != 0) { |
|||
throw error_already_set(); |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
struct tuple_item { |
|||
using key_type = size_t; |
|||
|
|||
static object get(handle obj, size_t index) { |
|||
PyObject *result = PyTuple_GetItem(obj.ptr(), static_cast<ssize_t>(index)); |
|||
if (!result) { throw error_already_set(); } |
|||
return reinterpret_borrow<object>(result); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
static void set(handle obj, size_t index, handle val) { |
|||
// PyTuple_SetItem steals a reference to 'val' |
|||
if (PyTuple_SetItem(obj.ptr(), static_cast<ssize_t>(index), val.inc_ref().ptr()) != 0) { |
|||
throw error_already_set(); |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
NAMESPACE_END(accessor_policies) |
|||
|
|||
struct dict_iterator { |
|||
public: |
|||
explicit dict_iterator(handle dict = handle(), ssize_t pos = -1) : dict(dict), pos(pos) { } |
|||
dict_iterator& operator++() { |
|||
if (!PyDict_Next(dict.ptr(), &pos, &key.ptr(), &value.ptr())) |
|||
pos = -1; |
|||
return *this; |
|||
} |
|||
std::pair<handle, handle> operator*() const { |
|||
return std::make_pair(key, value); |
|||
} |
|||
bool operator==(const dict_iterator &it) const { return it.pos == pos; } |
|||
bool operator!=(const dict_iterator &it) const { return it.pos != pos; } |
|||
private: |
|||
handle dict, key, value; |
|||
ssize_t pos = 0; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
inline bool PyIterable_Check(PyObject *obj) { |
|||
PyObject *iter = PyObject_GetIter(obj); |
|||
if (iter) { |
|||
Py_DECREF(iter); |
|||
return true; |
|||
} else { |
|||
PyErr_Clear(); |
|||
return false; |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
inline bool PyNone_Check(PyObject *o) { return o == Py_None; } |
|||
|
|||
inline bool PyUnicode_Check_Permissive(PyObject *o) { return PyUnicode_Check(o) || PYBIND11_BYTES_CHECK(o); } |
|||
|
|||
class kwargs_proxy : public handle { |
|||
public: |
|||
explicit kwargs_proxy(handle h) : handle(h) { } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
class args_proxy : public handle { |
|||
public: |
|||
explicit args_proxy(handle h) : handle(h) { } |
|||
kwargs_proxy operator*() const { return kwargs_proxy(*this); } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Python argument categories (using PEP 448 terms) |
|||
template <typename T> using is_keyword = std::is_base_of<arg, T>; |
|||
template <typename T> using is_s_unpacking = std::is_same<args_proxy, T>; // * unpacking |
|||
template <typename T> using is_ds_unpacking = std::is_same<kwargs_proxy, T>; // ** unpacking |
|||
template <typename T> using is_positional = bool_constant< |
|||
!is_keyword<T>::value && !is_s_unpacking<T>::value && !is_ds_unpacking<T>::value |
|||
>; |
|||
template <typename T> using is_keyword_or_ds = bool_constant< |
|||
is_keyword<T>::value || is_ds_unpacking<T>::value |
|||
>; |
|||
|
|||
// Call argument collector forward declarations |
|||
template <return_value_policy policy = return_value_policy::automatic_reference> |
|||
class simple_collector; |
|||
template <return_value_policy policy = return_value_policy::automatic_reference> |
|||
class unpacking_collector; |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_END(detail) |
|||
|
|||
// TODO: After the deprecated constructors are removed, this macro can be simplified by |
|||
// inheriting ctors: `using Parent::Parent`. It's not an option right now because |
|||
// the `using` statement triggers the parent deprecation warning even if the ctor |
|||
// isn't even used. |
|||
#define PYBIND11_OBJECT_COMMON(Name, Parent, CheckFun) \ |
|||
public: \ |
|||
PYBIND11_DEPRECATED("Use reinterpret_borrow<"#Name">() or reinterpret_steal<"#Name">()") \ |
|||
Name(handle h, bool is_borrowed) : Parent(is_borrowed ? Parent(h, borrowed) : Parent(h, stolen)) { } \ |
|||
Name(handle h, borrowed_t) : Parent(h, borrowed) { } \ |
|||
Name(handle h, stolen_t) : Parent(h, stolen) { } \ |
|||
PYBIND11_DEPRECATED("Use py::isinstance<py::python_type>(obj) instead") \ |
|||
bool check() const { return m_ptr != nullptr && (bool) CheckFun(m_ptr); } \ |
|||
static bool _check(handle h) { return h.ptr() != nullptr && CheckFun(h.ptr()); } |
|||
|
|||
#define PYBIND11_OBJECT_CVT(Name, Parent, CheckFun, ConvertFun) \ |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT_COMMON(Name, Parent, CheckFun) \ |
|||
/* This is deliberately not 'explicit' to allow implicit conversion from object: */ \ |
|||
Name(const object &o) : Parent(ConvertFun(o.ptr()), stolen) { if (!m_ptr) throw error_already_set(); } |
|||
|
|||
#define PYBIND11_OBJECT(Name, Parent, CheckFun) \ |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT_COMMON(Name, Parent, CheckFun) \ |
|||
/* This is deliberately not 'explicit' to allow implicit conversion from object: */ \ |
|||
Name(const object &o) : Parent(o) { } \ |
|||
Name(object &&o) : Parent(std::move(o)) { } |
|||
|
|||
#define PYBIND11_OBJECT_DEFAULT(Name, Parent, CheckFun) \ |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT(Name, Parent, CheckFun) \ |
|||
Name() : Parent() { } |
|||
|
|||
class iterator : public object { |
|||
public: |
|||
/** Caveat: copying an iterator does not (and cannot) clone the internal |
|||
state of the Python iterable */ |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT_DEFAULT(iterator, object, PyIter_Check) |
|||
|
|||
iterator& operator++() { |
|||
if (m_ptr) |
|||
advance(); |
|||
return *this; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
/** Caveat: this postincrement operator does not (and cannot) clone the |
|||
internal state of the Python iterable. It should only be used to |
|||
retrieve the current iterate using <tt>operator*()</tt> */ |
|||
iterator operator++(int) { |
|||
iterator rv(*this); |
|||
rv.value = value; |
|||
if (m_ptr) |
|||
advance(); |
|||
return rv; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
bool operator==(const iterator &it) const { return *it == **this; } |
|||
bool operator!=(const iterator &it) const { return *it != **this; } |
|||
|
|||
handle operator*() const { |
|||
if (!ready && m_ptr) { |
|||
auto& self = const_cast<iterator &>(*this); |
|||
self.advance(); |
|||
self.ready = true; |
|||
} |
|||
return value; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
private: |
|||
void advance() { value = reinterpret_steal<object>(PyIter_Next(m_ptr)); } |
|||
|
|||
private: |
|||
object value = {}; |
|||
bool ready = false; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
class iterable : public object { |
|||
public: |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT_DEFAULT(iterable, object, detail::PyIterable_Check) |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
class bytes; |
|||
|
|||
class str : public object { |
|||
public: |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT_CVT(str, object, detail::PyUnicode_Check_Permissive, raw_str) |
|||
|
|||
str(const char *c, size_t n) |
|||
: object(PyUnicode_FromStringAndSize(c, (ssize_t) n), stolen) { |
|||
if (!m_ptr) pybind11_fail("Could not allocate string object!"); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// 'explicit' is explicitly omitted from the following constructors to allow implicit conversion to py::str from C++ string-like objects |
|||
str(const char *c = "") |
|||
: object(PyUnicode_FromString(c), stolen) { |
|||
if (!m_ptr) pybind11_fail("Could not allocate string object!"); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
str(const std::string &s) : str(s.data(), s.size()) { } |
|||
|
|||
explicit str(const bytes &b); |
|||
|
|||
explicit str(handle h) : object(raw_str(h.ptr()), stolen) { } |
|||
|
|||
operator std::string() const { |
|||
object temp = *this; |
|||
if (PyUnicode_Check(m_ptr)) { |
|||
temp = reinterpret_steal<object>(PyUnicode_AsUTF8String(m_ptr)); |
|||
if (!temp) |
|||
pybind11_fail("Unable to extract string contents! (encoding issue)"); |
|||
} |
|||
char *buffer; |
|||
ssize_t length; |
|||
if (PYBIND11_BYTES_AS_STRING_AND_SIZE(temp.ptr(), &buffer, &length)) |
|||
pybind11_fail("Unable to extract string contents! (invalid type)"); |
|||
return std::string(buffer, (size_t) length); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
template <typename... Args> |
|||
str format(Args &&...args) const { |
|||
return attr("format")(std::forward<Args>(args)...); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
private: |
|||
/// Return string representation -- always returns a new reference, even if already a str |
|||
static PyObject *raw_str(PyObject *op) { |
|||
PyObject *str_value = PyObject_Str(op); |
|||
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3 |
|||
if (!str_value) throw error_already_set(); |
|||
PyObject *unicode = PyUnicode_FromEncodedObject(str_value, "utf-8", nullptr); |
|||
Py_XDECREF(str_value); str_value = unicode; |
|||
#endif |
|||
return str_value; |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
inline namespace literals { |
|||
/// String literal version of str |
|||
inline str operator"" _s(const char *s, size_t size) { return {s, size}; } |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
class bytes : public object { |
|||
public: |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT(bytes, object, PYBIND11_BYTES_CHECK) |
|||
|
|||
// Allow implicit conversion: |
|||
bytes(const char *c = "") |
|||
: object(PYBIND11_BYTES_FROM_STRING(c), stolen) { |
|||
if (!m_ptr) pybind11_fail("Could not allocate bytes object!"); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
bytes(const char *c, size_t n) |
|||
: object(PYBIND11_BYTES_FROM_STRING_AND_SIZE(c, (ssize_t) n), stolen) { |
|||
if (!m_ptr) pybind11_fail("Could not allocate bytes object!"); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Allow implicit conversion: |
|||
bytes(const std::string &s) : bytes(s.data(), s.size()) { } |
|||
|
|||
explicit bytes(const pybind11::str &s); |
|||
|
|||
operator std::string() const { |
|||
char *buffer; |
|||
ssize_t length; |
|||
if (PYBIND11_BYTES_AS_STRING_AND_SIZE(m_ptr, &buffer, &length)) |
|||
pybind11_fail("Unable to extract bytes contents!"); |
|||
return std::string(buffer, (size_t) length); |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
inline bytes::bytes(const pybind11::str &s) { |
|||
object temp = s; |
|||
if (PyUnicode_Check(s.ptr())) { |
|||
temp = reinterpret_steal<object>(PyUnicode_AsUTF8String(s.ptr())); |
|||
if (!temp) |
|||
pybind11_fail("Unable to extract string contents! (encoding issue)"); |
|||
} |
|||
char *buffer; |
|||
ssize_t length; |
|||
if (PYBIND11_BYTES_AS_STRING_AND_SIZE(temp.ptr(), &buffer, &length)) |
|||
pybind11_fail("Unable to extract string contents! (invalid type)"); |
|||
auto obj = reinterpret_steal<object>(PYBIND11_BYTES_FROM_STRING_AND_SIZE(buffer, length)); |
|||
if (!obj) |
|||
pybind11_fail("Could not allocate bytes object!"); |
|||
m_ptr = obj.release().ptr(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
inline str::str(const bytes& b) { |
|||
char *buffer; |
|||
ssize_t length; |
|||
if (PYBIND11_BYTES_AS_STRING_AND_SIZE(b.ptr(), &buffer, &length)) |
|||
pybind11_fail("Unable to extract bytes contents!"); |
|||
auto obj = reinterpret_steal<object>(PyUnicode_FromStringAndSize(buffer, (ssize_t) length)); |
|||
if (!obj) |
|||
pybind11_fail("Could not allocate string object!"); |
|||
m_ptr = obj.release().ptr(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
class none : public object { |
|||
public: |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT(none, object, detail::PyNone_Check) |
|||
none() : object(Py_None, borrowed) { } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
class bool_ : public object { |
|||
public: |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT_CVT(bool_, object, PyBool_Check, raw_bool) |
|||
bool_() : object(Py_False, borrowed) { } |
|||
// Allow implicit conversion from and to `bool`: |
|||
bool_(bool value) : object(value ? Py_True : Py_False, borrowed) { } |
|||
operator bool() const { return m_ptr && PyLong_AsLong(m_ptr) != 0; } |
|||
|
|||
private: |
|||
/// Return the truth value of an object -- always returns a new reference |
|||
static PyObject *raw_bool(PyObject *op) { |
|||
const auto value = PyObject_IsTrue(op); |
|||
if (value == -1) return nullptr; |
|||
return handle(value ? Py_True : Py_False).inc_ref().ptr(); |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
class int_ : public object { |
|||
public: |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT_CVT(int_, object, PYBIND11_LONG_CHECK, PyNumber_Long) |
|||
int_() : object(PyLong_FromLong(0), stolen) { } |
|||
// Allow implicit conversion from C++ integral types: |
|||
template <typename T, |
|||
detail::enable_if_t<std::is_integral<T>::value, int> = 0> |
|||
int_(T value) { |
|||
if (sizeof(T) <= sizeof(long)) { |
|||
if (std::is_signed<T>::value) |
|||
m_ptr = PyLong_FromLong((long) value); |
|||
else |
|||
m_ptr = PyLong_FromUnsignedLong((unsigned long) value); |
|||
} else { |
|||
if (std::is_signed<T>::value) |
|||
m_ptr = PyLong_FromLongLong((long long) value); |
|||
else |
|||
m_ptr = PyLong_FromUnsignedLongLong((unsigned long long) value); |
|||
} |
|||
if (!m_ptr) pybind11_fail("Could not allocate int object!"); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
template <typename T, |
|||
detail::enable_if_t<std::is_integral<T>::value, int> = 0> |
|||
operator T() const { |
|||
if (sizeof(T) <= sizeof(long)) { |
|||
if (std::is_signed<T>::value) |
|||
return (T) PyLong_AsLong(m_ptr); |
|||
else |
|||
return (T) PyLong_AsUnsignedLong(m_ptr); |
|||
} else { |
|||
if (std::is_signed<T>::value) |
|||
return (T) PYBIND11_LONG_AS_LONGLONG(m_ptr); |
|||
else |
|||
return (T) PYBIND11_LONG_AS_UNSIGNED_LONGLONG(m_ptr); |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
class float_ : public object { |
|||
public: |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT_CVT(float_, object, PyFloat_Check, PyNumber_Float) |
|||
// Allow implicit conversion from float/double: |
|||
float_(float value) : object(PyFloat_FromDouble((double) value), stolen) { |
|||
if (!m_ptr) pybind11_fail("Could not allocate float object!"); |
|||
} |
|||
float_(double value = .0) : object(PyFloat_FromDouble((double) value), stolen) { |
|||
if (!m_ptr) pybind11_fail("Could not allocate float object!"); |
|||
} |
|||
operator float() const { return (float) PyFloat_AsDouble(m_ptr); } |
|||
operator double() const { return (double) PyFloat_AsDouble(m_ptr); } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
class weakref : public object { |
|||
public: |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT_DEFAULT(weakref, object, PyWeakref_Check) |
|||
explicit weakref(handle obj, handle callback = {}) |
|||
: object(PyWeakref_NewRef(obj.ptr(), callback.ptr()), stolen) { |
|||
if (!m_ptr) pybind11_fail("Could not allocate weak reference!"); |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
class slice : public object { |
|||
public: |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT_DEFAULT(slice, object, PySlice_Check) |
|||
slice(ssize_t start_, ssize_t stop_, ssize_t step_) { |
|||
int_ start(start_), stop(stop_), step(step_); |
|||
m_ptr = PySlice_New(start.ptr(), stop.ptr(), step.ptr()); |
|||
if (!m_ptr) pybind11_fail("Could not allocate slice object!"); |
|||
} |
|||
bool compute(size_t length, size_t *start, size_t *stop, size_t *step, |
|||
size_t *slicelength) const { |
|||
return PySlice_GetIndicesEx((PYBIND11_SLICE_OBJECT *) m_ptr, |
|||
(ssize_t) length, (ssize_t *) start, |
|||
(ssize_t *) stop, (ssize_t *) step, |
|||
(ssize_t *) slicelength) == 0; |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
class capsule : public object { |
|||
public: |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT_DEFAULT(capsule, object, PyCapsule_CheckExact) |
|||
PYBIND11_DEPRECATED("Use reinterpret_borrow<capsule>() or reinterpret_steal<capsule>()") |
|||
capsule(PyObject *ptr, bool is_borrowed) : object(is_borrowed ? object(ptr, borrowed) : object(ptr, stolen)) { } |
|||
explicit capsule(const void *value, void (*destruct)(PyObject *) = nullptr) |
|||
: object(PyCapsule_New(const_cast<void*>(value), nullptr, destruct), stolen) { |
|||
if (!m_ptr) pybind11_fail("Could not allocate capsule object!"); |
|||
} |
|||
template <typename T> operator T *() const { |
|||
T * result = static_cast<T *>(PyCapsule_GetPointer(m_ptr, nullptr)); |
|||
if (!result) pybind11_fail("Unable to extract capsule contents!"); |
|||
return result; |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
class tuple : public object { |
|||
public: |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT_CVT(tuple, object, PyTuple_Check, PySequence_Tuple) |
|||
explicit tuple(size_t size = 0) : object(PyTuple_New((ssize_t) size), stolen) { |
|||
if (!m_ptr) pybind11_fail("Could not allocate tuple object!"); |
|||
} |
|||
size_t size() const { return (size_t) PyTuple_Size(m_ptr); } |
|||
detail::tuple_accessor operator[](size_t index) const { return {*this, index}; } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
class dict : public object { |
|||
public: |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT_CVT(dict, object, PyDict_Check, raw_dict) |
|||
dict() : object(PyDict_New(), stolen) { |
|||
if (!m_ptr) pybind11_fail("Could not allocate dict object!"); |
|||
} |
|||
template <typename... Args, |
|||
typename = detail::enable_if_t<detail::all_of_t<detail::is_keyword_or_ds, Args...>::value>, |
|||
// MSVC workaround: it can't compile an out-of-line definition, so defer the collector |
|||
typename collector = detail::deferred_t<detail::unpacking_collector<>, Args...>> |
|||
explicit dict(Args &&...args) : dict(collector(std::forward<Args>(args)...).kwargs()) { } |
|||
|
|||
size_t size() const { return (size_t) PyDict_Size(m_ptr); } |
|||
detail::dict_iterator begin() const { return (++detail::dict_iterator(*this, 0)); } |
|||
detail::dict_iterator end() const { return detail::dict_iterator(); } |
|||
void clear() const { PyDict_Clear(ptr()); } |
|||
bool contains(handle key) const { return PyDict_Contains(ptr(), key.ptr()) == 1; } |
|||
bool contains(const char *key) const { return PyDict_Contains(ptr(), pybind11::str(key).ptr()) == 1; } |
|||
|
|||
private: |
|||
/// Call the `dict` Python type -- always returns a new reference |
|||
static PyObject *raw_dict(PyObject *op) { |
|||
if (PyDict_Check(op)) |
|||
return handle(op).inc_ref().ptr(); |
|||
return PyObject_CallFunctionObjArgs((PyObject *) &PyDict_Type, op, nullptr); |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
class sequence : public object { |
|||
public: |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT(sequence, object, PySequence_Check) |
|||
size_t size() const { return (size_t) PySequence_Size(m_ptr); } |
|||
detail::sequence_accessor operator[](size_t index) const { return {*this, index}; } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
class list : public object { |
|||
public: |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT_CVT(list, object, PyList_Check, PySequence_List) |
|||
explicit list(size_t size = 0) : object(PyList_New((ssize_t) size), stolen) { |
|||
if (!m_ptr) pybind11_fail("Could not allocate list object!"); |
|||
} |
|||
size_t size() const { return (size_t) PyList_Size(m_ptr); } |
|||
detail::list_accessor operator[](size_t index) const { return {*this, index}; } |
|||
void append(handle h) const { PyList_Append(m_ptr, h.ptr()); } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
class args : public tuple { PYBIND11_OBJECT_DEFAULT(args, tuple, PyTuple_Check) }; |
|||
class kwargs : public dict { PYBIND11_OBJECT_DEFAULT(kwargs, dict, PyDict_Check) }; |
|||
|
|||
class set : public object { |
|||
public: |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT_CVT(set, object, PySet_Check, PySet_New) |
|||
set() : object(PySet_New(nullptr), stolen) { |
|||
if (!m_ptr) pybind11_fail("Could not allocate set object!"); |
|||
} |
|||
size_t size() const { return (size_t) PySet_Size(m_ptr); } |
|||
bool add(const object &object) const { return PySet_Add(m_ptr, object.ptr()) == 0; } |
|||
void clear() const { PySet_Clear(m_ptr); } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
class function : public object { |
|||
public: |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT_DEFAULT(function, object, PyCallable_Check) |
|||
bool is_cpp_function() const { |
|||
handle fun = detail::get_function(m_ptr); |
|||
return fun && PyCFunction_Check(fun.ptr()); |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
class buffer : public object { |
|||
public: |
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT_DEFAULT(buffer, object, PyObject_CheckBuffer) |
|||
|
|||
buffer_info request(bool writable = false) { |
|||
int flags = PyBUF_STRIDES | PyBUF_FORMAT; |
|||
if (writable) flags |= PyBUF_WRITABLE; |
|||
Py_buffer *view = new Py_buffer(); |
|||
if (PyObject_GetBuffer(m_ptr, view, flags) != 0) |
|||
throw error_already_set(); |
|||
return buffer_info(view); |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
class memoryview : public object { |
|||
public: |
|||
explicit memoryview(const buffer_info& info) { |
|||
static Py_buffer buf { }; |
|||
// Py_buffer uses signed sizes, strides and shape!.. |
|||
static std::vector<Py_ssize_t> py_strides { }; |
|||
static std::vector<Py_ssize_t> py_shape { }; |
|||
buf.buf = info.ptr; |
|||
buf.itemsize = (Py_ssize_t) info.itemsize; |
|||
buf.format = const_cast<char *>(info.format.c_str()); |
|||
buf.ndim = (int) info.ndim; |
|||
buf.len = (Py_ssize_t) info.size; |
|||
py_strides.clear(); |
|||
py_shape.clear(); |
|||
for (size_t i = 0; i < info.ndim; ++i) { |
|||
py_strides.push_back((Py_ssize_t) info.strides[i]); |
|||
py_shape.push_back((Py_ssize_t) info.shape[i]); |
|||
} |
|||
buf.strides = py_strides.data(); |
|||
buf.shape = py_shape.data(); |
|||
buf.suboffsets = nullptr; |
|||
buf.readonly = false; |
|||
buf.internal = nullptr; |
|||
|
|||
m_ptr = PyMemoryView_FromBuffer(&buf); |
|||
if (!m_ptr) |
|||
pybind11_fail("Unable to create memoryview from buffer descriptor"); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_OBJECT_CVT(memoryview, object, PyMemoryView_Check, PyMemoryView_FromObject) |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
inline size_t len(handle h) { |
|||
ssize_t result = PyObject_Length(h.ptr()); |
|||
if (result < 0) |
|||
pybind11_fail("Unable to compute length of object"); |
|||
return (size_t) result; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
inline str repr(handle h) { |
|||
PyObject *str_value = PyObject_Repr(h.ptr()); |
|||
if (!str_value) throw error_already_set(); |
|||
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3 |
|||
PyObject *unicode = PyUnicode_FromEncodedObject(str_value, "utf-8", nullptr); |
|||
Py_XDECREF(str_value); str_value = unicode; |
|||
if (!str_value) throw error_already_set(); |
|||
#endif |
|||
return reinterpret_steal<str>(str_value); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(detail) |
|||
template <typename D> iterator object_api<D>::begin() const { |
|||
return reinterpret_steal<iterator>(PyObject_GetIter(derived().ptr())); |
|||
} |
|||
template <typename D> iterator object_api<D>::end() const { |
|||
return {}; |
|||
} |
|||
template <typename D> item_accessor object_api<D>::operator[](handle key) const { |
|||
return {derived(), reinterpret_borrow<object>(key)}; |
|||
} |
|||
template <typename D> item_accessor object_api<D>::operator[](const char *key) const { |
|||
return {derived(), pybind11::str(key)}; |
|||
} |
|||
template <typename D> obj_attr_accessor object_api<D>::attr(handle key) const { |
|||
return {derived(), reinterpret_borrow<object>(key)}; |
|||
} |
|||
template <typename D> str_attr_accessor object_api<D>::attr(const char *key) const { |
|||
return {derived(), key}; |
|||
} |
|||
template <typename D> args_proxy object_api<D>::operator*() const { |
|||
return args_proxy(derived().ptr()); |
|||
} |
|||
template <typename D> template <typename T> bool object_api<D>::contains(T &&key) const { |
|||
return attr("__contains__")(std::forward<T>(key)).template cast<bool>(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
template <typename D> |
|||
pybind11::str object_api<D>::str() const { return pybind11::str(derived()); } |
|||
|
|||
template <typename D> |
|||
handle object_api<D>::get_type() const { return (PyObject *) Py_TYPE(derived().ptr()); } |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_END(detail) |
|||
NAMESPACE_END(pybind11) |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,256 @@ |
|||
/* |
|||
pybind11/stl.h: Transparent conversion for STL data types |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#pragma once |
|||
|
|||
#include "pybind11.h" |
|||
#include <set> |
|||
#include <unordered_set> |
|||
#include <map> |
|||
#include <unordered_map> |
|||
#include <iostream> |
|||
#include <list> |
|||
|
|||
#if defined(_MSC_VER) |
|||
#pragma warning(push) |
|||
#pragma warning(disable: 4127) // warning C4127: Conditional expression is constant |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
#ifdef __has_include |
|||
// std::optional (but including it in c++14 mode isn't allowed) |
|||
# if defined(PYBIND11_CPP17) && __has_include(<optional>) |
|||
# include <optional> |
|||
# define PYBIND11_HAS_OPTIONAL 1 |
|||
# endif |
|||
// std::experimental::optional (but not allowed in c++11 mode) |
|||
# if defined(PYBIND11_CPP14) && __has_include(<experimental/optional>) |
|||
# include <experimental/optional> |
|||
# if __cpp_lib_experimental_optional // just in case |
|||
# define PYBIND11_HAS_EXP_OPTIONAL 1 |
|||
# endif |
|||
# endif |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(pybind11) |
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(detail) |
|||
|
|||
template <typename Type, typename Key> struct set_caster { |
|||
using type = Type; |
|||
using key_conv = make_caster<Key>; |
|||
|
|||
bool load(handle src, bool convert) { |
|||
if (!isinstance<pybind11::set>(src)) |
|||
return false; |
|||
auto s = reinterpret_borrow<pybind11::set>(src); |
|||
value.clear(); |
|||
key_conv conv; |
|||
for (auto entry : s) { |
|||
if (!conv.load(entry, convert)) |
|||
return false; |
|||
value.insert(cast_op<Key>(conv)); |
|||
} |
|||
return true; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
static handle cast(const type &src, return_value_policy policy, handle parent) { |
|||
pybind11::set s; |
|||
for (auto const &value: src) { |
|||
auto value_ = reinterpret_steal<object>(key_conv::cast(value, policy, parent)); |
|||
if (!value_ || !s.add(value_)) |
|||
return handle(); |
|||
} |
|||
return s.release(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_TYPE_CASTER(type, _("Set[") + key_conv::name() + _("]")); |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
template <typename Type, typename Key, typename Value> struct map_caster { |
|||
using type = Type; |
|||
using key_conv = make_caster<Key>; |
|||
using value_conv = make_caster<Value>; |
|||
|
|||
bool load(handle src, bool convert) { |
|||
if (!isinstance<dict>(src)) |
|||
return false; |
|||
auto d = reinterpret_borrow<dict>(src); |
|||
key_conv kconv; |
|||
value_conv vconv; |
|||
value.clear(); |
|||
for (auto it : d) { |
|||
if (!kconv.load(it.first.ptr(), convert) || |
|||
!vconv.load(it.second.ptr(), convert)) |
|||
return false; |
|||
value.emplace(cast_op<Key>(kconv), cast_op<Value>(vconv)); |
|||
} |
|||
return true; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
static handle cast(const type &src, return_value_policy policy, handle parent) { |
|||
dict d; |
|||
for (auto const &kv: src) { |
|||
auto key = reinterpret_steal<object>(key_conv::cast(kv.first, policy, parent)); |
|||
auto value = reinterpret_steal<object>(value_conv::cast(kv.second, policy, parent)); |
|||
if (!key || !value) |
|||
return handle(); |
|||
d[key] = value; |
|||
} |
|||
return d.release(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_TYPE_CASTER(type, _("Dict[") + key_conv::name() + _(", ") + value_conv::name() + _("]")); |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
template <typename Type, typename Value> struct list_caster { |
|||
using type = Type; |
|||
using value_conv = make_caster<Value>; |
|||
|
|||
bool load(handle src, bool convert) { |
|||
if (!isinstance<sequence>(src)) |
|||
return false; |
|||
auto s = reinterpret_borrow<sequence>(src); |
|||
value_conv conv; |
|||
value.clear(); |
|||
reserve_maybe(s, &value); |
|||
for (auto it : s) { |
|||
if (!conv.load(it, convert)) |
|||
return false; |
|||
value.push_back(cast_op<Value>(conv)); |
|||
} |
|||
return true; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
template <typename T = Type, |
|||
enable_if_t<std::is_same<decltype(std::declval<T>().reserve(0)), void>::value, int> = 0> |
|||
void reserve_maybe(sequence s, Type *) { value.reserve(s.size()); } |
|||
void reserve_maybe(sequence, void *) { } |
|||
|
|||
static handle cast(const Type &src, return_value_policy policy, handle parent) { |
|||
list l(src.size()); |
|||
size_t index = 0; |
|||
for (auto const &value: src) { |
|||
auto value_ = reinterpret_steal<object>(value_conv::cast(value, policy, parent)); |
|||
if (!value_) |
|||
return handle(); |
|||
PyList_SET_ITEM(l.ptr(), index++, value_.release().ptr()); // steals a reference |
|||
} |
|||
return l.release(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_TYPE_CASTER(Type, _("List[") + value_conv::name() + _("]")); |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
template <typename Type, typename Alloc> struct type_caster<std::vector<Type, Alloc>> |
|||
: list_caster<std::vector<Type, Alloc>, Type> { }; |
|||
|
|||
template <typename Type, typename Alloc> struct type_caster<std::list<Type, Alloc>> |
|||
: list_caster<std::list<Type, Alloc>, Type> { }; |
|||
|
|||
template <typename Type, size_t Size> struct type_caster<std::array<Type, Size>> { |
|||
using array_type = std::array<Type, Size>; |
|||
using value_conv = make_caster<Type>; |
|||
|
|||
bool load(handle src, bool convert) { |
|||
if (!isinstance<list>(src)) |
|||
return false; |
|||
auto l = reinterpret_borrow<list>(src); |
|||
if (l.size() != Size) |
|||
return false; |
|||
value_conv conv; |
|||
size_t ctr = 0; |
|||
for (auto it : l) { |
|||
if (!conv.load(it, convert)) |
|||
return false; |
|||
value[ctr++] = cast_op<Type>(conv); |
|||
} |
|||
return true; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
static handle cast(const array_type &src, return_value_policy policy, handle parent) { |
|||
list l(Size); |
|||
size_t index = 0; |
|||
for (auto const &value: src) { |
|||
auto value_ = reinterpret_steal<object>(value_conv::cast(value, policy, parent)); |
|||
if (!value_) |
|||
return handle(); |
|||
PyList_SET_ITEM(l.ptr(), index++, value_.release().ptr()); // steals a reference |
|||
} |
|||
return l.release(); |
|||
} |
|||
PYBIND11_TYPE_CASTER(array_type, _("List[") + value_conv::name() + _("[") + _<Size>() + _("]]")); |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
template <typename Key, typename Compare, typename Alloc> struct type_caster<std::set<Key, Compare, Alloc>> |
|||
: set_caster<std::set<Key, Compare, Alloc>, Key> { }; |
|||
|
|||
template <typename Key, typename Hash, typename Equal, typename Alloc> struct type_caster<std::unordered_set<Key, Hash, Equal, Alloc>> |
|||
: set_caster<std::unordered_set<Key, Hash, Equal, Alloc>, Key> { }; |
|||
|
|||
template <typename Key, typename Value, typename Compare, typename Alloc> struct type_caster<std::map<Key, Value, Compare, Alloc>> |
|||
: map_caster<std::map<Key, Value, Compare, Alloc>, Key, Value> { }; |
|||
|
|||
template <typename Key, typename Value, typename Hash, typename Equal, typename Alloc> struct type_caster<std::unordered_map<Key, Value, Hash, Equal, Alloc>> |
|||
: map_caster<std::unordered_map<Key, Value, Hash, Equal, Alloc>, Key, Value> { }; |
|||
|
|||
// This type caster is intended to be used for std::optional and std::experimental::optional |
|||
template<typename T> struct optional_caster { |
|||
using value_conv = make_caster<typename T::value_type>; |
|||
|
|||
static handle cast(const T& src, return_value_policy policy, handle parent) { |
|||
if (!src) |
|||
return none().inc_ref(); |
|||
return value_conv::cast(*src, policy, parent); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
bool load(handle src, bool convert) { |
|||
if (!src) { |
|||
return false; |
|||
} else if (src.is_none()) { |
|||
value = {}; // nullopt |
|||
return true; |
|||
} |
|||
value_conv inner_caster; |
|||
if (!inner_caster.load(src, convert)) |
|||
return false; |
|||
|
|||
value.emplace(cast_op<typename T::value_type>(inner_caster)); |
|||
return true; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_TYPE_CASTER(T, _("Optional[") + value_conv::name() + _("]")); |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
#if PYBIND11_HAS_OPTIONAL |
|||
template<typename T> struct type_caster<std::optional<T>> |
|||
: public optional_caster<std::optional<T>> {}; |
|||
|
|||
template<> struct type_caster<std::nullopt_t> |
|||
: public void_caster<std::nullopt_t> {}; |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
#if PYBIND11_HAS_EXP_OPTIONAL |
|||
template<typename T> struct type_caster<std::experimental::optional<T>> |
|||
: public optional_caster<std::experimental::optional<T>> {}; |
|||
|
|||
template<> struct type_caster<std::experimental::nullopt_t> |
|||
: public void_caster<std::experimental::nullopt_t> {}; |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_END(detail) |
|||
|
|||
inline std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const handle &obj) { |
|||
os << (std::string) str(obj); |
|||
return os; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_END(pybind11) |
|||
|
|||
#if defined(_MSC_VER) |
|||
#pragma warning(pop) |
|||
#endif |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,541 @@ |
|||
/* |
|||
pybind11/std_bind.h: Binding generators for STL data types |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Sergey Lyskov and Wenzel Jakob |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#pragma once |
|||
|
|||
#include "common.h" |
|||
#include "operators.h" |
|||
|
|||
#include <algorithm> |
|||
#include <sstream> |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(pybind11) |
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(detail) |
|||
|
|||
/* SFINAE helper class used by 'is_comparable */ |
|||
template <typename T> struct container_traits { |
|||
template <typename T2> static std::true_type test_comparable(decltype(std::declval<const T2 &>() == std::declval<const T2 &>())*); |
|||
template <typename T2> static std::false_type test_comparable(...); |
|||
template <typename T2> static std::true_type test_value(typename T2::value_type *); |
|||
template <typename T2> static std::false_type test_value(...); |
|||
template <typename T2> static std::true_type test_pair(typename T2::first_type *, typename T2::second_type *); |
|||
template <typename T2> static std::false_type test_pair(...); |
|||
|
|||
static constexpr const bool is_comparable = std::is_same<std::true_type, decltype(test_comparable<T>(nullptr))>::value; |
|||
static constexpr const bool is_pair = std::is_same<std::true_type, decltype(test_pair<T>(nullptr, nullptr))>::value; |
|||
static constexpr const bool is_vector = std::is_same<std::true_type, decltype(test_value<T>(nullptr))>::value; |
|||
static constexpr const bool is_element = !is_pair && !is_vector; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/* Default: is_comparable -> std::false_type */ |
|||
template <typename T, typename SFINAE = void> |
|||
struct is_comparable : std::false_type { }; |
|||
|
|||
/* For non-map data structures, check whether operator== can be instantiated */ |
|||
template <typename T> |
|||
struct is_comparable< |
|||
T, enable_if_t<container_traits<T>::is_element && |
|||
container_traits<T>::is_comparable>> |
|||
: std::true_type { }; |
|||
|
|||
/* For a vector/map data structure, recursively check the value type (which is std::pair for maps) */ |
|||
template <typename T> |
|||
struct is_comparable<T, enable_if_t<container_traits<T>::is_vector>> { |
|||
static constexpr const bool value = |
|||
is_comparable<typename T::value_type>::value; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/* For pairs, recursively check the two data types */ |
|||
template <typename T> |
|||
struct is_comparable<T, enable_if_t<container_traits<T>::is_pair>> { |
|||
static constexpr const bool value = |
|||
is_comparable<typename T::first_type>::value && |
|||
is_comparable<typename T::second_type>::value; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/* Fallback functions */ |
|||
template <typename, typename, typename... Args> void vector_if_copy_constructible(const Args &...) { } |
|||
template <typename, typename, typename... Args> void vector_if_equal_operator(const Args &...) { } |
|||
template <typename, typename, typename... Args> void vector_if_insertion_operator(const Args &...) { } |
|||
template <typename, typename, typename... Args> void vector_modifiers(const Args &...) { } |
|||
|
|||
template<typename Vector, typename Class_> |
|||
void vector_if_copy_constructible(enable_if_t< |
|||
std::is_copy_constructible<Vector>::value && |
|||
std::is_copy_constructible<typename Vector::value_type>::value, Class_> &cl) { |
|||
|
|||
cl.def(pybind11::init<const Vector &>(), "Copy constructor"); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
template<typename Vector, typename Class_> |
|||
void vector_if_equal_operator(enable_if_t<is_comparable<Vector>::value, Class_> &cl) { |
|||
using T = typename Vector::value_type; |
|||
|
|||
cl.def(self == self); |
|||
cl.def(self != self); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("count", |
|||
[](const Vector &v, const T &x) { |
|||
return std::count(v.begin(), v.end(), x); |
|||
}, |
|||
arg("x"), |
|||
"Return the number of times ``x`` appears in the list" |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("remove", [](Vector &v, const T &x) { |
|||
auto p = std::find(v.begin(), v.end(), x); |
|||
if (p != v.end()) |
|||
v.erase(p); |
|||
else |
|||
throw pybind11::value_error(); |
|||
}, |
|||
arg("x"), |
|||
"Remove the first item from the list whose value is x. " |
|||
"It is an error if there is no such item." |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__contains__", |
|||
[](const Vector &v, const T &x) { |
|||
return std::find(v.begin(), v.end(), x) != v.end(); |
|||
}, |
|||
arg("x"), |
|||
"Return true the container contains ``x``" |
|||
); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Vector modifiers -- requires a copyable vector_type: |
|||
// (Technically, some of these (pop and __delitem__) don't actually require copyability, but it seems |
|||
// silly to allow deletion but not insertion, so include them here too.) |
|||
template <typename Vector, typename Class_> |
|||
void vector_modifiers(enable_if_t<std::is_copy_constructible<typename Vector::value_type>::value, Class_> &cl) { |
|||
using T = typename Vector::value_type; |
|||
using SizeType = typename Vector::size_type; |
|||
using DiffType = typename Vector::difference_type; |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("append", |
|||
[](Vector &v, const T &value) { v.push_back(value); }, |
|||
arg("x"), |
|||
"Add an item to the end of the list"); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__init__", [](Vector &v, iterable it) { |
|||
new (&v) Vector(); |
|||
try { |
|||
v.reserve(len(it)); |
|||
for (handle h : it) |
|||
v.push_back(h.cast<T>()); |
|||
} catch (...) { |
|||
v.~Vector(); |
|||
throw; |
|||
} |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("extend", |
|||
[](Vector &v, const Vector &src) { |
|||
v.reserve(v.size() + src.size()); |
|||
v.insert(v.end(), src.begin(), src.end()); |
|||
}, |
|||
arg("L"), |
|||
"Extend the list by appending all the items in the given list" |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("insert", |
|||
[](Vector &v, SizeType i, const T &x) { |
|||
v.insert(v.begin() + (DiffType) i, x); |
|||
}, |
|||
arg("i") , arg("x"), |
|||
"Insert an item at a given position." |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("pop", |
|||
[](Vector &v) { |
|||
if (v.empty()) |
|||
throw pybind11::index_error(); |
|||
T t = v.back(); |
|||
v.pop_back(); |
|||
return t; |
|||
}, |
|||
"Remove and return the last item" |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("pop", |
|||
[](Vector &v, SizeType i) { |
|||
if (i >= v.size()) |
|||
throw pybind11::index_error(); |
|||
T t = v[i]; |
|||
v.erase(v.begin() + (DiffType) i); |
|||
return t; |
|||
}, |
|||
arg("i"), |
|||
"Remove and return the item at index ``i``" |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__setitem__", |
|||
[](Vector &v, SizeType i, const T &t) { |
|||
if (i >= v.size()) |
|||
throw pybind11::index_error(); |
|||
v[i] = t; |
|||
} |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
/// Slicing protocol |
|||
cl.def("__getitem__", |
|||
[](const Vector &v, slice slice) -> Vector * { |
|||
size_t start, stop, step, slicelength; |
|||
|
|||
if (!slice.compute(v.size(), &start, &stop, &step, &slicelength)) |
|||
throw pybind11::error_already_set(); |
|||
|
|||
Vector *seq = new Vector(); |
|||
seq->reserve((size_t) slicelength); |
|||
|
|||
for (size_t i=0; i<slicelength; ++i) { |
|||
seq->push_back(v[start]); |
|||
start += step; |
|||
} |
|||
return seq; |
|||
}, |
|||
arg("s"), |
|||
"Retrieve list elements using a slice object" |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__setitem__", |
|||
[](Vector &v, slice slice, const Vector &value) { |
|||
size_t start, stop, step, slicelength; |
|||
if (!slice.compute(v.size(), &start, &stop, &step, &slicelength)) |
|||
throw pybind11::error_already_set(); |
|||
|
|||
if (slicelength != value.size()) |
|||
throw std::runtime_error("Left and right hand size of slice assignment have different sizes!"); |
|||
|
|||
for (size_t i=0; i<slicelength; ++i) { |
|||
v[start] = value[i]; |
|||
start += step; |
|||
} |
|||
}, |
|||
"Assign list elements using a slice object" |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__delitem__", |
|||
[](Vector &v, SizeType i) { |
|||
if (i >= v.size()) |
|||
throw pybind11::index_error(); |
|||
v.erase(v.begin() + DiffType(i)); |
|||
}, |
|||
"Delete the list elements at index ``i``" |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__delitem__", |
|||
[](Vector &v, slice slice) { |
|||
size_t start, stop, step, slicelength; |
|||
|
|||
if (!slice.compute(v.size(), &start, &stop, &step, &slicelength)) |
|||
throw pybind11::error_already_set(); |
|||
|
|||
if (step == 1 && false) { |
|||
v.erase(v.begin() + (DiffType) start, v.begin() + DiffType(start + slicelength)); |
|||
} else { |
|||
for (size_t i = 0; i < slicelength; ++i) { |
|||
v.erase(v.begin() + DiffType(start)); |
|||
start += step - 1; |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
}, |
|||
"Delete list elements using a slice object" |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// If the type has an operator[] that doesn't return a reference (most notably std::vector<bool>), |
|||
// we have to access by copying; otherwise we return by reference. |
|||
template <typename Vector> using vector_needs_copy = bool_constant< |
|||
!std::is_same<decltype(std::declval<Vector>()[typename Vector::size_type()]), typename Vector::value_type &>::value>; |
|||
|
|||
// The usual case: access and iterate by reference |
|||
template <typename Vector, typename Class_> |
|||
void vector_accessor(enable_if_t<!vector_needs_copy<Vector>::value, Class_> &cl) { |
|||
using T = typename Vector::value_type; |
|||
using SizeType = typename Vector::size_type; |
|||
using ItType = typename Vector::iterator; |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__getitem__", |
|||
[](Vector &v, SizeType i) -> T & { |
|||
if (i >= v.size()) |
|||
throw pybind11::index_error(); |
|||
return v[i]; |
|||
}, |
|||
return_value_policy::reference_internal // ref + keepalive |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__iter__", |
|||
[](Vector &v) { |
|||
return pybind11::make_iterator< |
|||
return_value_policy::reference_internal, ItType, ItType, T&>( |
|||
v.begin(), v.end()); |
|||
}, |
|||
keep_alive<0, 1>() /* Essential: keep list alive while iterator exists */ |
|||
); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// The case for special objects, like std::vector<bool>, that have to be returned-by-copy: |
|||
template <typename Vector, typename Class_> |
|||
void vector_accessor(enable_if_t<vector_needs_copy<Vector>::value, Class_> &cl) { |
|||
using T = typename Vector::value_type; |
|||
using SizeType = typename Vector::size_type; |
|||
using ItType = typename Vector::iterator; |
|||
cl.def("__getitem__", |
|||
[](const Vector &v, SizeType i) -> T { |
|||
if (i >= v.size()) |
|||
throw pybind11::index_error(); |
|||
return v[i]; |
|||
} |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__iter__", |
|||
[](Vector &v) { |
|||
return pybind11::make_iterator< |
|||
return_value_policy::copy, ItType, ItType, T>( |
|||
v.begin(), v.end()); |
|||
}, |
|||
keep_alive<0, 1>() /* Essential: keep list alive while iterator exists */ |
|||
); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
template <typename Vector, typename Class_> auto vector_if_insertion_operator(Class_ &cl, std::string const &name) |
|||
-> decltype(std::declval<std::ostream&>() << std::declval<typename Vector::value_type>(), void()) { |
|||
using size_type = typename Vector::size_type; |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__repr__", |
|||
[name](Vector &v) { |
|||
std::ostringstream s; |
|||
s << name << '['; |
|||
for (size_type i=0; i < v.size(); ++i) { |
|||
s << v[i]; |
|||
if (i != v.size() - 1) |
|||
s << ", "; |
|||
} |
|||
s << ']'; |
|||
return s.str(); |
|||
}, |
|||
"Return the canonical string representation of this list." |
|||
); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_END(detail) |
|||
|
|||
// |
|||
// std::vector |
|||
// |
|||
template <typename Vector, typename holder_type = std::unique_ptr<Vector>, typename... Args> |
|||
pybind11::class_<Vector, holder_type> bind_vector(pybind11::module &m, std::string const &name, Args&&... args) { |
|||
using Class_ = pybind11::class_<Vector, holder_type>; |
|||
|
|||
Class_ cl(m, name.c_str(), std::forward<Args>(args)...); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def(pybind11::init<>()); |
|||
|
|||
// Register copy constructor (if possible) |
|||
detail::vector_if_copy_constructible<Vector, Class_>(cl); |
|||
|
|||
// Register comparison-related operators and functions (if possible) |
|||
detail::vector_if_equal_operator<Vector, Class_>(cl); |
|||
|
|||
// Register stream insertion operator (if possible) |
|||
detail::vector_if_insertion_operator<Vector, Class_>(cl, name); |
|||
|
|||
// Modifiers require copyable vector value type |
|||
detail::vector_modifiers<Vector, Class_>(cl); |
|||
|
|||
// Accessor and iterator; return by value if copyable, otherwise we return by ref + keep-alive |
|||
detail::vector_accessor<Vector, Class_>(cl); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__bool__", |
|||
[](const Vector &v) -> bool { |
|||
return !v.empty(); |
|||
}, |
|||
"Check whether the list is nonempty" |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__len__", &Vector::size); |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
#if 0 |
|||
// C++ style functions deprecated, leaving it here as an example |
|||
cl.def(pybind11::init<size_type>()); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("resize", |
|||
(void (Vector::*) (size_type count)) & Vector::resize, |
|||
"changes the number of elements stored"); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("erase", |
|||
[](Vector &v, SizeType i) { |
|||
if (i >= v.size()) |
|||
throw pybind11::index_error(); |
|||
v.erase(v.begin() + i); |
|||
}, "erases element at index ``i``"); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("empty", &Vector::empty, "checks whether the container is empty"); |
|||
cl.def("size", &Vector::size, "returns the number of elements"); |
|||
cl.def("push_back", (void (Vector::*)(const T&)) &Vector::push_back, "adds an element to the end"); |
|||
cl.def("pop_back", &Vector::pop_back, "removes the last element"); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("max_size", &Vector::max_size, "returns the maximum possible number of elements"); |
|||
cl.def("reserve", &Vector::reserve, "reserves storage"); |
|||
cl.def("capacity", &Vector::capacity, "returns the number of elements that can be held in currently allocated storage"); |
|||
cl.def("shrink_to_fit", &Vector::shrink_to_fit, "reduces memory usage by freeing unused memory"); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("clear", &Vector::clear, "clears the contents"); |
|||
cl.def("swap", &Vector::swap, "swaps the contents"); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("front", [](Vector &v) { |
|||
if (v.size()) return v.front(); |
|||
else throw pybind11::index_error(); |
|||
}, "access the first element"); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("back", [](Vector &v) { |
|||
if (v.size()) return v.back(); |
|||
else throw pybind11::index_error(); |
|||
}, "access the last element "); |
|||
|
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
return cl; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
// |
|||
// std::map, std::unordered_map |
|||
// |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(detail) |
|||
|
|||
/* Fallback functions */ |
|||
template <typename, typename, typename... Args> void map_if_insertion_operator(const Args &...) { } |
|||
template <typename, typename, typename... Args> void map_assignment(const Args &...) { } |
|||
|
|||
// Map assignment when copy-assignable: just copy the value |
|||
template <typename Map, typename Class_> |
|||
void map_assignment(enable_if_t<std::is_copy_assignable<typename Map::mapped_type>::value, Class_> &cl) { |
|||
using KeyType = typename Map::key_type; |
|||
using MappedType = typename Map::mapped_type; |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__setitem__", |
|||
[](Map &m, const KeyType &k, const MappedType &v) { |
|||
auto it = m.find(k); |
|||
if (it != m.end()) it->second = v; |
|||
else m.emplace(k, v); |
|||
} |
|||
); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Not copy-assignable, but still copy-constructible: we can update the value by erasing and reinserting |
|||
template<typename Map, typename Class_> |
|||
void map_assignment(enable_if_t< |
|||
!std::is_copy_assignable<typename Map::mapped_type>::value && |
|||
std::is_copy_constructible<typename Map::mapped_type>::value, |
|||
Class_> &cl) { |
|||
using KeyType = typename Map::key_type; |
|||
using MappedType = typename Map::mapped_type; |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__setitem__", |
|||
[](Map &m, const KeyType &k, const MappedType &v) { |
|||
// We can't use m[k] = v; because value type might not be default constructable |
|||
auto r = m.emplace(k, v); |
|||
if (!r.second) { |
|||
// value type is not copy assignable so the only way to insert it is to erase it first... |
|||
m.erase(r.first); |
|||
m.emplace(k, v); |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
template <typename Map, typename Class_> auto map_if_insertion_operator(Class_ &cl, std::string const &name) |
|||
-> decltype(std::declval<std::ostream&>() << std::declval<typename Map::key_type>() << std::declval<typename Map::mapped_type>(), void()) { |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__repr__", |
|||
[name](Map &m) { |
|||
std::ostringstream s; |
|||
s << name << '{'; |
|||
bool f = false; |
|||
for (auto const &kv : m) { |
|||
if (f) |
|||
s << ", "; |
|||
s << kv.first << ": " << kv.second; |
|||
f = true; |
|||
} |
|||
s << '}'; |
|||
return s.str(); |
|||
}, |
|||
"Return the canonical string representation of this map." |
|||
); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_END(detail) |
|||
|
|||
template <typename Map, typename holder_type = std::unique_ptr<Map>, typename... Args> |
|||
pybind11::class_<Map, holder_type> bind_map(module &m, const std::string &name, Args&&... args) { |
|||
using KeyType = typename Map::key_type; |
|||
using MappedType = typename Map::mapped_type; |
|||
using Class_ = pybind11::class_<Map, holder_type>; |
|||
|
|||
Class_ cl(m, name.c_str(), std::forward<Args>(args)...); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def(pybind11::init<>()); |
|||
|
|||
// Register stream insertion operator (if possible) |
|||
detail::map_if_insertion_operator<Map, Class_>(cl, name); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__bool__", |
|||
[](const Map &m) -> bool { return !m.empty(); }, |
|||
"Check whether the map is nonempty" |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__iter__", |
|||
[](Map &m) { return pybind11::make_key_iterator(m.begin(), m.end()); }, |
|||
pybind11::keep_alive<0, 1>() /* Essential: keep list alive while iterator exists */ |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("items", |
|||
[](Map &m) { return pybind11::make_iterator(m.begin(), m.end()); }, |
|||
pybind11::keep_alive<0, 1>() /* Essential: keep list alive while iterator exists */ |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__getitem__", |
|||
[](Map &m, const KeyType &k) -> MappedType & { |
|||
auto it = m.find(k); |
|||
if (it == m.end()) |
|||
throw pybind11::key_error(); |
|||
return it->second; |
|||
}, |
|||
return_value_policy::reference_internal // ref + keepalive |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
// Assignment provided only if the type is copyable |
|||
detail::map_assignment<Map, Class_>(cl); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__delitem__", |
|||
[](Map &m, const KeyType &k) { |
|||
auto it = m.find(k); |
|||
if (it == m.end()) |
|||
throw pybind11::key_error(); |
|||
return m.erase(it); |
|||
} |
|||
); |
|||
|
|||
cl.def("__len__", &Map::size); |
|||
|
|||
return cl; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_END(pybind11) |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,53 @@ |
|||
/* |
|||
pybind11/typeid.h: Compiler-independent access to type identifiers |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#pragma once |
|||
|
|||
#include <cstdio> |
|||
#include <cstdlib> |
|||
|
|||
#if defined(__GNUG__) |
|||
#include <cxxabi.h> |
|||
#endif |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(pybind11) |
|||
NAMESPACE_BEGIN(detail) |
|||
/// Erase all occurrences of a substring |
|||
inline void erase_all(std::string &string, const std::string &search) { |
|||
for (size_t pos = 0;;) { |
|||
pos = string.find(search, pos); |
|||
if (pos == std::string::npos) break; |
|||
string.erase(pos, search.length()); |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_NOINLINE inline void clean_type_id(std::string &name) { |
|||
#if defined(__GNUG__) |
|||
int status = 0; |
|||
std::unique_ptr<char, void (*)(void *)> res { |
|||
abi::__cxa_demangle(name.c_str(), nullptr, nullptr, &status), std::free }; |
|||
if (status == 0) |
|||
name = res.get(); |
|||
#else |
|||
detail::erase_all(name, "class "); |
|||
detail::erase_all(name, "struct "); |
|||
detail::erase_all(name, "enum "); |
|||
#endif |
|||
detail::erase_all(name, "pybind11::"); |
|||
} |
|||
NAMESPACE_END(detail) |
|||
|
|||
/// Return a string representation of a C++ type |
|||
template <typename T> static std::string type_id() { |
|||
std::string name(typeid(T).name()); |
|||
detail::clean_type_id(name); |
|||
return name; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
NAMESPACE_END(pybind11) |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,11 @@ |
|||
from ._version import version_info, __version__ # noqa: F401 imported but unused |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def get_include(*args, **kwargs): |
|||
import os |
|||
try: |
|||
from pip import locations |
|||
return os.path.dirname( |
|||
locations.distutils_scheme('pybind11', *args, **kwargs)['headers']) |
|||
except ImportError: |
|||
return 'include' |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@ |
|||
version_info = (1, 9, 'dev0') |
|||
__version__ = '.'.join(map(str, version_info)) |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,11 @@ |
|||
[bdist_wheel] |
|||
universal=1 |
|||
|
|||
[flake8] |
|||
show_source = True |
|||
exclude = .git, __pycache__, build, dist, docs, tools, venv |
|||
ignore = |
|||
# line too long |
|||
E501, |
|||
# required for pretty matrix formating: multiple spaces after `,` and `[` |
|||
E201, E241 |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,74 @@ |
|||
#!/usr/bin/env python |
|||
|
|||
# Setup script for PyPI; use CMakeFile.txt to build extension modules |
|||
|
|||
from setuptools import setup |
|||
from pybind11 import __version__ |
|||
|
|||
setup( |
|||
name='pybind11', |
|||
version=__version__, |
|||
description='Seamless operability between C++11 and Python', |
|||
author='Wenzel Jakob', |
|||
author_email='wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch', |
|||
url='https://github.com/wjakob/pybind11', |
|||
download_url='https://github.com/wjakob/pybind11/tarball/v' + __version__, |
|||
packages=['pybind11'], |
|||
license='BSD', |
|||
headers=[ |
|||
'include/pybind11/attr.h', |
|||
'include/pybind11/cast.h', |
|||
'include/pybind11/chrono.h', |
|||
'include/pybind11/common.h', |
|||
'include/pybind11/complex.h', |
|||
'include/pybind11/descr.h', |
|||
'include/pybind11/eigen.h', |
|||
'include/pybind11/eval.h', |
|||
'include/pybind11/functional.h', |
|||
'include/pybind11/numpy.h', |
|||
'include/pybind11/operators.h', |
|||
'include/pybind11/options.h', |
|||
'include/pybind11/pybind11.h', |
|||
'include/pybind11/pytypes.h', |
|||
'include/pybind11/stl.h', |
|||
'include/pybind11/stl_bind.h', |
|||
'include/pybind11/typeid.h', |
|||
], |
|||
classifiers=[ |
|||
'Development Status :: 5 - Production/Stable', |
|||
'Intended Audience :: Developers', |
|||
'Topic :: Software Development :: Libraries :: Python Modules', |
|||
'Topic :: Utilities', |
|||
'Programming Language :: C++', |
|||
'Programming Language :: Python :: 2.7', |
|||
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3', |
|||
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.2', |
|||
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.3', |
|||
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.4', |
|||
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.5', |
|||
'License :: OSI Approved :: BSD License', |
|||
], |
|||
keywords='C++11, Python bindings', |
|||
long_description="""pybind11 is a lightweight header library that exposes |
|||
C++ types in Python and vice versa, mainly to create Python bindings of |
|||
existing C++ code. Its goals and syntax are similar to the excellent |
|||
Boost.Python library by David Abrahams: to minimize boilerplate code in |
|||
traditional extension modules by inferring type information using compile-time |
|||
introspection. |
|||
|
|||
The main issue with Boost.Python-and the reason for creating such a similar |
|||
project-is Boost. Boost is an enormously large and complex suite of utility |
|||
libraries that works with almost every C++ compiler in existence. This |
|||
compatibility has its cost: arcane template tricks and workarounds are |
|||
necessary to support the oldest and buggiest of compiler specimens. Now that |
|||
C++11-compatible compilers are widely available, this heavy machinery has |
|||
become an excessively large and unnecessary dependency. |
|||
|
|||
Think of this library as a tiny self-contained version of Boost.Python with |
|||
everything stripped away that isn't relevant for binding generation. Without |
|||
comments, the core header files only require ~2.5K lines of code and depend on |
|||
Python (2.7 or 3.x) and the C++ standard library. This compact implementation |
|||
was possible thanks to some of the new C++11 language features (specifically: |
|||
tuples, lambda functions and variadic templates). Since its creation, this |
|||
library has grown beyond Boost.Python in many ways, leading to dramatically |
|||
simpler binding code in many common situations.""") |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,111 @@ |
|||
if(NOT CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE AND NOT CMAKE_CONFIGURATION_TYPES) |
|||
message(STATUS "Setting tests build type to MinSizeRel as none was specified") |
|||
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE MinSizeRel CACHE STRING "Choose the type of build." FORCE) |
|||
set_property(CACHE CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE PROPERTY STRINGS "Debug" "Release" |
|||
"MinSizeRel" "RelWithDebInfo") |
|||
endif() |
|||
|
|||
# Full set of test files (you can override these; see below) |
|||
set(PYBIND11_TEST_FILES |
|||
test_alias_initialization.cpp |
|||
test_buffers.cpp |
|||
test_callbacks.cpp |
|||
test_chrono.cpp |
|||
test_class_args.cpp |
|||
test_constants_and_functions.cpp |
|||
test_copy_move_policies.cpp |
|||
test_docstring_options.cpp |
|||
test_eigen.cpp |
|||
test_enum.cpp |
|||
test_eval.cpp |
|||
test_exceptions.cpp |
|||
test_inheritance.cpp |
|||
test_issues.cpp |
|||
test_keep_alive.cpp |
|||
test_kwargs_and_defaults.cpp |
|||
test_methods_and_attributes.cpp |
|||
test_modules.cpp |
|||
test_multiple_inheritance.cpp |
|||
test_numpy_array.cpp |
|||
test_numpy_dtypes.cpp |
|||
test_numpy_vectorize.cpp |
|||
test_opaque_types.cpp |
|||
test_operator_overloading.cpp |
|||
test_pickling.cpp |
|||
test_python_types.cpp |
|||
test_sequences_and_iterators.cpp |
|||
test_smart_ptr.cpp |
|||
test_stl_binders.cpp |
|||
test_virtual_functions.cpp |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
# Invoking cmake with something like: |
|||
# cmake -DPYBIND11_TEST_OVERRIDE="test_issues.cpp;test_picking.cpp" .. |
|||
# lets you override the tests that get compiled and run. You can restore to all tests with: |
|||
# cmake -DPYBIND11_TEST_OVERRIDE= .. |
|||
if (PYBIND11_TEST_OVERRIDE) |
|||
set(PYBIND11_TEST_FILES ${PYBIND11_TEST_OVERRIDE}) |
|||
endif() |
|||
|
|||
string(REPLACE ".cpp" ".py" PYBIND11_PYTEST_FILES "${PYBIND11_TEST_FILES}") |
|||
|
|||
# Check if Eigen is available; if not, remove from PYBIND11_TEST_FILES (but |
|||
# keep it in PYBIND11_PYTEST_FILES, so that we get the "eigen is not installed" |
|||
# skip message). |
|||
list(FIND PYBIND11_TEST_FILES test_eigen.cpp PYBIND11_TEST_FILES_EIGEN_I) |
|||
if(PYBIND11_TEST_FILES_EIGEN_I GREATER -1) |
|||
find_package(Eigen3 QUIET) |
|||
|
|||
if(EIGEN3_FOUND) |
|||
message(STATUS "Building tests with Eigen v${EIGEN3_VERSION}") |
|||
else() |
|||
list(REMOVE_AT PYBIND11_TEST_FILES ${PYBIND11_TEST_FILES_EIGEN_I}) |
|||
message(STATUS "Building tests WITHOUT Eigen") |
|||
endif() |
|||
endif() |
|||
|
|||
# Create the binding library |
|||
pybind11_add_module(pybind11_tests pybind11_tests.cpp |
|||
${PYBIND11_TEST_FILES} ${PYBIND11_HEADERS}) |
|||
|
|||
pybind11_enable_warnings(pybind11_tests) |
|||
|
|||
if(EIGEN3_FOUND) |
|||
target_include_directories(pybind11_tests PRIVATE ${EIGEN3_INCLUDE_DIR}) |
|||
target_compile_definitions(pybind11_tests PRIVATE -DPYBIND11_TEST_EIGEN) |
|||
endif() |
|||
|
|||
set(testdir ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/tests) |
|||
|
|||
# Always write the output file directly into the 'tests' directory (even on MSVC) |
|||
if(NOT CMAKE_LIBRARY_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY) |
|||
set_target_properties(pybind11_tests PROPERTIES LIBRARY_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY ${testdir}) |
|||
foreach(config ${CMAKE_CONFIGURATION_TYPES}) |
|||
string(TOUPPER ${config} config) |
|||
set_target_properties(pybind11_tests PROPERTIES LIBRARY_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY_${config} ${testdir}) |
|||
endforeach() |
|||
endif() |
|||
|
|||
# Make sure pytest is found or produce a fatal error |
|||
if(NOT PYBIND11_PYTEST_FOUND) |
|||
execute_process(COMMAND ${PYTHON_EXECUTABLE} -m pytest --version --noconftest OUTPUT_QUIET ERROR_QUIET |
|||
RESULT_VARIABLE PYBIND11_EXEC_PYTHON_ERR) |
|||
if(PYBIND11_EXEC_PYTHON_ERR) |
|||
message(FATAL_ERROR "Running the tests requires pytest. Please install it manually (try: ${PYTHON_EXECUTABLE} -m pip install pytest)") |
|||
endif() |
|||
set(PYBIND11_PYTEST_FOUND TRUE CACHE INTERNAL "") |
|||
endif() |
|||
|
|||
# A single command to compile and run the tests |
|||
add_custom_target(pytest COMMAND ${PYTHON_EXECUTABLE} -m pytest -rws ${PYBIND11_PYTEST_FILES} |
|||
DEPENDS pybind11_tests WORKING_DIRECTORY ${testdir}) |
|||
|
|||
if(PYBIND11_TEST_OVERRIDE) |
|||
add_custom_command(TARGET pytest POST_BUILD |
|||
COMMAND ${CMAKE_COMMAND} -E echo "Note: not all tests run: -DPYBIND11_TEST_OVERRIDE is in effect") |
|||
endif() |
|||
|
|||
# And another to show the .so size and, if a previous size, compare it: |
|||
add_custom_command(TARGET pybind11_tests POST_BUILD |
|||
COMMAND ${PYTHON_EXECUTABLE} ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/tools/libsize.py |
|||
$<TARGET_FILE:pybind11_tests> ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/sosize-$<TARGET_FILE_NAME:pybind11_tests>.txt) |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,227 @@ |
|||
"""pytest configuration |
|||
|
|||
Extends output capture as needed by pybind11: ignore constructors, optional unordered lines. |
|||
Adds docstring and exceptions message sanitizers: ignore Python 2 vs 3 differences. |
|||
""" |
|||
|
|||
import pytest |
|||
import textwrap |
|||
import difflib |
|||
import re |
|||
import sys |
|||
import contextlib |
|||
|
|||
_unicode_marker = re.compile(r'u(\'[^\']*\')') |
|||
_long_marker = re.compile(r'([0-9])L') |
|||
_hexadecimal = re.compile(r'0x[0-9a-fA-F]+') |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def _strip_and_dedent(s): |
|||
"""For triple-quote strings""" |
|||
return textwrap.dedent(s.lstrip('\n').rstrip()) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def _split_and_sort(s): |
|||
"""For output which does not require specific line order""" |
|||
return sorted(_strip_and_dedent(s).splitlines()) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def _make_explanation(a, b): |
|||
"""Explanation for a failed assert -- the a and b arguments are List[str]""" |
|||
return ["--- actual / +++ expected"] + [line.strip('\n') for line in difflib.ndiff(a, b)] |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
class Output(object): |
|||
"""Basic output post-processing and comparison""" |
|||
def __init__(self, string): |
|||
self.string = string |
|||
self.explanation = [] |
|||
|
|||
def __str__(self): |
|||
return self.string |
|||
|
|||
def __eq__(self, other): |
|||
# Ignore constructor/destructor output which is prefixed with "###" |
|||
a = [line for line in self.string.strip().splitlines() if not line.startswith("###")] |
|||
b = _strip_and_dedent(other).splitlines() |
|||
if a == b: |
|||
return True |
|||
else: |
|||
self.explanation = _make_explanation(a, b) |
|||
return False |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
class Unordered(Output): |
|||
"""Custom comparison for output without strict line ordering""" |
|||
def __eq__(self, other): |
|||
a = _split_and_sort(self.string) |
|||
b = _split_and_sort(other) |
|||
if a == b: |
|||
return True |
|||
else: |
|||
self.explanation = _make_explanation(a, b) |
|||
return False |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
class Capture(object): |
|||
def __init__(self, capfd): |
|||
self.capfd = capfd |
|||
self.out = "" |
|||
self.err = "" |
|||
|
|||
def __enter__(self): |
|||
self.capfd.readouterr() |
|||
return self |
|||
|
|||
def __exit__(self, *_): |
|||
self.out, self.err = self.capfd.readouterr() |
|||
|
|||
def __eq__(self, other): |
|||
a = Output(self.out) |
|||
b = other |
|||
if a == b: |
|||
return True |
|||
else: |
|||
self.explanation = a.explanation |
|||
return False |
|||
|
|||
def __str__(self): |
|||
return self.out |
|||
|
|||
def __contains__(self, item): |
|||
return item in self.out |
|||
|
|||
@property |
|||
def unordered(self): |
|||
return Unordered(self.out) |
|||
|
|||
@property |
|||
def stderr(self): |
|||
return Output(self.err) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
@pytest.fixture |
|||
def capture(capfd): |
|||
"""Extended `capfd` with context manager and custom equality operators""" |
|||
return Capture(capfd) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
class SanitizedString(object): |
|||
def __init__(self, sanitizer): |
|||
self.sanitizer = sanitizer |
|||
self.string = "" |
|||
self.explanation = [] |
|||
|
|||
def __call__(self, thing): |
|||
self.string = self.sanitizer(thing) |
|||
return self |
|||
|
|||
def __eq__(self, other): |
|||
a = self.string |
|||
b = _strip_and_dedent(other) |
|||
if a == b: |
|||
return True |
|||
else: |
|||
self.explanation = _make_explanation(a.splitlines(), b.splitlines()) |
|||
return False |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def _sanitize_general(s): |
|||
s = s.strip() |
|||
s = s.replace("pybind11_tests.", "m.") |
|||
s = s.replace("unicode", "str") |
|||
s = _long_marker.sub(r"\1", s) |
|||
s = _unicode_marker.sub(r"\1", s) |
|||
return s |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def _sanitize_docstring(thing): |
|||
s = thing.__doc__ |
|||
s = _sanitize_general(s) |
|||
return s |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
@pytest.fixture |
|||
def doc(): |
|||
"""Sanitize docstrings and add custom failure explanation""" |
|||
return SanitizedString(_sanitize_docstring) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def _sanitize_message(thing): |
|||
s = str(thing) |
|||
s = _sanitize_general(s) |
|||
s = _hexadecimal.sub("0", s) |
|||
return s |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
@pytest.fixture |
|||
def msg(): |
|||
"""Sanitize messages and add custom failure explanation""" |
|||
return SanitizedString(_sanitize_message) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
# noinspection PyUnusedLocal |
|||
def pytest_assertrepr_compare(op, left, right): |
|||
"""Hook to insert custom failure explanation""" |
|||
if hasattr(left, 'explanation'): |
|||
return left.explanation |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
@contextlib.contextmanager |
|||
def suppress(exception): |
|||
"""Suppress the desired exception""" |
|||
try: |
|||
yield |
|||
except exception: |
|||
pass |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def pytest_namespace(): |
|||
"""Add import suppression and test requirements to `pytest` namespace""" |
|||
try: |
|||
import numpy as np |
|||
except ImportError: |
|||
np = None |
|||
try: |
|||
import scipy |
|||
except ImportError: |
|||
scipy = None |
|||
try: |
|||
from pybind11_tests import have_eigen |
|||
except ImportError: |
|||
have_eigen = False |
|||
|
|||
skipif = pytest.mark.skipif |
|||
return { |
|||
'suppress': suppress, |
|||
'requires_numpy': skipif(not np, reason="numpy is not installed"), |
|||
'requires_scipy': skipif(not np, reason="scipy is not installed"), |
|||
'requires_eigen_and_numpy': skipif(not have_eigen or not np, |
|||
reason="eigen and/or numpy are not installed"), |
|||
'requires_eigen_and_scipy': skipif(not have_eigen or not scipy, |
|||
reason="eigen and/or scipy are not installed"), |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def _test_import_pybind11(): |
|||
"""Early diagnostic for test module initialization errors |
|||
|
|||
When there is an error during initialization, the first import will report the |
|||
real error while all subsequent imports will report nonsense. This import test |
|||
is done early (in the pytest configuration file, before any tests) in order to |
|||
avoid the noise of having all tests fail with identical error messages. |
|||
|
|||
Any possible exception is caught here and reported manually *without* the stack |
|||
trace. This further reduces noise since the trace would only show pytest internals |
|||
which are not useful for debugging pybind11 module issues. |
|||
""" |
|||
# noinspection PyBroadException |
|||
try: |
|||
import pybind11_tests # noqa: F401 imported but unused |
|||
except Exception as e: |
|||
print("Failed to import pybind11_tests from pytest:") |
|||
print(" {}: {}".format(type(e).__name__, e)) |
|||
sys.exit(1) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
_test_import_pybind11() |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,249 @@ |
|||
#pragma once |
|||
/* |
|||
tests/constructor_stats.h -- framework for printing and tracking object |
|||
instance lifetimes in example/test code. |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Jason Rhinelander <jason@imaginary.ca> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
|
|||
This header provides a few useful tools for writing examples or tests that want to check and/or |
|||
display object instance lifetimes. It requires that you include this header and add the following |
|||
function calls to constructors: |
|||
|
|||
class MyClass { |
|||
MyClass() { ...; print_default_created(this); } |
|||
~MyClass() { ...; print_destroyed(this); } |
|||
MyClass(const MyClass &c) { ...; print_copy_created(this); } |
|||
MyClass(MyClass &&c) { ...; print_move_created(this); } |
|||
MyClass(int a, int b) { ...; print_created(this, a, b); } |
|||
MyClass &operator=(const MyClass &c) { ...; print_copy_assigned(this); } |
|||
MyClass &operator=(MyClass &&c) { ...; print_move_assigned(this); } |
|||
|
|||
... |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
You can find various examples of these in several of the existing example .cpp files. (Of course |
|||
you don't need to add any of the above constructors/operators that you don't actually have, except |
|||
for the destructor). |
|||
|
|||
Each of these will print an appropriate message such as: |
|||
|
|||
### MyClass @ 0x2801910 created via default constructor |
|||
### MyClass @ 0x27fa780 created 100 200 |
|||
### MyClass @ 0x2801910 destroyed |
|||
### MyClass @ 0x27fa780 destroyed |
|||
|
|||
You can also include extra arguments (such as the 100, 200 in the output above, coming from the |
|||
value constructor) for all of the above methods which will be included in the output. |
|||
|
|||
For testing, each of these also keeps track the created instances and allows you to check how many |
|||
of the various constructors have been invoked from the Python side via code such as: |
|||
|
|||
from example import ConstructorStats |
|||
cstats = ConstructorStats.get(MyClass) |
|||
print(cstats.alive()) |
|||
print(cstats.default_constructions) |
|||
|
|||
Note that `.alive()` should usually be the first thing you call as it invokes Python's garbage |
|||
collector to actually destroy objects that aren't yet referenced. |
|||
|
|||
For everything except copy and move constructors and destructors, any extra values given to the |
|||
print_...() function is stored in a class-specific values list which you can retrieve and inspect |
|||
from the ConstructorStats instance `.values()` method. |
|||
|
|||
In some cases, when you need to track instances of a C++ class not registered with pybind11, you |
|||
need to add a function returning the ConstructorStats for the C++ class; this can be done with: |
|||
|
|||
m.def("get_special_cstats", &ConstructorStats::get<SpecialClass>, py::return_value_policy::reference) |
|||
|
|||
Finally, you can suppress the output messages, but keep the constructor tracking (for |
|||
inspection/testing in python) by using the functions with `print_` replaced with `track_` (e.g. |
|||
`track_copy_created(this)`). |
|||
|
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#include "pybind11_tests.h" |
|||
#include <unordered_map> |
|||
#include <list> |
|||
#include <typeindex> |
|||
#include <sstream> |
|||
|
|||
class ConstructorStats { |
|||
protected: |
|||
std::unordered_map<void*, int> _instances; // Need a map rather than set because members can shared address with parents |
|||
std::list<std::string> _values; // Used to track values (e.g. of value constructors) |
|||
public: |
|||
int default_constructions = 0; |
|||
int copy_constructions = 0; |
|||
int move_constructions = 0; |
|||
int copy_assignments = 0; |
|||
int move_assignments = 0; |
|||
|
|||
void copy_created(void *inst) { |
|||
created(inst); |
|||
copy_constructions++; |
|||
} |
|||
void move_created(void *inst) { |
|||
created(inst); |
|||
move_constructions++; |
|||
} |
|||
void default_created(void *inst) { |
|||
created(inst); |
|||
default_constructions++; |
|||
} |
|||
void created(void *inst) { |
|||
++_instances[inst]; |
|||
}; |
|||
void destroyed(void *inst) { |
|||
if (--_instances[inst] < 0) |
|||
throw std::runtime_error("cstats.destroyed() called with unknown instance; potential double-destruction or a missing cstats.created()"); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
int alive() { |
|||
// Force garbage collection to ensure any pending destructors are invoked: |
|||
py::module::import("gc").attr("collect")(); |
|||
int total = 0; |
|||
for (const auto &p : _instances) if (p.second > 0) total += p.second; |
|||
return total; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
void value() {} // Recursion terminator |
|||
// Takes one or more values, converts them to strings, then stores them. |
|||
template <typename T, typename... Tmore> void value(const T &v, Tmore &&...args) { |
|||
std::ostringstream oss; |
|||
oss << v; |
|||
_values.push_back(oss.str()); |
|||
value(std::forward<Tmore>(args)...); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Move out stored values |
|||
py::list values() { |
|||
py::list l; |
|||
for (const auto &v : _values) l.append(py::cast(v)); |
|||
_values.clear(); |
|||
return l; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Gets constructor stats from a C++ type index |
|||
static ConstructorStats& get(std::type_index type) { |
|||
static std::unordered_map<std::type_index, ConstructorStats> all_cstats; |
|||
return all_cstats[type]; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Gets constructor stats from a C++ type |
|||
template <typename T> static ConstructorStats& get() { |
|||
return get(typeid(T)); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Gets constructor stats from a Python class |
|||
static ConstructorStats& get(py::object class_) { |
|||
auto &internals = py::detail::get_internals(); |
|||
const std::type_index *t1 = nullptr, *t2 = nullptr; |
|||
try { |
|||
auto *type_info = internals.registered_types_py.at(class_.ptr()); |
|||
for (auto &p : internals.registered_types_cpp) { |
|||
if (p.second == type_info) { |
|||
if (t1) { |
|||
t2 = &p.first; |
|||
break; |
|||
} |
|||
t1 = &p.first; |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
catch (std::out_of_range) {} |
|||
if (!t1) throw std::runtime_error("Unknown class passed to ConstructorStats::get()"); |
|||
auto &cs1 = get(*t1); |
|||
// If we have both a t1 and t2 match, one is probably the trampoline class; return whichever |
|||
// has more constructions (typically one or the other will be 0) |
|||
if (t2) { |
|||
auto &cs2 = get(*t2); |
|||
int cs1_total = cs1.default_constructions + cs1.copy_constructions + cs1.move_constructions + (int) cs1._values.size(); |
|||
int cs2_total = cs2.default_constructions + cs2.copy_constructions + cs2.move_constructions + (int) cs2._values.size(); |
|||
if (cs2_total > cs1_total) return cs2; |
|||
} |
|||
return cs1; |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
// To track construction/destruction, you need to call these methods from the various |
|||
// constructors/operators. The ones that take extra values record the given values in the |
|||
// constructor stats values for later inspection. |
|||
template <class T> void track_copy_created(T *inst) { ConstructorStats::get<T>().copy_created(inst); } |
|||
template <class T> void track_move_created(T *inst) { ConstructorStats::get<T>().move_created(inst); } |
|||
template <class T, typename... Values> void track_copy_assigned(T *, Values &&...values) { |
|||
auto &cst = ConstructorStats::get<T>(); |
|||
cst.copy_assignments++; |
|||
cst.value(std::forward<Values>(values)...); |
|||
} |
|||
template <class T, typename... Values> void track_move_assigned(T *, Values &&...values) { |
|||
auto &cst = ConstructorStats::get<T>(); |
|||
cst.move_assignments++; |
|||
cst.value(std::forward<Values>(values)...); |
|||
} |
|||
template <class T, typename... Values> void track_default_created(T *inst, Values &&...values) { |
|||
auto &cst = ConstructorStats::get<T>(); |
|||
cst.default_created(inst); |
|||
cst.value(std::forward<Values>(values)...); |
|||
} |
|||
template <class T, typename... Values> void track_created(T *inst, Values &&...values) { |
|||
auto &cst = ConstructorStats::get<T>(); |
|||
cst.created(inst); |
|||
cst.value(std::forward<Values>(values)...); |
|||
} |
|||
template <class T, typename... Values> void track_destroyed(T *inst) { |
|||
ConstructorStats::get<T>().destroyed(inst); |
|||
} |
|||
template <class T, typename... Values> void track_values(T *, Values &&...values) { |
|||
ConstructorStats::get<T>().value(std::forward<Values>(values)...); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
/// Don't cast pointers to Python, print them as strings |
|||
inline const char *format_ptrs(const char *p) { return p; } |
|||
template <typename T> |
|||
py::str format_ptrs(T *p) { return "{:#x}"_s.format(reinterpret_cast<std::uintptr_t>(p)); } |
|||
template <typename T> |
|||
auto format_ptrs(T &&x) -> decltype(std::forward<T>(x)) { return std::forward<T>(x); } |
|||
|
|||
template <class T, typename... Output> |
|||
void print_constr_details(T *inst, const std::string &action, Output &&...output) { |
|||
py::print("###", py::type_id<T>(), "@", format_ptrs(inst), action, |
|||
format_ptrs(std::forward<Output>(output))...); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Verbose versions of the above: |
|||
template <class T, typename... Values> void print_copy_created(T *inst, Values &&...values) { // NB: this prints, but doesn't store, given values |
|||
print_constr_details(inst, "created via copy constructor", values...); |
|||
track_copy_created(inst); |
|||
} |
|||
template <class T, typename... Values> void print_move_created(T *inst, Values &&...values) { // NB: this prints, but doesn't store, given values |
|||
print_constr_details(inst, "created via move constructor", values...); |
|||
track_move_created(inst); |
|||
} |
|||
template <class T, typename... Values> void print_copy_assigned(T *inst, Values &&...values) { |
|||
print_constr_details(inst, "assigned via copy assignment", values...); |
|||
track_copy_assigned(inst, values...); |
|||
} |
|||
template <class T, typename... Values> void print_move_assigned(T *inst, Values &&...values) { |
|||
print_constr_details(inst, "assigned via move assignment", values...); |
|||
track_move_assigned(inst, values...); |
|||
} |
|||
template <class T, typename... Values> void print_default_created(T *inst, Values &&...values) { |
|||
print_constr_details(inst, "created via default constructor", values...); |
|||
track_default_created(inst, values...); |
|||
} |
|||
template <class T, typename... Values> void print_created(T *inst, Values &&...values) { |
|||
print_constr_details(inst, "created", values...); |
|||
track_created(inst, values...); |
|||
} |
|||
template <class T, typename... Values> void print_destroyed(T *inst, Values &&...values) { // Prints but doesn't store given values |
|||
print_constr_details(inst, "destroyed", values...); |
|||
track_destroyed(inst); |
|||
} |
|||
template <class T, typename... Values> void print_values(T *inst, Values &&...values) { |
|||
print_constr_details(inst, ":", values...); |
|||
track_values(inst, values...); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
@ -0,0 +1,175 @@ |
|||
#if !defined(__OBJECT_H) |
|||
#define __OBJECT_H |
|||
|
|||
#include <atomic> |
|||
#include "constructor_stats.h" |
|||
|
|||
/// Reference counted object base class |
|||
class Object { |
|||
public: |
|||
/// Default constructor |
|||
Object() { print_default_created(this); } |
|||
|
|||
/// Copy constructor |
|||
Object(const Object &) : m_refCount(0) { print_copy_created(this); } |
|||
|
|||
/// Return the current reference count |
|||
int getRefCount() const { return m_refCount; }; |
|||
|
|||
/// Increase the object's reference count by one |
|||
void incRef() const { ++m_refCount; } |
|||
|
|||
/** \brief Decrease the reference count of |
|||
* the object and possibly deallocate it. |
|||
* |
|||
* The object will automatically be deallocated once |
|||
* the reference count reaches zero. |
|||
*/ |
|||
void decRef(bool dealloc = true) const { |
|||
--m_refCount; |
|||
if (m_refCount == 0 && dealloc) |
|||
delete this; |
|||
else if (m_refCount < 0) |
|||
throw std::runtime_error("Internal error: reference count < 0!"); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
virtual std::string toString() const = 0; |
|||
protected: |
|||
/** \brief Virtual protected deconstructor. |
|||
* (Will only be called by \ref ref) |
|||
*/ |
|||
virtual ~Object() { print_destroyed(this); } |
|||
private: |
|||
mutable std::atomic<int> m_refCount { 0 }; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
// Tag class used to track constructions of ref objects. When we track constructors, below, we |
|||
// track and print out the actual class (e.g. ref<MyObject>), and *also* add a fake tracker for |
|||
// ref_tag. This lets us check that the total number of ref<Anything> constructors/destructors is |
|||
// correct without having to check each individual ref<Whatever> type individually. |
|||
class ref_tag {}; |
|||
|
|||
/** |
|||
* \brief Reference counting helper |
|||
* |
|||
* The \a ref refeference template is a simple wrapper to store a |
|||
* pointer to an object. It takes care of increasing and decreasing |
|||
* the reference count of the object. When the last reference goes |
|||
* out of scope, the associated object will be deallocated. |
|||
* |
|||
* \ingroup libcore |
|||
*/ |
|||
template <typename T> class ref { |
|||
public: |
|||
/// Create a nullptr reference |
|||
ref() : m_ptr(nullptr) { print_default_created(this); track_default_created((ref_tag*) this); } |
|||
|
|||
/// Construct a reference from a pointer |
|||
ref(T *ptr) : m_ptr(ptr) { |
|||
if (m_ptr) ((Object *) m_ptr)->incRef(); |
|||
|
|||
print_created(this, "from pointer", m_ptr); track_created((ref_tag*) this, "from pointer"); |
|||
|
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
/// Copy constructor |
|||
ref(const ref &r) : m_ptr(r.m_ptr) { |
|||
if (m_ptr) |
|||
((Object *) m_ptr)->incRef(); |
|||
|
|||
print_copy_created(this, "with pointer", m_ptr); track_copy_created((ref_tag*) this); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
/// Move constructor |
|||
ref(ref &&r) : m_ptr(r.m_ptr) { |
|||
r.m_ptr = nullptr; |
|||
|
|||
print_move_created(this, "with pointer", m_ptr); track_move_created((ref_tag*) this); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
/// Destroy this reference |
|||
~ref() { |
|||
if (m_ptr) |
|||
((Object *) m_ptr)->decRef(); |
|||
|
|||
print_destroyed(this); track_destroyed((ref_tag*) this); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
/// Move another reference into the current one |
|||
ref& operator=(ref&& r) { |
|||
print_move_assigned(this, "pointer", r.m_ptr); track_move_assigned((ref_tag*) this); |
|||
|
|||
if (*this == r) |
|||
return *this; |
|||
if (m_ptr) |
|||
((Object *) m_ptr)->decRef(); |
|||
m_ptr = r.m_ptr; |
|||
r.m_ptr = nullptr; |
|||
return *this; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
/// Overwrite this reference with another reference |
|||
ref& operator=(const ref& r) { |
|||
print_copy_assigned(this, "pointer", r.m_ptr); track_copy_assigned((ref_tag*) this); |
|||
|
|||
if (m_ptr == r.m_ptr) |
|||
return *this; |
|||
if (m_ptr) |
|||
((Object *) m_ptr)->decRef(); |
|||
m_ptr = r.m_ptr; |
|||
if (m_ptr) |
|||
((Object *) m_ptr)->incRef(); |
|||
return *this; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
/// Overwrite this reference with a pointer to another object |
|||
ref& operator=(T *ptr) { |
|||
print_values(this, "assigned pointer"); track_values((ref_tag*) this, "assigned pointer"); |
|||
|
|||
if (m_ptr == ptr) |
|||
return *this; |
|||
if (m_ptr) |
|||
((Object *) m_ptr)->decRef(); |
|||
m_ptr = ptr; |
|||
if (m_ptr) |
|||
((Object *) m_ptr)->incRef(); |
|||
return *this; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
/// Compare this reference with another reference |
|||
bool operator==(const ref &r) const { return m_ptr == r.m_ptr; } |
|||
|
|||
/// Compare this reference with another reference |
|||
bool operator!=(const ref &r) const { return m_ptr != r.m_ptr; } |
|||
|
|||
/// Compare this reference with a pointer |
|||
bool operator==(const T* ptr) const { return m_ptr == ptr; } |
|||
|
|||
/// Compare this reference with a pointer |
|||
bool operator!=(const T* ptr) const { return m_ptr != ptr; } |
|||
|
|||
/// Access the object referenced by this reference |
|||
T* operator->() { return m_ptr; } |
|||
|
|||
/// Access the object referenced by this reference |
|||
const T* operator->() const { return m_ptr; } |
|||
|
|||
/// Return a C++ reference to the referenced object |
|||
T& operator*() { return *m_ptr; } |
|||
|
|||
/// Return a const C++ reference to the referenced object |
|||
const T& operator*() const { return *m_ptr; } |
|||
|
|||
/// Return a pointer to the referenced object |
|||
operator T* () { return m_ptr; } |
|||
|
|||
/// Return a const pointer to the referenced object |
|||
T* get() { return m_ptr; } |
|||
|
|||
/// Return a pointer to the referenced object |
|||
const T* get() const { return m_ptr; } |
|||
private: |
|||
T *m_ptr; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
#endif /* __OBJECT_H */ |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@ |
|||
/*
|
|||
tests/pybind11_tests.cpp -- pybind example plugin |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#include "pybind11_tests.h"
|
|||
#include "constructor_stats.h"
|
|||
|
|||
std::list<std::function<void(py::module &)>> &initializers() { |
|||
static std::list<std::function<void(py::module &)>> inits; |
|||
return inits; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
test_initializer::test_initializer(std::function<void(py::module &)> initializer) { |
|||
initializers().push_back(std::move(initializer)); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
void bind_ConstructorStats(py::module &m) { |
|||
py::class_<ConstructorStats>(m, "ConstructorStats") |
|||
.def("alive", &ConstructorStats::alive) |
|||
.def("values", &ConstructorStats::values) |
|||
.def_readwrite("default_constructions", &ConstructorStats::default_constructions) |
|||
.def_readwrite("copy_assignments", &ConstructorStats::copy_assignments) |
|||
.def_readwrite("move_assignments", &ConstructorStats::move_assignments) |
|||
.def_readwrite("copy_constructions", &ConstructorStats::copy_constructions) |
|||
.def_readwrite("move_constructions", &ConstructorStats::move_constructions) |
|||
.def_static("get", (ConstructorStats &(*)(py::object)) &ConstructorStats::get, py::return_value_policy::reference_internal); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
PYBIND11_PLUGIN(pybind11_tests) { |
|||
py::module m("pybind11_tests", "pybind example plugin"); |
|||
|
|||
bind_ConstructorStats(m); |
|||
|
|||
for (const auto &initializer : initializers()) |
|||
initializer(m); |
|||
|
|||
if (!py::hasattr(m, "have_eigen")) m.attr("have_eigen") = py::cast(false); |
|||
|
|||
return m.ptr(); |
|||
} |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,12 @@ |
|||
#pragma once |
|||
#include <pybind11/pybind11.h> |
|||
#include <functional> |
|||
#include <list> |
|||
|
|||
namespace py = pybind11; |
|||
using namespace pybind11::literals; |
|||
|
|||
class test_initializer { |
|||
public: |
|||
test_initializer(std::function<void(py::module &)> initializer); |
|||
}; |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,62 @@ |
|||
/*
|
|||
tests/test_alias_initialization.cpp -- test cases and example of different trampoline |
|||
initialization modes |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch>, Jason Rhinelander <jason@imaginary.ca> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#include "pybind11_tests.h"
|
|||
|
|||
test_initializer alias_initialization([](py::module &m) { |
|||
// don't invoke Python dispatch classes by default when instantiating C++ classes that were not
|
|||
// extended on the Python side
|
|||
struct A { |
|||
virtual ~A() {} |
|||
virtual void f() { py::print("A.f()"); } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
struct PyA : A { |
|||
PyA() { py::print("PyA.PyA()"); } |
|||
~PyA() { py::print("PyA.~PyA()"); } |
|||
|
|||
void f() override { |
|||
py::print("PyA.f()"); |
|||
PYBIND11_OVERLOAD(void, A, f); |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
auto call_f = [](A *a) { a->f(); }; |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<A, PyA>(m, "A") |
|||
.def(py::init<>()) |
|||
.def("f", &A::f); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("call_f", call_f); |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
// ... unless we explicitly request it, as in this example:
|
|||
struct A2 { |
|||
virtual ~A2() {} |
|||
virtual void f() { py::print("A2.f()"); } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
struct PyA2 : A2 { |
|||
PyA2() { py::print("PyA2.PyA2()"); } |
|||
~PyA2() { py::print("PyA2.~PyA2()"); } |
|||
void f() override { |
|||
py::print("PyA2.f()"); |
|||
PYBIND11_OVERLOAD(void, A2, f); |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<A2, PyA2>(m, "A2") |
|||
.def(py::init_alias<>()) |
|||
.def("f", &A2::f); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("call_f", [](A2 *a2) { a2->f(); }); |
|||
|
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
@ -0,0 +1,79 @@ |
|||
import gc |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_alias_delay_initialization1(capture): |
|||
"""A only initializes its trampoline class when we inherit from it; if we just |
|||
create and use an A instance directly, the trampoline initialization is bypassed |
|||
and we only initialize an A() instead (for performance reasons). |
|||
""" |
|||
from pybind11_tests import A, call_f |
|||
|
|||
class B(A): |
|||
def __init__(self): |
|||
super(B, self).__init__() |
|||
|
|||
def f(self): |
|||
print("In python f()") |
|||
|
|||
# C++ version |
|||
with capture: |
|||
a = A() |
|||
call_f(a) |
|||
del a |
|||
gc.collect() |
|||
assert capture == "A.f()" |
|||
|
|||
# Python version |
|||
with capture: |
|||
b = B() |
|||
call_f(b) |
|||
del b |
|||
gc.collect() |
|||
assert capture == """ |
|||
PyA.PyA() |
|||
PyA.f() |
|||
In python f() |
|||
PyA.~PyA() |
|||
""" |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_alias_delay_initialization2(capture): |
|||
"""A2, unlike the above, is configured to always initialize the alias; while |
|||
the extra initialization and extra class layer has small virtual dispatch |
|||
performance penalty, it also allows us to do more things with the trampoline |
|||
class such as defining local variables and performing construction/destruction. |
|||
""" |
|||
from pybind11_tests import A2, call_f |
|||
|
|||
class B2(A2): |
|||
def __init__(self): |
|||
super(B2, self).__init__() |
|||
|
|||
def f(self): |
|||
print("In python B2.f()") |
|||
|
|||
# No python subclass version |
|||
with capture: |
|||
a2 = A2() |
|||
call_f(a2) |
|||
del a2 |
|||
gc.collect() |
|||
assert capture == """ |
|||
PyA2.PyA2() |
|||
PyA2.f() |
|||
A2.f() |
|||
PyA2.~PyA2() |
|||
""" |
|||
|
|||
# Python subclass version |
|||
with capture: |
|||
b2 = B2() |
|||
call_f(b2) |
|||
del b2 |
|||
gc.collect() |
|||
assert capture == """ |
|||
PyA2.PyA2() |
|||
PyA2.f() |
|||
In python B2.f() |
|||
PyA2.~PyA2() |
|||
""" |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,117 @@ |
|||
/*
|
|||
tests/test_buffers.cpp -- supporting Pythons' buffer protocol |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#include "pybind11_tests.h"
|
|||
#include "constructor_stats.h"
|
|||
|
|||
class Matrix { |
|||
public: |
|||
Matrix(size_t rows, size_t cols) : m_rows(rows), m_cols(cols) { |
|||
print_created(this, std::to_string(m_rows) + "x" + std::to_string(m_cols) + " matrix"); |
|||
m_data = new float[rows*cols]; |
|||
memset(m_data, 0, sizeof(float) * rows * cols); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
Matrix(const Matrix &s) : m_rows(s.m_rows), m_cols(s.m_cols) { |
|||
print_copy_created(this, std::to_string(m_rows) + "x" + std::to_string(m_cols) + " matrix"); |
|||
m_data = new float[m_rows * m_cols]; |
|||
memcpy(m_data, s.m_data, sizeof(float) * m_rows * m_cols); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
Matrix(Matrix &&s) : m_rows(s.m_rows), m_cols(s.m_cols), m_data(s.m_data) { |
|||
print_move_created(this); |
|||
s.m_rows = 0; |
|||
s.m_cols = 0; |
|||
s.m_data = nullptr; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
~Matrix() { |
|||
print_destroyed(this, std::to_string(m_rows) + "x" + std::to_string(m_cols) + " matrix"); |
|||
delete[] m_data; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
Matrix &operator=(const Matrix &s) { |
|||
print_copy_assigned(this, std::to_string(m_rows) + "x" + std::to_string(m_cols) + " matrix"); |
|||
delete[] m_data; |
|||
m_rows = s.m_rows; |
|||
m_cols = s.m_cols; |
|||
m_data = new float[m_rows * m_cols]; |
|||
memcpy(m_data, s.m_data, sizeof(float) * m_rows * m_cols); |
|||
return *this; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
Matrix &operator=(Matrix &&s) { |
|||
print_move_assigned(this, std::to_string(m_rows) + "x" + std::to_string(m_cols) + " matrix"); |
|||
if (&s != this) { |
|||
delete[] m_data; |
|||
m_rows = s.m_rows; m_cols = s.m_cols; m_data = s.m_data; |
|||
s.m_rows = 0; s.m_cols = 0; s.m_data = nullptr; |
|||
} |
|||
return *this; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
float operator()(size_t i, size_t j) const { |
|||
return m_data[i*m_cols + j]; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
float &operator()(size_t i, size_t j) { |
|||
return m_data[i*m_cols + j]; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
float *data() { return m_data; } |
|||
|
|||
size_t rows() const { return m_rows; } |
|||
size_t cols() const { return m_cols; } |
|||
private: |
|||
size_t m_rows; |
|||
size_t m_cols; |
|||
float *m_data; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
test_initializer buffers([](py::module &m) { |
|||
py::class_<Matrix> mtx(m, "Matrix"); |
|||
|
|||
mtx.def(py::init<size_t, size_t>()) |
|||
/// Construct from a buffer
|
|||
.def("__init__", [](Matrix &v, py::buffer b) { |
|||
py::buffer_info info = b.request(); |
|||
if (info.format != py::format_descriptor<float>::format() || info.ndim != 2) |
|||
throw std::runtime_error("Incompatible buffer format!"); |
|||
new (&v) Matrix(info.shape[0], info.shape[1]); |
|||
memcpy(v.data(), info.ptr, sizeof(float) * v.rows() * v.cols()); |
|||
}) |
|||
|
|||
.def("rows", &Matrix::rows) |
|||
.def("cols", &Matrix::cols) |
|||
|
|||
/// Bare bones interface
|
|||
.def("__getitem__", [](const Matrix &m, std::pair<size_t, size_t> i) { |
|||
if (i.first >= m.rows() || i.second >= m.cols()) |
|||
throw py::index_error(); |
|||
return m(i.first, i.second); |
|||
}) |
|||
.def("__setitem__", [](Matrix &m, std::pair<size_t, size_t> i, float v) { |
|||
if (i.first >= m.rows() || i.second >= m.cols()) |
|||
throw py::index_error(); |
|||
m(i.first, i.second) = v; |
|||
}) |
|||
/// Provide buffer access
|
|||
.def_buffer([](Matrix &m) -> py::buffer_info { |
|||
return py::buffer_info( |
|||
m.data(), /* Pointer to buffer */ |
|||
sizeof(float), /* Size of one scalar */ |
|||
py::format_descriptor<float>::format(), /* Python struct-style format descriptor */ |
|||
2, /* Number of dimensions */ |
|||
{ m.rows(), m.cols() }, /* Buffer dimensions */ |
|||
{ sizeof(float) * m.rows(), /* Strides (in bytes) for each index */ |
|||
sizeof(float) } |
|||
); |
|||
}) |
|||
; |
|||
}); |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,57 @@ |
|||
import pytest |
|||
from pybind11_tests import Matrix, ConstructorStats |
|||
|
|||
with pytest.suppress(ImportError): |
|||
import numpy as np |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
@pytest.requires_numpy |
|||
def test_to_python(): |
|||
m = Matrix(5, 5) |
|||
|
|||
assert m[2, 3] == 0 |
|||
m[2, 3] = 4 |
|||
assert m[2, 3] == 4 |
|||
|
|||
m2 = np.array(m, copy=False) |
|||
assert m2.shape == (5, 5) |
|||
assert abs(m2).sum() == 4 |
|||
assert m2[2, 3] == 4 |
|||
m2[2, 3] = 5 |
|||
assert m2[2, 3] == 5 |
|||
|
|||
cstats = ConstructorStats.get(Matrix) |
|||
assert cstats.alive() == 1 |
|||
del m |
|||
assert cstats.alive() == 1 |
|||
del m2 # holds an m reference |
|||
assert cstats.alive() == 0 |
|||
assert cstats.values() == ["5x5 matrix"] |
|||
assert cstats.copy_constructions == 0 |
|||
# assert cstats.move_constructions >= 0 # Don't invoke any |
|||
assert cstats.copy_assignments == 0 |
|||
assert cstats.move_assignments == 0 |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
@pytest.requires_numpy |
|||
def test_from_python(): |
|||
with pytest.raises(RuntimeError) as excinfo: |
|||
Matrix(np.array([1, 2, 3])) # trying to assign a 1D array |
|||
assert str(excinfo.value) == "Incompatible buffer format!" |
|||
|
|||
m3 = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]).astype(np.float32) |
|||
m4 = Matrix(m3) |
|||
|
|||
for i in range(m4.rows()): |
|||
for j in range(m4.cols()): |
|||
assert m3[i, j] == m4[i, j] |
|||
|
|||
cstats = ConstructorStats.get(Matrix) |
|||
assert cstats.alive() == 1 |
|||
del m3, m4 |
|||
assert cstats.alive() == 0 |
|||
assert cstats.values() == ["2x3 matrix"] |
|||
assert cstats.copy_constructions == 0 |
|||
# assert cstats.move_constructions >= 0 # Don't invoke any |
|||
assert cstats.copy_assignments == 0 |
|||
assert cstats.move_assignments == 0 |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,149 @@ |
|||
/*
|
|||
tests/test_callbacks.cpp -- callbacks |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#include "pybind11_tests.h"
|
|||
#include "constructor_stats.h"
|
|||
#include <pybind11/functional.h>
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
py::object test_callback1(py::object func) { |
|||
return func(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
py::tuple test_callback2(py::object func) { |
|||
return func("Hello", 'x', true, 5); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
std::string test_callback3(const std::function<int(int)> &func) { |
|||
return "func(43) = " + std::to_string(func(43)); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
std::function<int(int)> test_callback4() { |
|||
return [](int i) { return i+1; }; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
py::cpp_function test_callback5() { |
|||
return py::cpp_function([](int i) { return i+1; }, |
|||
py::arg("number")); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
int dummy_function(int i) { return i + 1; } |
|||
int dummy_function2(int i, int j) { return i + j; } |
|||
std::function<int(int)> roundtrip(std::function<int(int)> f, bool expect_none = false) { |
|||
if (expect_none && f) { |
|||
throw std::runtime_error("Expected None to be converted to empty std::function"); |
|||
} |
|||
return f; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
std::string test_dummy_function(const std::function<int(int)> &f) { |
|||
using fn_type = int (*)(int); |
|||
auto result = f.target<fn_type>(); |
|||
if (!result) { |
|||
auto r = f(1); |
|||
return "can't convert to function pointer: eval(1) = " + std::to_string(r); |
|||
} else if (*result == dummy_function) { |
|||
auto r = (*result)(1); |
|||
return "matches dummy_function: eval(1) = " + std::to_string(r); |
|||
} else { |
|||
return "argument does NOT match dummy_function. This should never happen!"; |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
struct Payload { |
|||
Payload() { |
|||
print_default_created(this); |
|||
} |
|||
~Payload() { |
|||
print_destroyed(this); |
|||
} |
|||
Payload(const Payload &) { |
|||
print_copy_created(this); |
|||
} |
|||
Payload(Payload &&) { |
|||
print_move_created(this); |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
/// Something to trigger a conversion error
|
|||
struct Unregistered {}; |
|||
|
|||
test_initializer callbacks([](py::module &m) { |
|||
m.def("test_callback1", &test_callback1); |
|||
m.def("test_callback2", &test_callback2); |
|||
m.def("test_callback3", &test_callback3); |
|||
m.def("test_callback4", &test_callback4); |
|||
m.def("test_callback5", &test_callback5); |
|||
|
|||
// Test keyword args and generalized unpacking
|
|||
m.def("test_tuple_unpacking", [](py::function f) { |
|||
auto t1 = py::make_tuple(2, 3); |
|||
auto t2 = py::make_tuple(5, 6); |
|||
return f("positional", 1, *t1, 4, *t2); |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("test_dict_unpacking", [](py::function f) { |
|||
auto d1 = py::dict("key"_a="value", "a"_a=1); |
|||
auto d2 = py::dict(); |
|||
auto d3 = py::dict("b"_a=2); |
|||
return f("positional", 1, **d1, **d2, **d3); |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("test_keyword_args", [](py::function f) { |
|||
return f("x"_a=10, "y"_a=20); |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("test_unpacking_and_keywords1", [](py::function f) { |
|||
auto args = py::make_tuple(2); |
|||
auto kwargs = py::dict("d"_a=4); |
|||
return f(1, *args, "c"_a=3, **kwargs); |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("test_unpacking_and_keywords2", [](py::function f) { |
|||
auto kwargs1 = py::dict("a"_a=1); |
|||
auto kwargs2 = py::dict("c"_a=3, "d"_a=4); |
|||
return f("positional", *py::make_tuple(1), 2, *py::make_tuple(3, 4), 5, |
|||
"key"_a="value", **kwargs1, "b"_a=2, **kwargs2, "e"_a=5); |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("test_unpacking_error1", [](py::function f) { |
|||
auto kwargs = py::dict("x"_a=3); |
|||
return f("x"_a=1, "y"_a=2, **kwargs); // duplicate ** after keyword
|
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("test_unpacking_error2", [](py::function f) { |
|||
auto kwargs = py::dict("x"_a=3); |
|||
return f(**kwargs, "x"_a=1); // duplicate keyword after **
|
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("test_arg_conversion_error1", [](py::function f) { |
|||
f(234, Unregistered(), "kw"_a=567); |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("test_arg_conversion_error2", [](py::function f) { |
|||
f(234, "expected_name"_a=Unregistered(), "kw"_a=567); |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
/* Test cleanup of lambda closure */ |
|||
m.def("test_cleanup", []() -> std::function<void(void)> { |
|||
Payload p; |
|||
|
|||
return [p]() { |
|||
/* p should be cleaned up when the returned function is garbage collected */ |
|||
}; |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
/* Test if passing a function pointer from C++ -> Python -> C++ yields the original pointer */ |
|||
m.def("dummy_function", &dummy_function); |
|||
m.def("dummy_function2", &dummy_function2); |
|||
m.def("roundtrip", &roundtrip, py::arg("f"), py::arg("expect_none")=false); |
|||
m.def("test_dummy_function", &test_dummy_function); |
|||
// Export the payload constructor statistics for testing purposes:
|
|||
m.def("payload_cstats", &ConstructorStats::get<Payload>); |
|||
}); |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,98 @@ |
|||
import pytest |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_callbacks(): |
|||
from functools import partial |
|||
from pybind11_tests import (test_callback1, test_callback2, test_callback3, |
|||
test_callback4, test_callback5) |
|||
|
|||
def func1(): |
|||
return "func1" |
|||
|
|||
def func2(a, b, c, d): |
|||
return "func2", a, b, c, d |
|||
|
|||
def func3(a): |
|||
return "func3({})".format(a) |
|||
|
|||
assert test_callback1(func1) == "func1" |
|||
assert test_callback2(func2) == ("func2", "Hello", "x", True, 5) |
|||
assert test_callback1(partial(func2, 1, 2, 3, 4)) == ("func2", 1, 2, 3, 4) |
|||
assert test_callback1(partial(func3, "partial")) == "func3(partial)" |
|||
assert test_callback3(lambda i: i + 1) == "func(43) = 44" |
|||
|
|||
f = test_callback4() |
|||
assert f(43) == 44 |
|||
f = test_callback5() |
|||
assert f(number=43) == 44 |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_keyword_args_and_generalized_unpacking(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import (test_tuple_unpacking, test_dict_unpacking, test_keyword_args, |
|||
test_unpacking_and_keywords1, test_unpacking_and_keywords2, |
|||
test_unpacking_error1, test_unpacking_error2, |
|||
test_arg_conversion_error1, test_arg_conversion_error2) |
|||
|
|||
def f(*args, **kwargs): |
|||
return args, kwargs |
|||
|
|||
assert test_tuple_unpacking(f) == (("positional", 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6), {}) |
|||
assert test_dict_unpacking(f) == (("positional", 1), {"key": "value", "a": 1, "b": 2}) |
|||
assert test_keyword_args(f) == ((), {"x": 10, "y": 20}) |
|||
assert test_unpacking_and_keywords1(f) == ((1, 2), {"c": 3, "d": 4}) |
|||
assert test_unpacking_and_keywords2(f) == ( |
|||
("positional", 1, 2, 3, 4, 5), |
|||
{"key": "value", "a": 1, "b": 2, "c": 3, "d": 4, "e": 5} |
|||
) |
|||
|
|||
with pytest.raises(TypeError) as excinfo: |
|||
test_unpacking_error1(f) |
|||
assert "Got multiple values for keyword argument" in str(excinfo.value) |
|||
|
|||
with pytest.raises(TypeError) as excinfo: |
|||
test_unpacking_error2(f) |
|||
assert "Got multiple values for keyword argument" in str(excinfo.value) |
|||
|
|||
with pytest.raises(RuntimeError) as excinfo: |
|||
test_arg_conversion_error1(f) |
|||
assert "Unable to convert call argument" in str(excinfo.value) |
|||
|
|||
with pytest.raises(RuntimeError) as excinfo: |
|||
test_arg_conversion_error2(f) |
|||
assert "Unable to convert call argument" in str(excinfo.value) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_lambda_closure_cleanup(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import test_cleanup, payload_cstats |
|||
|
|||
test_cleanup() |
|||
cstats = payload_cstats() |
|||
assert cstats.alive() == 0 |
|||
assert cstats.copy_constructions == 1 |
|||
assert cstats.move_constructions >= 1 |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_cpp_function_roundtrip(): |
|||
"""Test if passing a function pointer from C++ -> Python -> C++ yields the original pointer""" |
|||
from pybind11_tests import dummy_function, dummy_function2, test_dummy_function, roundtrip |
|||
|
|||
assert test_dummy_function(dummy_function) == "matches dummy_function: eval(1) = 2" |
|||
assert test_dummy_function(roundtrip(dummy_function)) == "matches dummy_function: eval(1) = 2" |
|||
assert roundtrip(None, expect_none=True) is None |
|||
assert test_dummy_function(lambda x: x + 2) == "can't convert to function pointer: eval(1) = 3" |
|||
|
|||
with pytest.raises(TypeError) as excinfo: |
|||
test_dummy_function(dummy_function2) |
|||
assert "incompatible function arguments" in str(excinfo.value) |
|||
|
|||
with pytest.raises(TypeError) as excinfo: |
|||
test_dummy_function(lambda x, y: x + y) |
|||
assert any(s in str(excinfo.value) for s in ("missing 1 required positional argument", |
|||
"takes exactly 2 arguments")) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_function_signatures(doc): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import test_callback3, test_callback4 |
|||
|
|||
assert doc(test_callback3) == "test_callback3(arg0: Callable[[int], int]) -> str" |
|||
assert doc(test_callback4) == "test_callback4() -> Callable[[int], int]" |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,59 @@ |
|||
/*
|
|||
tests/test_chrono.cpp -- test conversions to/from std::chrono types |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Trent Houliston <trent@houliston.me> and |
|||
Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
#include "pybind11_tests.h"
|
|||
#include "constructor_stats.h"
|
|||
#include <pybind11/chrono.h>
|
|||
|
|||
// Return the current time off the wall clock
|
|||
std::chrono::system_clock::time_point test_chrono1() { |
|||
return std::chrono::system_clock::now(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Round trip the passed in system clock time
|
|||
std::chrono::system_clock::time_point test_chrono2(std::chrono::system_clock::time_point t) { |
|||
return t; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Round trip the passed in duration
|
|||
std::chrono::system_clock::duration test_chrono3(std::chrono::system_clock::duration d) { |
|||
return d; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Difference between two passed in time_points
|
|||
std::chrono::system_clock::duration test_chrono4(std::chrono::system_clock::time_point a, std::chrono::system_clock::time_point b) { |
|||
return a - b; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Return the current time off the steady_clock
|
|||
std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point test_chrono5() { |
|||
return std::chrono::steady_clock::now(); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Round trip a steady clock timepoint
|
|||
std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point test_chrono6(std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point t) { |
|||
return t; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
// Roundtrip a duration in microseconds from a float argument
|
|||
std::chrono::microseconds test_chrono7(std::chrono::microseconds t) { |
|||
return t; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
test_initializer chrono([] (py::module &m) { |
|||
m.def("test_chrono1", &test_chrono1); |
|||
m.def("test_chrono2", &test_chrono2); |
|||
m.def("test_chrono3", &test_chrono3); |
|||
m.def("test_chrono4", &test_chrono4); |
|||
m.def("test_chrono5", &test_chrono5); |
|||
m.def("test_chrono6", &test_chrono6); |
|||
m.def("test_chrono7", &test_chrono7); |
|||
}); |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,116 @@ |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_chrono_system_clock(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import test_chrono1 |
|||
import datetime |
|||
|
|||
# Get the time from both c++ and datetime |
|||
date1 = test_chrono1() |
|||
date2 = datetime.datetime.today() |
|||
|
|||
# The returned value should be a datetime |
|||
assert isinstance(date1, datetime.datetime) |
|||
|
|||
# The numbers should vary by a very small amount (time it took to execute) |
|||
diff = abs(date1 - date2) |
|||
|
|||
# There should never be a days/seconds difference |
|||
assert diff.days == 0 |
|||
assert diff.seconds == 0 |
|||
|
|||
# We test that no more than about 0.5 seconds passes here |
|||
# This makes sure that the dates created are very close to the same |
|||
# but if the testing system is incredibly overloaded this should still pass |
|||
assert diff.microseconds < 500000 |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_chrono_system_clock_roundtrip(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import test_chrono2 |
|||
import datetime |
|||
|
|||
date1 = datetime.datetime.today() |
|||
|
|||
# Roundtrip the time |
|||
date2 = test_chrono2(date1) |
|||
|
|||
# The returned value should be a datetime |
|||
assert isinstance(date2, datetime.datetime) |
|||
|
|||
# They should be identical (no information lost on roundtrip) |
|||
diff = abs(date1 - date2) |
|||
assert diff.days == 0 |
|||
assert diff.seconds == 0 |
|||
assert diff.microseconds == 0 |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_chrono_duration_roundtrip(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import test_chrono3 |
|||
import datetime |
|||
|
|||
# Get the difference between two times (a timedelta) |
|||
date1 = datetime.datetime.today() |
|||
date2 = datetime.datetime.today() |
|||
diff = date2 - date1 |
|||
|
|||
# Make sure this is a timedelta |
|||
assert isinstance(diff, datetime.timedelta) |
|||
|
|||
cpp_diff = test_chrono3(diff) |
|||
|
|||
assert cpp_diff.days == diff.days |
|||
assert cpp_diff.seconds == diff.seconds |
|||
assert cpp_diff.microseconds == diff.microseconds |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_chrono_duration_subtraction_equivalence(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import test_chrono4 |
|||
import datetime |
|||
|
|||
date1 = datetime.datetime.today() |
|||
date2 = datetime.datetime.today() |
|||
|
|||
diff = date2 - date1 |
|||
cpp_diff = test_chrono4(date2, date1) |
|||
|
|||
assert cpp_diff.days == diff.days |
|||
assert cpp_diff.seconds == diff.seconds |
|||
assert cpp_diff.microseconds == diff.microseconds |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_chrono_steady_clock(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import test_chrono5 |
|||
import datetime |
|||
|
|||
time1 = test_chrono5() |
|||
time2 = test_chrono5() |
|||
|
|||
assert isinstance(time1, datetime.timedelta) |
|||
assert isinstance(time2, datetime.timedelta) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_chrono_steady_clock_roundtrip(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import test_chrono6 |
|||
import datetime |
|||
|
|||
time1 = datetime.timedelta(days=10, seconds=10, microseconds=100) |
|||
time2 = test_chrono6(time1) |
|||
|
|||
assert isinstance(time2, datetime.timedelta) |
|||
|
|||
# They should be identical (no information lost on roundtrip) |
|||
assert time1.days == time2.days |
|||
assert time1.seconds == time2.seconds |
|||
assert time1.microseconds == time2.microseconds |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_floating_point_duration(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import test_chrono7 |
|||
import datetime |
|||
|
|||
# Test using 35.525123 seconds as an example floating point number in seconds |
|||
time = test_chrono7(35.525123) |
|||
|
|||
assert isinstance(time, datetime.timedelta) |
|||
|
|||
assert time.seconds == 35 |
|||
assert 525122 <= time.microseconds <= 525123 |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,68 @@ |
|||
/*
|
|||
tests/test_class_args.cpp -- tests that various way of defining a class work |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#include "pybind11_tests.h"
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
template <int N> class BreaksBase {}; |
|||
template <int N> class BreaksTramp : public BreaksBase<N> {}; |
|||
// These should all compile just fine:
|
|||
typedef py::class_<BreaksBase<1>, std::unique_ptr<BreaksBase<1>>, BreaksTramp<1>> DoesntBreak1; |
|||
typedef py::class_<BreaksBase<2>, BreaksTramp<2>, std::unique_ptr<BreaksBase<2>>> DoesntBreak2; |
|||
typedef py::class_<BreaksBase<3>, std::unique_ptr<BreaksBase<3>>> DoesntBreak3; |
|||
typedef py::class_<BreaksBase<4>, BreaksTramp<4>> DoesntBreak4; |
|||
typedef py::class_<BreaksBase<5>> DoesntBreak5; |
|||
typedef py::class_<BreaksBase<6>, std::shared_ptr<BreaksBase<6>>, BreaksTramp<6>> DoesntBreak6; |
|||
typedef py::class_<BreaksBase<7>, BreaksTramp<7>, std::shared_ptr<BreaksBase<7>>> DoesntBreak7; |
|||
typedef py::class_<BreaksBase<8>, std::shared_ptr<BreaksBase<8>>> DoesntBreak8; |
|||
#define CHECK_BASE(N) static_assert(std::is_same<typename DoesntBreak##N::type, BreaksBase<N>>::value, \
|
|||
"DoesntBreak" #N " has wrong type!") |
|||
CHECK_BASE(1); CHECK_BASE(2); CHECK_BASE(3); CHECK_BASE(4); CHECK_BASE(5); CHECK_BASE(6); CHECK_BASE(7); CHECK_BASE(8); |
|||
#define CHECK_ALIAS(N) static_assert(DoesntBreak##N::has_alias && std::is_same<typename DoesntBreak##N::type_alias, BreaksTramp<N>>::value, \
|
|||
"DoesntBreak" #N " has wrong type_alias!") |
|||
#define CHECK_NOALIAS(N) static_assert(!DoesntBreak##N::has_alias && std::is_void<typename DoesntBreak##N::type_alias>::value, \
|
|||
"DoesntBreak" #N " has type alias, but shouldn't!") |
|||
CHECK_ALIAS(1); CHECK_ALIAS(2); CHECK_NOALIAS(3); CHECK_ALIAS(4); CHECK_NOALIAS(5); CHECK_ALIAS(6); CHECK_ALIAS(7); CHECK_NOALIAS(8); |
|||
#define CHECK_HOLDER(N, TYPE) static_assert(std::is_same<typename DoesntBreak##N::holder_type, std::TYPE##_ptr<BreaksBase<N>>>::value, \
|
|||
"DoesntBreak" #N " has wrong holder_type!") |
|||
CHECK_HOLDER(1, unique); CHECK_HOLDER(2, unique); CHECK_HOLDER(3, unique); CHECK_HOLDER(4, unique); CHECK_HOLDER(5, unique); |
|||
CHECK_HOLDER(6, shared); CHECK_HOLDER(7, shared); CHECK_HOLDER(8, shared); |
|||
|
|||
// There's no nice way to test that these fail because they fail to compile; leave them here,
|
|||
// though, so that they can be manually tested by uncommenting them (and seeing that compilation
|
|||
// failures occurs).
|
|||
|
|||
// We have to actually look into the type: the typedef alone isn't enough to instantiate the type:
|
|||
#define CHECK_BROKEN(N) static_assert(std::is_same<typename Breaks##N::type, BreaksBase<-N>>::value, \
|
|||
"Breaks1 has wrong type!"); |
|||
|
|||
//// Two holder classes:
|
|||
//typedef py::class_<BreaksBase<-1>, std::unique_ptr<BreaksBase<-1>>, std::unique_ptr<BreaksBase<-1>>> Breaks1;
|
|||
//CHECK_BROKEN(1);
|
|||
//// Two aliases:
|
|||
//typedef py::class_<BreaksBase<-2>, BreaksTramp<-2>, BreaksTramp<-2>> Breaks2;
|
|||
//CHECK_BROKEN(2);
|
|||
//// Holder + 2 aliases
|
|||
//typedef py::class_<BreaksBase<-3>, std::unique_ptr<BreaksBase<-3>>, BreaksTramp<-3>, BreaksTramp<-3>> Breaks3;
|
|||
//CHECK_BROKEN(3);
|
|||
//// Alias + 2 holders
|
|||
//typedef py::class_<BreaksBase<-4>, std::unique_ptr<BreaksBase<-4>>, BreaksTramp<-4>, std::shared_ptr<BreaksBase<-4>>> Breaks4;
|
|||
//CHECK_BROKEN(4);
|
|||
//// Invalid option (not a subclass or holder)
|
|||
//typedef py::class_<BreaksBase<-5>, BreaksTramp<-4>> Breaks5;
|
|||
//CHECK_BROKEN(5);
|
|||
//// Invalid option: multiple inheritance not supported:
|
|||
//template <> struct BreaksBase<-8> : BreaksBase<-6>, BreaksBase<-7> {};
|
|||
//typedef py::class_<BreaksBase<-8>, BreaksBase<-6>, BreaksBase<-7>> Breaks8;
|
|||
//CHECK_BROKEN(8);
|
|||
|
|||
test_initializer class_args([](py::module &m) { |
|||
// Just test that this compiled okay
|
|||
m.def("class_args_noop", []() {}); |
|||
}); |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,6 @@ |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_class_args(): |
|||
# There's basically nothing to test here; just make sure the code compiled and declared its definition |
|||
from pybind11_tests import class_args_noop |
|||
class_args_noop() |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,55 @@ |
|||
/*
|
|||
tests/test_constants_and_functions.cpp -- global constants and functions, enumerations, raw byte strings |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#include "pybind11_tests.h"
|
|||
|
|||
enum MyEnum { EFirstEntry = 1, ESecondEntry }; |
|||
|
|||
std::string test_function1() { |
|||
return "test_function()"; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
std::string test_function2(MyEnum k) { |
|||
return "test_function(enum=" + std::to_string(k) + ")"; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
std::string test_function3(int i) { |
|||
return "test_function(" + std::to_string(i) + ")"; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
py::bytes return_bytes() { |
|||
const char *data = "\x01\x00\x02\x00"; |
|||
return std::string(data, 4); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
std::string print_bytes(py::bytes bytes) { |
|||
std::string ret = "bytes["; |
|||
const auto value = static_cast<std::string>(bytes); |
|||
for (size_t i = 0; i < value.length(); ++i) { |
|||
ret += std::to_string(static_cast<int>(value[i])) + " "; |
|||
} |
|||
ret.back() = ']'; |
|||
return ret; |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
test_initializer constants_and_functions([](py::module &m) { |
|||
m.attr("some_constant") = py::int_(14); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("test_function", &test_function1); |
|||
m.def("test_function", &test_function2); |
|||
m.def("test_function", &test_function3); |
|||
|
|||
py::enum_<MyEnum>(m, "MyEnum") |
|||
.value("EFirstEntry", EFirstEntry) |
|||
.value("ESecondEntry", ESecondEntry) |
|||
.export_values(); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("return_bytes", &return_bytes); |
|||
m.def("print_bytes", &print_bytes); |
|||
}); |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@ |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_constants(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import some_constant |
|||
|
|||
assert some_constant == 14 |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_function_overloading(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import MyEnum, test_function |
|||
|
|||
assert test_function() == "test_function()" |
|||
assert test_function(7) == "test_function(7)" |
|||
assert test_function(MyEnum.EFirstEntry) == "test_function(enum=1)" |
|||
assert test_function(MyEnum.ESecondEntry) == "test_function(enum=2)" |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_bytes(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import return_bytes, print_bytes |
|||
|
|||
assert print_bytes(return_bytes()) == "bytes[1 0 2 0]" |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@ |
|||
/*
|
|||
tests/test_copy_move_policies.cpp -- 'copy' and 'move' |
|||
return value policies |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Ben North <ben@redfrontdoor.org> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#include "pybind11_tests.h"
|
|||
|
|||
template <typename derived> |
|||
struct empty { |
|||
static const derived& get_one() { return instance_; } |
|||
static derived instance_; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
struct lacking_copy_ctor : public empty<lacking_copy_ctor> { |
|||
lacking_copy_ctor() {} |
|||
lacking_copy_ctor(const lacking_copy_ctor& other) = delete; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
template <> lacking_copy_ctor empty<lacking_copy_ctor>::instance_ = {}; |
|||
|
|||
struct lacking_move_ctor : public empty<lacking_move_ctor> { |
|||
lacking_move_ctor() {} |
|||
lacking_move_ctor(const lacking_move_ctor& other) = delete; |
|||
lacking_move_ctor(lacking_move_ctor&& other) = delete; |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
template <> lacking_move_ctor empty<lacking_move_ctor>::instance_ = {}; |
|||
|
|||
test_initializer copy_move_policies([](py::module &m) { |
|||
py::class_<lacking_copy_ctor>(m, "lacking_copy_ctor") |
|||
.def_static("get_one", &lacking_copy_ctor::get_one, |
|||
py::return_value_policy::copy); |
|||
py::class_<lacking_move_ctor>(m, "lacking_move_ctor") |
|||
.def_static("get_one", &lacking_move_ctor::get_one, |
|||
py::return_value_policy::move); |
|||
}); |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@ |
|||
import pytest |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_lacking_copy_ctor(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import lacking_copy_ctor |
|||
with pytest.raises(RuntimeError) as excinfo: |
|||
lacking_copy_ctor.get_one() |
|||
assert "the object is non-copyable!" in str(excinfo.value) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_lacking_move_ctor(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import lacking_move_ctor |
|||
with pytest.raises(RuntimeError) as excinfo: |
|||
lacking_move_ctor.get_one() |
|||
assert "the object is neither movable nor copyable!" in str(excinfo.value) |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,53 @@ |
|||
/*
|
|||
tests/test_docstring_options.cpp -- generation of docstrings and signatures |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#include "pybind11_tests.h"
|
|||
|
|||
struct DocstringTestFoo { |
|||
int value; |
|||
void setValue(int v) { value = v; } |
|||
int getValue() const { return value; } |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
test_initializer docstring_generation([](py::module &m) { |
|||
|
|||
{ |
|||
py::options options; |
|||
options.disable_function_signatures(); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("test_function1", [](int, int) {}, py::arg("a"), py::arg("b")); |
|||
m.def("test_function2", [](int, int) {}, py::arg("a"), py::arg("b"), "A custom docstring"); |
|||
|
|||
options.enable_function_signatures(); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("test_function3", [](int, int) {}, py::arg("a"), py::arg("b")); |
|||
m.def("test_function4", [](int, int) {}, py::arg("a"), py::arg("b"), "A custom docstring"); |
|||
|
|||
options.disable_function_signatures().disable_user_defined_docstrings(); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("test_function5", [](int, int) {}, py::arg("a"), py::arg("b"), "A custom docstring"); |
|||
|
|||
{ |
|||
py::options nested_options; |
|||
nested_options.enable_user_defined_docstrings(); |
|||
m.def("test_function6", [](int, int) {}, py::arg("a"), py::arg("b"), "A custom docstring"); |
|||
} |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
m.def("test_function7", [](int, int) {}, py::arg("a"), py::arg("b"), "A custom docstring"); |
|||
|
|||
{ |
|||
py::options options; |
|||
options.disable_user_defined_docstrings(); |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<DocstringTestFoo>(m, "DocstringTestFoo", "This is a class docstring") |
|||
.def_property("value_prop", &DocstringTestFoo::getValue, &DocstringTestFoo::setValue, "This is a property docstring") |
|||
; |
|||
} |
|||
}); |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@ |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_docstring_options(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import (test_function1, test_function2, test_function3, |
|||
test_function4, test_function5, test_function6, |
|||
test_function7, DocstringTestFoo) |
|||
|
|||
# options.disable_function_signatures() |
|||
assert not test_function1.__doc__ |
|||
|
|||
assert test_function2.__doc__ == "A custom docstring" |
|||
|
|||
# options.enable_function_signatures() |
|||
assert test_function3.__doc__ .startswith("test_function3(a: int, b: int) -> None") |
|||
|
|||
assert test_function4.__doc__ .startswith("test_function4(a: int, b: int) -> None") |
|||
assert test_function4.__doc__ .endswith("A custom docstring\n") |
|||
|
|||
# options.disable_function_signatures() |
|||
# options.disable_user_defined_docstrings() |
|||
assert not test_function5.__doc__ |
|||
|
|||
# nested options.enable_user_defined_docstrings() |
|||
assert test_function6.__doc__ == "A custom docstring" |
|||
|
|||
# RAII destructor |
|||
assert test_function7.__doc__ .startswith("test_function7(a: int, b: int) -> None") |
|||
assert test_function7.__doc__ .endswith("A custom docstring\n") |
|||
|
|||
# Suppression of user-defined docstrings for non-function objects |
|||
assert not DocstringTestFoo.__doc__ |
|||
assert not DocstringTestFoo.value_prop.__doc__ |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,134 @@ |
|||
/*
|
|||
tests/eigen.cpp -- automatic conversion of Eigen types |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#include "pybind11_tests.h"
|
|||
#include <pybind11/eigen.h>
|
|||
#include <Eigen/Cholesky>
|
|||
|
|||
Eigen::VectorXf double_col(const Eigen::VectorXf& x) |
|||
{ return 2.0f * x; } |
|||
|
|||
Eigen::RowVectorXf double_row(const Eigen::RowVectorXf& x) |
|||
{ return 2.0f * x; } |
|||
|
|||
Eigen::MatrixXf double_mat_cm(const Eigen::MatrixXf& x) |
|||
{ return 2.0f * x; } |
|||
|
|||
// Different ways of passing via Eigen::Ref; the first and second are the Eigen-recommended
|
|||
Eigen::MatrixXd cholesky1(Eigen::Ref<Eigen::MatrixXd> &x) { return x.llt().matrixL(); } |
|||
Eigen::MatrixXd cholesky2(const Eigen::Ref<const Eigen::MatrixXd> &x) { return x.llt().matrixL(); } |
|||
Eigen::MatrixXd cholesky3(const Eigen::Ref<Eigen::MatrixXd> &x) { return x.llt().matrixL(); } |
|||
Eigen::MatrixXd cholesky4(Eigen::Ref<const Eigen::MatrixXd> &x) { return x.llt().matrixL(); } |
|||
Eigen::MatrixXd cholesky5(Eigen::Ref<Eigen::MatrixXd> x) { return x.llt().matrixL(); } |
|||
Eigen::MatrixXd cholesky6(Eigen::Ref<const Eigen::MatrixXd> x) { return x.llt().matrixL(); } |
|||
|
|||
typedef Eigen::Matrix<float, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::RowMajor> MatrixXfRowMajor; |
|||
MatrixXfRowMajor double_mat_rm(const MatrixXfRowMajor& x) |
|||
{ return 2.0f * x; } |
|||
|
|||
test_initializer eigen([](py::module &m) { |
|||
typedef Eigen::Matrix<float, 5, 6, Eigen::RowMajor> FixedMatrixR; |
|||
typedef Eigen::Matrix<float, 5, 6> FixedMatrixC; |
|||
typedef Eigen::Matrix<float, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::RowMajor> DenseMatrixR; |
|||
typedef Eigen::Matrix<float, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic> DenseMatrixC; |
|||
typedef Eigen::SparseMatrix<float, Eigen::RowMajor> SparseMatrixR; |
|||
typedef Eigen::SparseMatrix<float> SparseMatrixC; |
|||
|
|||
m.attr("have_eigen") = py::cast(true); |
|||
|
|||
// Non-symmetric matrix with zero elements
|
|||
Eigen::MatrixXf mat(5, 6); |
|||
mat << 0, 3, 0, 0, 0, 11, 22, 0, 0, 0, 17, 11, 7, 5, 0, 1, 0, 11, 0, |
|||
0, 0, 0, 0, 11, 0, 0, 14, 0, 8, 11; |
|||
|
|||
m.def("double_col", &double_col); |
|||
m.def("double_row", &double_row); |
|||
m.def("double_mat_cm", &double_mat_cm); |
|||
m.def("double_mat_rm", &double_mat_rm); |
|||
m.def("cholesky1", &cholesky1); |
|||
m.def("cholesky2", &cholesky2); |
|||
m.def("cholesky3", &cholesky3); |
|||
m.def("cholesky4", &cholesky4); |
|||
m.def("cholesky5", &cholesky5); |
|||
m.def("cholesky6", &cholesky6); |
|||
|
|||
// Returns diagonals: a vector-like object with an inner stride != 1
|
|||
m.def("diagonal", [](const Eigen::Ref<const Eigen::MatrixXd> &x) { return x.diagonal(); }); |
|||
m.def("diagonal_1", [](const Eigen::Ref<const Eigen::MatrixXd> &x) { return x.diagonal<1>(); }); |
|||
m.def("diagonal_n", [](const Eigen::Ref<const Eigen::MatrixXd> &x, int index) { return x.diagonal(index); }); |
|||
|
|||
// Return a block of a matrix (gives non-standard strides)
|
|||
m.def("block", [](const Eigen::Ref<const Eigen::MatrixXd> &x, int start_row, int start_col, int block_rows, int block_cols) { |
|||
return x.block(start_row, start_col, block_rows, block_cols); |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
// Returns a DiagonalMatrix with diagonal (1,2,3,...)
|
|||
m.def("incr_diag", [](int k) { |
|||
Eigen::DiagonalMatrix<int, Eigen::Dynamic> m(k); |
|||
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) m.diagonal()[i] = i+1; |
|||
return m; |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
// Returns a SelfAdjointView referencing the lower triangle of m
|
|||
m.def("symmetric_lower", [](const Eigen::MatrixXi &m) { |
|||
return m.selfadjointView<Eigen::Lower>(); |
|||
}); |
|||
// Returns a SelfAdjointView referencing the lower triangle of m
|
|||
m.def("symmetric_upper", [](const Eigen::MatrixXi &m) { |
|||
return m.selfadjointView<Eigen::Upper>(); |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("fixed_r", [mat]() -> FixedMatrixR { |
|||
return FixedMatrixR(mat); |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("fixed_c", [mat]() -> FixedMatrixC { |
|||
return FixedMatrixC(mat); |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("fixed_passthrough_r", [](const FixedMatrixR &m) -> FixedMatrixR { |
|||
return m; |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("fixed_passthrough_c", [](const FixedMatrixC &m) -> FixedMatrixC { |
|||
return m; |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("dense_r", [mat]() -> DenseMatrixR { |
|||
return DenseMatrixR(mat); |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("dense_c", [mat]() -> DenseMatrixC { |
|||
return DenseMatrixC(mat); |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("dense_passthrough_r", [](const DenseMatrixR &m) -> DenseMatrixR { |
|||
return m; |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("dense_passthrough_c", [](const DenseMatrixC &m) -> DenseMatrixC { |
|||
return m; |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("sparse_r", [mat]() -> SparseMatrixR { |
|||
return Eigen::SparseView<Eigen::MatrixXf>(mat); |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("sparse_c", [mat]() -> SparseMatrixC { |
|||
return Eigen::SparseView<Eigen::MatrixXf>(mat); |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("sparse_passthrough_r", [](const SparseMatrixR &m) -> SparseMatrixR { |
|||
return m; |
|||
}); |
|||
|
|||
m.def("sparse_passthrough_c", [](const SparseMatrixC &m) -> SparseMatrixC { |
|||
return m; |
|||
}); |
|||
}); |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,135 @@ |
|||
import pytest |
|||
|
|||
with pytest.suppress(ImportError): |
|||
import numpy as np |
|||
|
|||
ref = np.array([[ 0, 3, 0, 0, 0, 11], |
|||
[22, 0, 0, 0, 17, 11], |
|||
[ 7, 5, 0, 1, 0, 11], |
|||
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 11], |
|||
[ 0, 0, 14, 0, 8, 11]]) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def assert_equal_ref(mat): |
|||
np.testing.assert_array_equal(mat, ref) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def assert_sparse_equal_ref(sparse_mat): |
|||
assert_equal_ref(sparse_mat.todense()) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
@pytest.requires_eigen_and_numpy |
|||
def test_fixed(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import fixed_r, fixed_c, fixed_passthrough_r, fixed_passthrough_c |
|||
|
|||
assert_equal_ref(fixed_c()) |
|||
assert_equal_ref(fixed_r()) |
|||
assert_equal_ref(fixed_passthrough_r(fixed_r())) |
|||
assert_equal_ref(fixed_passthrough_c(fixed_c())) |
|||
assert_equal_ref(fixed_passthrough_r(fixed_c())) |
|||
assert_equal_ref(fixed_passthrough_c(fixed_r())) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
@pytest.requires_eigen_and_numpy |
|||
def test_dense(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import dense_r, dense_c, dense_passthrough_r, dense_passthrough_c |
|||
|
|||
assert_equal_ref(dense_r()) |
|||
assert_equal_ref(dense_c()) |
|||
assert_equal_ref(dense_passthrough_r(dense_r())) |
|||
assert_equal_ref(dense_passthrough_c(dense_c())) |
|||
assert_equal_ref(dense_passthrough_r(dense_c())) |
|||
assert_equal_ref(dense_passthrough_c(dense_r())) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
@pytest.requires_eigen_and_numpy |
|||
def test_nonunit_stride_from_python(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import double_row, double_col, double_mat_cm, double_mat_rm |
|||
|
|||
counting_mat = np.arange(9.0, dtype=np.float32).reshape((3, 3)) |
|||
first_row = counting_mat[0, :] |
|||
first_col = counting_mat[:, 0] |
|||
assert np.array_equal(double_row(first_row), 2.0 * first_row) |
|||
assert np.array_equal(double_col(first_row), 2.0 * first_row) |
|||
assert np.array_equal(double_row(first_col), 2.0 * first_col) |
|||
assert np.array_equal(double_col(first_col), 2.0 * first_col) |
|||
|
|||
counting_3d = np.arange(27.0, dtype=np.float32).reshape((3, 3, 3)) |
|||
slices = [counting_3d[0, :, :], counting_3d[:, 0, :], counting_3d[:, :, 0]] |
|||
for slice_idx, ref_mat in enumerate(slices): |
|||
assert np.array_equal(double_mat_cm(ref_mat), 2.0 * ref_mat) |
|||
assert np.array_equal(double_mat_rm(ref_mat), 2.0 * ref_mat) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
@pytest.requires_eigen_and_numpy |
|||
def test_nonunit_stride_to_python(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import diagonal, diagonal_1, diagonal_n, block |
|||
|
|||
assert np.all(diagonal(ref) == ref.diagonal()) |
|||
assert np.all(diagonal_1(ref) == ref.diagonal(1)) |
|||
for i in range(-5, 7): |
|||
assert np.all(diagonal_n(ref, i) == ref.diagonal(i)), "diagonal_n({})".format(i) |
|||
|
|||
assert np.all(block(ref, 2, 1, 3, 3) == ref[2:5, 1:4]) |
|||
assert np.all(block(ref, 1, 4, 4, 2) == ref[1:, 4:]) |
|||
assert np.all(block(ref, 1, 4, 3, 2) == ref[1:4, 4:]) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
@pytest.requires_eigen_and_numpy |
|||
def test_eigen_ref_to_python(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import cholesky1, cholesky2, cholesky3, cholesky4, cholesky5, cholesky6 |
|||
|
|||
chols = [cholesky1, cholesky2, cholesky3, cholesky4, cholesky5, cholesky6] |
|||
for i, chol in enumerate(chols, start=1): |
|||
mymat = chol(np.array([[1, 2, 4], [2, 13, 23], [4, 23, 77]])) |
|||
assert np.all(mymat == np.array([[1, 0, 0], [2, 3, 0], [4, 5, 6]])), "cholesky{}".format(i) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
@pytest.requires_eigen_and_numpy |
|||
def test_special_matrix_objects(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import incr_diag, symmetric_upper, symmetric_lower |
|||
|
|||
assert np.all(incr_diag(7) == np.diag([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])) |
|||
|
|||
asymm = np.array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4], |
|||
[ 5, 6, 7, 8], |
|||
[ 9, 10, 11, 12], |
|||
[13, 14, 15, 16]]) |
|||
symm_lower = np.array(asymm) |
|||
symm_upper = np.array(asymm) |
|||
for i in range(4): |
|||
for j in range(i + 1, 4): |
|||
symm_lower[i, j] = symm_lower[j, i] |
|||
symm_upper[j, i] = symm_upper[i, j] |
|||
|
|||
assert np.all(symmetric_lower(asymm) == symm_lower) |
|||
assert np.all(symmetric_upper(asymm) == symm_upper) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
@pytest.requires_eigen_and_numpy |
|||
def test_dense_signature(doc): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import double_col, double_row, double_mat_rm |
|||
|
|||
assert doc(double_col) == "double_col(arg0: numpy.ndarray[float32[m, 1]]) -> numpy.ndarray[float32[m, 1]]" |
|||
assert doc(double_row) == "double_row(arg0: numpy.ndarray[float32[1, n]]) -> numpy.ndarray[float32[1, n]]" |
|||
assert doc(double_mat_rm) == "double_mat_rm(arg0: numpy.ndarray[float32[m, n]]) -> numpy.ndarray[float32[m, n]]" |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
@pytest.requires_eigen_and_scipy |
|||
def test_sparse(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import sparse_r, sparse_c, sparse_passthrough_r, sparse_passthrough_c |
|||
|
|||
assert_sparse_equal_ref(sparse_r()) |
|||
assert_sparse_equal_ref(sparse_c()) |
|||
assert_sparse_equal_ref(sparse_passthrough_r(sparse_r())) |
|||
assert_sparse_equal_ref(sparse_passthrough_c(sparse_c())) |
|||
assert_sparse_equal_ref(sparse_passthrough_r(sparse_c())) |
|||
assert_sparse_equal_ref(sparse_passthrough_c(sparse_r())) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
@pytest.requires_eigen_and_scipy |
|||
def test_sparse_signature(doc): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import sparse_passthrough_r, sparse_passthrough_c |
|||
|
|||
assert doc(sparse_passthrough_r) == "sparse_passthrough_r(arg0: scipy.sparse.csr_matrix[float32]) -> scipy.sparse.csr_matrix[float32]" |
|||
assert doc(sparse_passthrough_c) == "sparse_passthrough_c(arg0: scipy.sparse.csc_matrix[float32]) -> scipy.sparse.csc_matrix[float32]" |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,68 @@ |
|||
/*
|
|||
tests/test_enums.cpp -- enumerations |
|||
|
|||
Copyright (c) 2016 Wenzel Jakob <wenzel.jakob@epfl.ch> |
|||
|
|||
All rights reserved. Use of this source code is governed by a |
|||
BSD-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file. |
|||
*/ |
|||
|
|||
#include "pybind11_tests.h"
|
|||
|
|||
enum UnscopedEnum { |
|||
EOne = 1, |
|||
ETwo |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
enum class ScopedEnum { |
|||
Two = 2, |
|||
Three |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
enum Flags { |
|||
Read = 4, |
|||
Write = 2, |
|||
Execute = 1 |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
class ClassWithUnscopedEnum { |
|||
public: |
|||
enum EMode { |
|||
EFirstMode = 1, |
|||
ESecondMode |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
static EMode test_function(EMode mode) { |
|||
return mode; |
|||
} |
|||
}; |
|||
|
|||
std::string test_scoped_enum(ScopedEnum z) { |
|||
return "ScopedEnum::" + std::string(z == ScopedEnum::Two ? "Two" : "Three"); |
|||
} |
|||
|
|||
test_initializer enums([](py::module &m) { |
|||
m.def("test_scoped_enum", &test_scoped_enum); |
|||
|
|||
py::enum_<UnscopedEnum>(m, "UnscopedEnum", py::arithmetic()) |
|||
.value("EOne", EOne) |
|||
.value("ETwo", ETwo) |
|||
.export_values(); |
|||
|
|||
py::enum_<ScopedEnum>(m, "ScopedEnum", py::arithmetic()) |
|||
.value("Two", ScopedEnum::Two) |
|||
.value("Three", ScopedEnum::Three); |
|||
|
|||
py::enum_<Flags>(m, "Flags", py::arithmetic()) |
|||
.value("Read", Flags::Read) |
|||
.value("Write", Flags::Write) |
|||
.value("Execute", Flags::Execute) |
|||
.export_values(); |
|||
|
|||
py::class_<ClassWithUnscopedEnum> exenum_class(m, "ClassWithUnscopedEnum"); |
|||
exenum_class.def_static("test_function", &ClassWithUnscopedEnum::test_function); |
|||
py::enum_<ClassWithUnscopedEnum::EMode>(exenum_class, "EMode") |
|||
.value("EFirstMode", ClassWithUnscopedEnum::EFirstMode) |
|||
.value("ESecondMode", ClassWithUnscopedEnum::ESecondMode) |
|||
.export_values(); |
|||
}); |
|||
@ -0,0 +1,108 @@ |
|||
import pytest |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_unscoped_enum(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import UnscopedEnum, EOne |
|||
|
|||
assert str(UnscopedEnum.EOne) == "UnscopedEnum.EOne" |
|||
assert str(UnscopedEnum.ETwo) == "UnscopedEnum.ETwo" |
|||
assert str(EOne) == "UnscopedEnum.EOne" |
|||
|
|||
# no TypeError exception for unscoped enum ==/!= int comparisons |
|||
y = UnscopedEnum.ETwo |
|||
assert y == 2 |
|||
assert y != 3 |
|||
|
|||
assert int(UnscopedEnum.ETwo) == 2 |
|||
assert str(UnscopedEnum(2)) == "UnscopedEnum.ETwo" |
|||
|
|||
# order |
|||
assert UnscopedEnum.EOne < UnscopedEnum.ETwo |
|||
assert UnscopedEnum.EOne < 2 |
|||
assert UnscopedEnum.ETwo > UnscopedEnum.EOne |
|||
assert UnscopedEnum.ETwo > 1 |
|||
assert UnscopedEnum.ETwo <= 2 |
|||
assert UnscopedEnum.ETwo >= 2 |
|||
assert UnscopedEnum.EOne <= UnscopedEnum.ETwo |
|||
assert UnscopedEnum.EOne <= 2 |
|||
assert UnscopedEnum.ETwo >= UnscopedEnum.EOne |
|||
assert UnscopedEnum.ETwo >= 1 |
|||
assert not (UnscopedEnum.ETwo < UnscopedEnum.EOne) |
|||
assert not (2 < UnscopedEnum.EOne) |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_scoped_enum(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import ScopedEnum, test_scoped_enum |
|||
|
|||
assert test_scoped_enum(ScopedEnum.Three) == "ScopedEnum::Three" |
|||
z = ScopedEnum.Two |
|||
assert test_scoped_enum(z) == "ScopedEnum::Two" |
|||
|
|||
# expected TypeError exceptions for scoped enum ==/!= int comparisons |
|||
with pytest.raises(TypeError): |
|||
assert z == 2 |
|||
with pytest.raises(TypeError): |
|||
assert z != 3 |
|||
|
|||
# order |
|||
assert ScopedEnum.Two < ScopedEnum.Three |
|||
assert ScopedEnum.Three > ScopedEnum.Two |
|||
assert ScopedEnum.Two <= ScopedEnum.Three |
|||
assert ScopedEnum.Two <= ScopedEnum.Two |
|||
assert ScopedEnum.Two >= ScopedEnum.Two |
|||
assert ScopedEnum.Three >= ScopedEnum.Two |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_implicit_conversion(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import ClassWithUnscopedEnum |
|||
|
|||
assert str(ClassWithUnscopedEnum.EMode.EFirstMode) == "EMode.EFirstMode" |
|||
assert str(ClassWithUnscopedEnum.EFirstMode) == "EMode.EFirstMode" |
|||
|
|||
f = ClassWithUnscopedEnum.test_function |
|||
first = ClassWithUnscopedEnum.EFirstMode |
|||
second = ClassWithUnscopedEnum.ESecondMode |
|||
|
|||
assert f(first) == 1 |
|||
|
|||
assert f(first) == f(first) |
|||
assert not f(first) != f(first) |
|||
|
|||
assert f(first) != f(second) |
|||
assert not f(first) == f(second) |
|||
|
|||
assert f(first) == int(f(first)) |
|||
assert not f(first) != int(f(first)) |
|||
|
|||
assert f(first) != int(f(second)) |
|||
assert not f(first) == int(f(second)) |
|||
|
|||
# noinspection PyDictCreation |
|||
x = {f(first): 1, f(second): 2} |
|||
x[f(first)] = 3 |
|||
x[f(second)] = 4 |
|||
# Hashing test |
|||
assert str(x) == "{EMode.EFirstMode: 3, EMode.ESecondMode: 4}" |
|||
|
|||
|
|||
def test_binary_operators(): |
|||
from pybind11_tests import Flags |
|||
|
|||
assert int(Flags.Read) == 4 |
|||
assert int(Flags.Write) == 2 |
|||
assert int(Flags.Execute) == 1 |
|||
assert int(Flags.Read | Flags.Write | Flags.Execute) == 7 |
|||
assert int(Flags.Read | Flags.Write) == 6 |
|||
assert int(Flags.Read | Flags.Execute) == 5 |
|||
assert int(Flags.Write | Flags.Execute) == 3 |
|||
assert int(Flags.Write | 1) == 3 |
|||
|
|||
state = Flags.Read | Flags.Write |
|||
assert (state & Flags.Read) != 0 |
|||
assert (state & Flags.Write) != 0 |
|||
assert (state & Flags.Execute) == 0 |
|||
assert (state & 1) == 0 |
|||
|
|||
state2 = ~state |
|||
assert state2 == -7 |
|||
assert int(state ^ state2) == -1 |
|||
Some files were not shown because too many files changed in this diff
Reference in new issue
xxxxxxxxxx